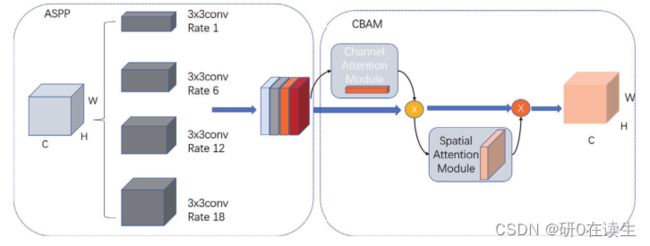
改进版ASPP(2):ASPP模块中加入CBAM(卷积注意力模块),即CBAM_ASPP
1、ASPP模型结构
![]()
空洞空间卷积池化金字塔(atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP))通过对于输入的特征以不同的采样率进行采样,即从不同尺度提取输入特征,然后将所获取的特征进行融合,得到最终的特征提取结果。
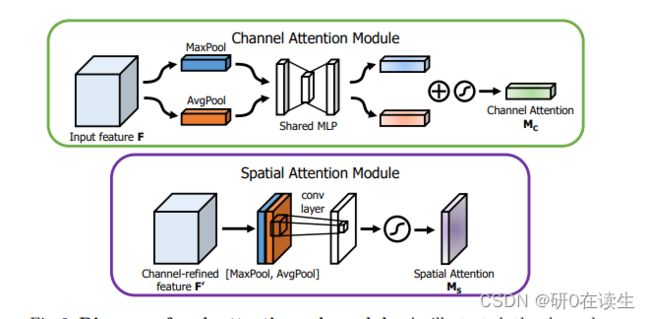
2、CBAM结构
CBAM包含CAM(Channel Attention Module)和SAM(Spartial Attention Module)两个子模块,分别在通道上和空间上添加注意力机制。这样不仅可以节约参数和计算力,而且保证了其能够做为即插即用的模块集成到现有的网络架构中去。
CBAM代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class CBAMLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16, spatial_kernel=7):
super(CBAMLayer, self).__init__()
# channel attention 压缩H,W为1
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
# shared MLP
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
# Conv2d比Linear方便操作
# nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False)
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, 1, bias=False),
# inplace=True直接替换,节省内存
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel,bias=False)
nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, 1, bias=False)
)
# spatial attention
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size=spatial_kernel,
padding=spatial_kernel // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
max_out = self.mlp(self.max_pool(x))
avg_out = self.mlp(self.avg_pool(x))
channel_out = self.sigmoid(max_out + avg_out)
x = channel_out * x
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
# print('max_out:',max_out.shape)
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
# print('avg_out:',avg_out.shape)
a=torch.cat([max_out, avg_out], dim=1)
# print('a:',a.shape)
spatial_out = self.sigmoid(self.conv(torch.cat([max_out, avg_out], dim=1)))
# print('spatial:',spatial_out.shape)
x = spatial_out * x
# print('x:',x.shape)
return x
(如果要直接使用下面的CBAM_ASPP改进代码,建议将这块代码新建py文件保存,然后在CBAM_ASPP所在python文件中导入CBAMLayer类)
3、改进ASPP:CBAM_ASPP结构
该改进方式与之前的SE_ASPP改进方式相同(感兴趣的可以点击了解SE_ASPP),也是把CBAM产生的权重值与原本输入的各个特征进行相乘,作为输入特征,可以直接使用。代码如下
class (nn.Module): ##加入通道注意力机制
def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_out, rate=1, bn_mom=0.1):
super(CBAM_ASPP, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, 1, 1, padding=0, dilation=rate, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(dim_out, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, 3, 1, padding=6 * rate, dilation=6 * rate, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(dim_out, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, 3, 1, padding=12 * rate, dilation=12 * rate, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(dim_out, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, 3, 1, padding=18 * rate, dilation=18 * rate, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(dim_out, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.branch5_conv = nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.branch5_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(dim_out, momentum=bn_mom)
self.branch5_relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv_cat = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim_out * 5, dim_out, 1, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(dim_out, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
# print('dim_in:',dim_in)
# print('dim_out:',dim_out)
self.cbam=CABAMLayer(in_planes=dim_out*5)
def forward(self, x):
[b, c, row, col] = x.size()
conv1x1 = self.branch1(x)
conv3x3_1 = self.branch2(x)
conv3x3_2 = self.branch3(x)
conv3x3_3 = self.branch4(x)
global_feature = torch.mean(x, 2, True)
global_feature = torch.mean(global_feature, 3, True)
global_feature = self.branch5_conv(global_feature)
global_feature = self.branch5_bn(global_feature)
global_feature = self.branch5_relu(global_feature)
global_feature = F.interpolate(global_feature, (row, col), None, 'bilinear', True)
feature_cat = torch.cat([conv1x1, conv3x3_1, conv3x3_2, conv3x3_3, global_feature], dim=1)
# print('feature:',feature_cat.shape)
# 加入cbam注意力机制
cbamaspp=self.cbam(feature_cat)
result1=self.conv_cat(cbamaspp)
return result
Reference
[1].Z. Zhu et al., “Semantic Segmentation of FOD Using an Improved Deeplab V3+ Model,” 2022 12th International Conference on CYBER Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), 2022, pp. 791-796, doi: 10.1109/CYBER55403.2022.9907730.
[2].Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, JY., Kweon, I.S. (2018). CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. ECCV 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11211. Springer, Cham.