matlab训练unet,轻松学Pytorch – 构建UNet实现道路裂纹检测
原标题:轻松学Pytorch – 构建UNet实现道路裂纹检测
微信公众号:OpenCV学堂
关注获取更多计算机视觉与深度学习知识
大家好,我又好久没有给大家更新这个系列了,但是我内心一直没有忘记要更新pytorch初学者系列文章,今天给大家分享一下Pytorch如何构建UNet网络并实现模型训练与测试,实现一个道路裂纹检测!
数据集
CrackForest数据集,包括118张标注数据,37张验证与测试数据。数据集的目录有groundtruth、image、seg三个子目录,分别是标注数据、原始图像、分割信息。其中标注信息是matlab格式的文件,通过字典方式实现数据存储与读写,seg文件本质是text文件,按行来组织信息,前面几行是图像属性与格式化信息,data部分的格式如下:
Seg_num+空格+row_index+空格+column1+column2
空格表示space,
seg_num值为0或者1
row_index表示当前行
column1表示开始列位置
column2 表示结束列位置
假设seg中描述的图像宽度为480,高度为320,表示第一行的分割信息表示如下:
00 0 479 表示图像第一行从列0到列479为0,黑色
1200 141 151 表示图像中第200行中列141到151为1,白色
最终解释上述数据集生成的mask数据显示如下:大小均为(480x320)
Pytorch中定义对应数据集类的代码实现如下:
classSegmentationDataset( Dataset):
def__init__( self, image_dir, mask_dir):
self.images = []
self.masks = []
files = os.listdir(image_dir)
sfiles = os.listdir(mask_dir)
fori inrange(len(sfiles)):
img_file = os.path.join(image_dir, files[i])
mask_file = os.path.join(mask_dir, sfiles[i])
# print(img_file, mask_file)
self.images.append(img_file)
self.masks.append(mask_file)
def__len__( self):
returnlen( self.images)
defnum_of_samples( self):
returnlen( self.images)
def__getitem__( self, idx):
iftorch.is_tensor(idx):
idx = idx.tolist
image_path = self.images[idx]
mask_path = self.masks[idx]
else:
image_path = self.images[idx]
mask_path = self.masks[idx]
img = cv.imread(image_path, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # BGR order
mask = cv.imread(mask_path, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 输入图像
img = np.float32(img) / 255.0
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0)
# 目标标签0 ~ 1, 对于
mask[mask <= 128] = 0
mask[mask > 128] = 1
mask = np.expand_dims(mask, 0)
sample = { 'image': torch.from_numpy(img), 'mask': torch.from_numpy(mask),}
returnsample
模型构建
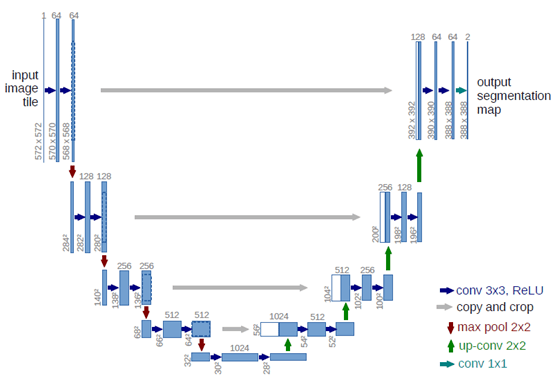
UNet网络是图像语义分割网络,整个网络可以分为两个部分来解释。第一部分是编码网络,不断的降低分辨率,实现图像特征提取;第二部分是解码网络,不断提升分辨率同时尝试重建图像有用信息,最终输出结果。网络模型结构如下:
代码实现如下:
代码实现如下classUNetModel( torch. nn. Module):
def__init__( self, in_features= 1, out_features= 2, init_features= 32):
super(UNetModel, self).__init_ _
features = init_features
self.encode_layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_features, out_channels=features, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features, out_channels=features, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.pool1 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size= 2, stride= 2)
self.encode_layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features, out_channels=features* 2, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features* 2),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 2, out_channels=features* 2, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 2),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.pool2 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size= 2, stride= 2)
self.encode_layer3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 2, out_channels=features* 4, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 4),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 4, out_channels=features* 4, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 4),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.pool3 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size= 2, stride= 2)
self.encode_layer4 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 4, out_channels=features* 8, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 8),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 8, out_channels=features* 8, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 8),
torch.nn.ReLU,
)
self.pool4 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size= 2, stride= 2)
self.encode_decode_layer = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 8, out_channels=features* 16, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 16),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 16, out_channels=features* 16, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 16),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.upconv4 = torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(
features * 16, features * 8, kernel_size= 2, stride= 2
)
self.decode_layer4 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 16, out_channels=features* 8, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features* 8),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 8, out_channels=features* 8, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 8),
torch.nn.ReLU,
)
self.upconv3 = torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(
features * 8, features * 4, kernel_size= 2, stride= 2
)
self.decode_layer3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 8, out_channels=features* 4, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 4),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 4, out_channels=features* 4, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 4),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.upconv2 = torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(
features * 4, features * 2, kernel_size= 2, stride= 2
)
self.decode_layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 4, out_channels=features* 2, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 2),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 2, out_channels=features* 2, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features * 2),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.upconv1 = torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(
features * 2, features, kernel_size= 2, stride= 2
)
self.decode_layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features* 2, out_channels=features, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features),
torch.nn.ReLU,
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features, out_channels=features, kernel_size= 3, padding= 1, stride= 1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=features),
torch.nn.ReLU
)
self.out_layer = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=features, out_channels=out_features, kernel_size= 1, padding= 0, stride= 1),
)
defforward( self, x):
enc1 = self.encode_layer1(x)
enc2 = self.encode_layer2( self.pool1(enc1))
enc3 = self.encode_layer3( self.pool2(enc2))
enc4 = self.encode_layer4( self.pool3(enc3))
bottleneck = self.encode_decode_layer( self.pool4(enc4))
dec4 = self.upconv4(bottleneck)
dec4 = torch.cat((dec4, enc4), dim= 1)
dec4 = self.decode_layer4(dec4)
dec3 = self.upconv3(dec4)
dec3 = torch.cat((dec3, enc3), dim= 1)
dec3 = self.decode_layer3(dec3)
dec2 = self.upconv2(dec3)
dec2 = torch.cat((dec2, enc2), dim= 1)
dec2 = self.decode_layer2(dec2)
dec1 = self.upconv1(dec2)
dec1 = torch.cat((dec1, enc1), dim= 1)
dec1 = self.decode_layer1(dec1)
out = self.out_layer(dec1)
returnout
训练过程
基于像素的交叉熵损失与Adam优化器实现模型训练,输入图像格式为:
NCHW= 2x1x320x480
如果硬件条件允许,建议把batchSize可以开4或者8、16尝试做对比测试。这里我训练了15个epoch,训练部分的代码如下:
index= 0
forepoch in range(num_epochs):
train_loss = 0. 0
fori_batch, sample_batched in enumerate(dataloader):
images_batch, target_labels =
sample_batched[ 'image'], sample_batched[ 'mask']
iftrain_on_gpu:
images_batch, target_labels = images_batch.cuda, target_labels.cuda
optimizer.zero_grad
# forward pass: compute predicted outputs by passing inputs to the model
m_label_out _= unet(images_batch)
# calculate the batch loss
target_labels = target_labels.contiguous.view(- 1)
m_label_out _= m_label_out _.transpose( 1, 3).transpose( 1, 2).contiguous.view(- 1, 2)
target_labels = target_labels.long
loss = cross_loss(m_label_out _, target_labels)
# backward pass: compute gradient of the loss with respect to model parameters
loss.backward
# perform a single optimization step (parameter update)
optimizer.step
# update training loss
train_loss += loss.item
ifindex% 100== 0:
print( 'step: {} tcurrent Loss: {:.6f} '.format( index, loss.item))
index+= 1
# 计算平均损失
train_loss = train_loss / num_train_samples
# 显示训练集与验证集的损失函数
print( 'Epoch: {} tTraining Loss: {:.6f} '.format(epoch, train_loss))
# save model
unet.eval
torch.save(unet, 'unet_road_model.pt')
模型测试
对训练生成的UNet模型,使用下面的代码进行测试与验证。测试运行代码如下:
cnn_model = torch. load( "./unet_road_model.pt")
root_dir = "D:/pytorch/CrackForest-dataset/test"
fileNames = os.listdir(root_dir)
forf infileNames:
image = cv.imread( os. path.join(root_dir, f), cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
h, w = image.shape
img = np.float32(image) / 255.0
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0)
x_input = torch.from_numpy(img).view( 1, 1, h, w)
probs = cnn_model(x_input.cuda)
m_label_out_ = probs.transpose( 1, 3).transpose( 1, 2).contiguous.view( -1, 2)
_, output= m_label_out_.data. max(dim= 1)
output[ output> 0] = 255
predic_ = output.view(h, w).cpu.detach.numpy
print(predic_.shape)
cv.imshow( "input", image)
result = cv.resize(np.uint8(predic_), (w, h))
cv.imshow( "unet-segmentation-demo", result)
cv.waitKey( 0)
cv.destroyAllWindows
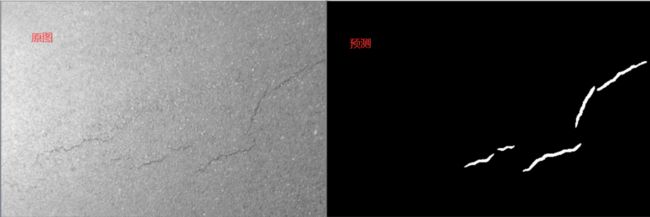
运行结果如下:
无裂纹道路
有裂纹道路
君子藏器于身,待时而动返回搜狐,查看更多
责任编辑: