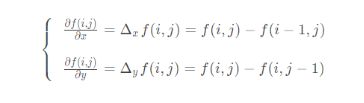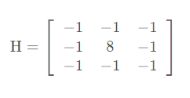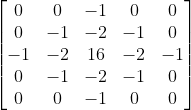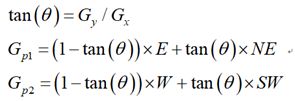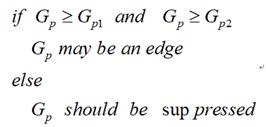OpenCV学习笔记16_常用边缘检测算法
边缘检测
文章目录
-
- 边缘检测
- 一、边缘检测的理解
- 二、常用边缘检测算子
-
- 1、普通梯度算子:
- 2、Roberts算子:
- 3、Prewitt算子:
- 4、Sobel算子:
- 5、拉普拉斯算子:
- 6、LoG算子:
- 7、Canny算子:
-
- 1.图像降噪
- 2.计算图像梯度
- 3.非极大值抑制
- 4.阈值筛选
- 三、结果
- 四、代码
一、边缘检测的理解
边缘一般是指图像在某一局部强度剧烈变化的区域。强度变化一般有两种情况:
阶跃变化:
像数值从低到高变化,图像从暗到亮
边缘检测实际上是找到两种强度变化的集合。
既然边缘是灰度变化最剧烈的位置,最直观的想法就是求差分(相邻像素点的差值)。
用差分的方法进行边缘检测必须使差分的方向和边缘的方向相垂直,这就需要对图像的不同方向分别进行差分运算,增加了运算量。一般可将边缘分为水平边缘、垂直边缘和对角线边缘。
对于第一种情况:一阶差分的峰值为边缘点,二阶差分的零点为边缘点。
对于第二种情况:一阶差分的零点为边缘点,二阶差分的峰值为边缘点。
二、常用边缘检测算子
1、普通梯度算子:
普通梯度算子也叫正交梯度算子,分别求像素点上方与像素点的梯度和像素点左边与像素点的梯度值。
D x ( m , n ) = f ( m , n ) − f ( m − 1 , n ) Dx\left(m,n\right)=f\left(m,n\right)-f\left(m-1,n\right) Dx(m,n)=f(m,n)−f(m−1,n)
D y ( m , n ) = f ( m , n ) − f ( m , n − 1 ) Dy\left(m,n\right)=f\left(m,n\right)-f\left(m,n-1\right) Dy(m,n)=f(m,n)−f(m,n−1)
D ( m , n ) = ( D x 2 + D y 2 ) D\left(m,n\right)=\sqrt{\left(Dx^2+Dy^2\right)} D(m,n)=(Dx2+Dy2)
左侧算子:
[ 0 0 − 1 1 ] \left[\begin{matrix}\\0&0\\-1&1\\\end{matrix}\right] [0−101]
上侧算子:
[ 0 − 1 0 1 ] \left[\begin{matrix}\\0&-1\\0&1\\\end{matrix}\right] [00−11]
2、Roberts算子:
Roberts算子与普通梯度算子类似,都是取一阶的差分作为梯度,区别在于取值的位置:
D x ( m , n ) = f ( m , n ) − f ( m − 1 , n − 1 ) Dx\left(m,n\right)=f\left(m,n\right)-f\left(m-1,n-1\right) Dx(m,n)=f(m,n)−f(m−1,n−1)
D y ( m , n ) = f ( m − 1 , n ) − f ( m , n − 1 ) Dy\left(m,n\right)=f\left(m-1,n\right)-f\left(m,n-1\right) Dy(m,n)=f(m−1,n)−f(m,n−1)
D ( m , n ) = ( D x 2 + D y 2 ) D\left(m,n\right)=\sqrt{\left(Dx^2+Dy^2\right)} D(m,n)=(Dx2+Dy2)
正对角算子:
[ − 1 0 0 1 ] \left[\begin{matrix}\\-1&0\\0&1\\\end{matrix}\right] [−1001]
斜对角算子:
[ 0 1 − 1 0 ] \left[\begin{matrix}\\0&1\\-1&0\\\end{matrix}\right] [0−110]
3、Prewitt算子:
Prewitt结合了差分与邻域平均的思想,其卷积核如下
水平卷积核:
1 3 ∗ [ − 1 0 1 − 1 0 1 − 1 0 1 ] \frac{1}{3}*\left[\begin{matrix}-1&0&1\\-1&0&1\\-1&0&1\\\end{matrix}\right] 31∗⎣⎡−1−1−1000111⎦⎤
垂直卷积核:
1 3 ∗ [ − 1 − 1 − 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 ] \frac{1}{3}*\left[\begin{matrix}-1&-1&-1\\ 0&0&0\\1&1&1\\\end{matrix}\right] 31∗⎣⎡−101−101−101⎦⎤
4、Sobel算子:
Sobel算子是在Prewitt算子的基础上加入了权值的思想,离像素点越近权值越高。
水平卷积核:
1 5 ∗ [ − 1 0 1 − 2 0 2 − 1 0 1 ] \frac{1}{5}*\left[\begin{matrix}-1&0&1\\ -2&0&2\\-1&0&1\\\end{matrix}\right] 51∗⎣⎡−1−2−1000121⎦⎤
垂直卷积核:
1 5 ∗ [ − 1 − 2 − 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 ] \frac{1}{5}*\left[\begin{matrix}-1&-2&-1\\ 0&0&0\\1&2&1\\\end{matrix}\right] 51∗⎣⎡−101−202−101⎦⎤
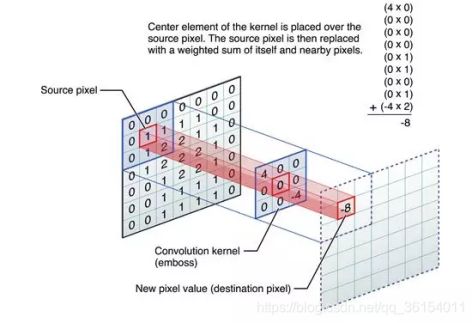
5、拉普拉斯算子:
(有点懒,用的以前的blog (- -) )
拉普拉斯变换是工程数学中常用的一种积分变换;
拉普拉斯算子是n维欧几里得空间的一个二阶微分算子;

具有各向同性,对数字图像的一阶导数为:
然后通过滑动卷积核,就可以得到整张图片的卷积结果。
6、LoG算子:
全称为Laplacian of Gaussian,就是高斯拉普拉斯算子,原理为对高斯分布公式进行二阶微分
高斯函数为:
G σ ( x , y ) = 1 2 π σ 2 exp ( − x 2 + y 2 2 σ 2 ) G_{\sigma}(x, y)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi \sigma^{2}}} \exp \left(-\frac{x^{2}+y^{2}}{2 \sigma^{2}}\right) Gσ(x,y)=2πσ21exp(−2σ2x2+y2)
对其求二次偏导得:
L o G ≜ Δ G σ ( x , y ) = ∂ 2 ∂ x 2 G σ ( x , y ) + ∂ 2 ∂ y 2 G σ ( x , y ) = x 2 + y 2 − 2 σ 2 σ 4 e − ( x 2 + y 2 ) / 2 σ 2 L o G \triangleq \Delta G_{\sigma}(x, y)=\frac{\partial^{2}}{\partial x^{2}} G_{\sigma}(x, y)+\frac{\partial^{2}}{\partial y^{2}} G_{\sigma}(x, y)=\frac{x^{2}+y^{2}-2 \sigma^{2}}{\sigma^{4}} e^{-\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right) / 2 \sigma^{2}} LoG≜ΔGσ(x,y)=∂x2∂2Gσ(x,y)+∂y2∂2Gσ(x,y)=σ4x2+y2−2σ2e−(x2+y2)/2σ2
直接构造卷积模板的计算量较大,效率较低,
所以一般采用近似的方式,常用近似的5x5的LOG算子:
7、Canny算子:
Canny算子分为四步:图像降噪、计算图像梯度、非极大值抑制、阈值筛选
1.图像降噪
梯度算子本质上是描述图像灰度突出值的算子,所以受到噪声影响很大,因为噪声表现为突出的异常数据点,所以第一步需要降噪,一般使用高斯滤波降噪;
2.计算图像梯度
计算图像梯度能够得到图像的边缘,因为梯度是灰度变化明显的地方,而边缘也是灰度变化明显的地方。当然这一步只能得到可能的边缘。因为灰度变化的地方可能是边缘,也可能不是边缘。这一步就有了所有可能是边缘的集合。
在OpenCV中默认使用Sobel算子作为梯度算子。
3.非极大值抑制
通常灰度变化的地方都比较集中,将局部范围内的梯度方向上,
灰度变化最大的保留下来,其它的不保留,这样可以剔除掉一大部分的点。
将有多个像素宽的边缘变成一个单像素宽的边缘。
这一步的主要目的为瘦边缘,需要结合梯度方向与梯度值来判断;
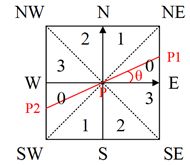
将梯度分为8个方向,分别为E、NE、N、NW、W、SW、S、SE(这实际上也为像素点),
其中0代表0度到45度,1代表45度到90度,2代表-90度到-45度,3代表-45度到0度。
像素点P的梯度方向为 θ \theta θ,则像素点P1和P2的梯度线性插值为:
4.阈值筛选
通过非极大值抑制后,仍然有很多的可能边缘点,
进一步的设置一个双阈值,即低阈值(low),高阈值(high)。
灰度变化大于high的,设置为强边缘像素,低于low的,剔除。
在low和high之间的设置为弱边缘。
进一步判断,如果其领域内有强边缘像素,保留,如果没有,剔除。
OpenCV的函数有两种:
第一种为输入两个不同的互相正交的梯度图:
CV_EXPORTS_W void Canny( InputArray dx, InputArray dy,
OutputArray edges,
double threshold1, double threshold2,
bool L2gradient = false );
InputArray dx:x方向的梯度算子,如sobel算子的x算子;
InputArray dx:y方向的梯度算子,如sobel算子的y算子;
double threshold1,最小阈值,小于此阈值这不为边缘;
double threshold2,最大阈值,大于此阈值为强边缘;
第二种输入为8位灰度图
CV_EXPORTS_W void Canny( InputArray image, OutputArray edges,
double threshold1, double threshold2,
int apertureSize = 3, bool L2gradient = false );
默认梯度算子为Sobel算子
apertureSize为Sobel算子的大小
三、结果
普通梯度算子(不明显):

roberts算子:
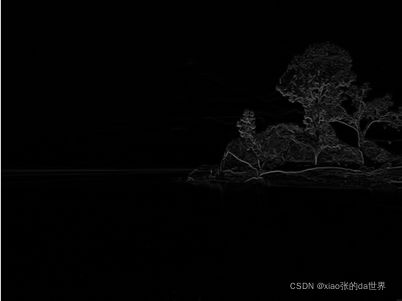
prewiit算子:

sobel算子:

拉普拉斯算子:

LoG算子:

Canny算子(简单抑制非极大值):

OpenCV中的Canny算子(插值抑制):

四、代码
#include (i, j) >= s)
// {
// dst.at(i, j) = 255;
// }
//
// }
//
// }
}
void Roberts(Mat src_roberts, Mat & dst)
{
Mat gauss, gray;
GaussianBlur(src_roberts, gauss, Size(3, 3), 0.8, 0.8);
cvtColor(src_roberts, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat dst_x, dst_y;
Mat out(Size(gray.size()), gray.type());
dst = out;
Mat kernel_x = (Mat_<double>(2, 2) << -1, 0, 0, 1);
Mat kernel_y = (Mat_<double>(2, 2) << 0, -1, 1, 0);
filter2D(gray, dst_x, -1, kernel_x);
filter2D(gray, dst_y, -1, kernel_y);
double s = 0.0;
int n = src_roberts.cols*src_roberts.rows;
for (int i = 0; i < src_roberts.rows; i++)
{
uchar* ptr_x = dst_x.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_y = dst_y.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_dst = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src_roberts.cols; j++)
{
ptr_dst[j] = sqrt(ptr_x[j] * ptr_x[j] + ptr_y[j] * ptr_y[j]);
s += ptr_dst[j];
}
}
s = s / n;
// for (int i = 0; i < src_roberts.rows; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 0; j < src_roberts.cols; j++)
// {
// if (dst.at(i,j)>=s)
// {
// dst.at(i, j) = 255;
// }
//
// }
//
// }
}
void Prewiit(Mat src_Prewiit, Mat & dst)
{
Mat gauss, gray;
GaussianBlur(src_Prewiit, gauss, Size(3, 3), 0.8, 0.8);
cvtColor(gauss, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat dst_x, dst_y;
Mat out(Size(gray.size()), gray.type());
dst = out;
Mat kernel_x = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0/3, 0, -1.0/3, 1.0 / 3, 0, -1.0 / 3, 1.0 / 3, 0, -1.0 / 3);
Mat kernel_y = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0 / 3, 1.0/3, 1.0 / 3,0,0,0, -1.0 / 3, -1.0 / 3, -1.0 / 3);
filter2D(gray, dst_x, -1, kernel_x);
filter2D(gray, dst_y, -1, kernel_y);
double s = 0.0;
int n = gray.cols*gray.rows;
for (int i = 0; i < src_Prewiit.rows; i++)
{
uchar* ptr_x = dst_x.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_y = dst_y.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_dst = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src_Prewiit.cols; j++)
{
ptr_dst[j] = sqrt(ptr_x[j] * ptr_x[j] + ptr_y[j] * ptr_y[j]);
s += ptr_dst[j];
}
}
s = s / n;
// for (int i = 0; i < src_Prewiit.rows; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 0; j < src_Prewiit.cols; j++)
// {
// if (dst.at(i, j) >= s)
// {
// dst.at(i, j) = 255;
// }
//
// }
//
// }
}
void Sobel(Mat src_sobel, Mat & dst)
{
Mat gauss, gray;
GaussianBlur(src_sobel, gauss, Size(3, 3), 0.8, 0.8);
cvtColor(gauss, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat dst_x, dst_y;
Mat out(Size(gray.size()), gray.type());
dst = out;
Mat kernel_x = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0 / 5, 0, -1.0 / 3, 2.0 / 5, 0, -2.0 / 5, 1.0 / 3, 0, -1.0 / 3);
Mat kernel_y = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0 / 5, 2.0 / 5, 1.0 / 5, 0, 0, 0, -1.0 / 5, -2.0 / 5, -1.0 / 5);
filter2D(gray, dst_x, -1, kernel_x);
filter2D(gray, dst_y, -1, kernel_y);
double s = 0.0;
int n = gray.cols*gray.rows;
for (int i = 0; i < src_sobel.rows; i++)
{
uchar* ptr_x = dst_x.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_y = dst_y.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_dst = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src_sobel.cols; j++)
{
ptr_dst[j] = sqrt(ptr_x[j] * ptr_x[j] + ptr_y[j] * ptr_y[j]);
s += ptr_dst[j];
}
}
s = s / n;
// for (int i = 0; i < src_sobel.rows; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 0; j < src_sobel.cols; j++)
// {
// if (dst.at(i, j) >= s)
// {
// dst.at(i, j) = 255;
// }
//
// }
//
// }
}
void Laplacian(Mat src_lap, Mat & dst)
{
Mat gauss, gray;
GaussianBlur(src_lap, gauss, Size(3, 3), 0.8, 0.8);
cvtColor(gauss, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat kernel = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 0, -1.0, 0, -1.0, 4, -1.0,0, -1.0, 0);
filter2D(gray, dst, -1, kernel);
double s = 0.0;
double n = gray.cols*gray.rows/4;
for (int i = 0; i < src_lap.rows; i++)
{
uchar* ptr_dst = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src_lap.cols; j++)
{
s += ptr_dst[j];
}
}
s = s / n;
for (int i = 0; i < src_lap.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < src_lap.cols; j++)
{
if (dst.at<uchar>(i, j) >= s)
{
dst.at<uchar>(i, j) = 255;
}
}
}
}
void LapofGaussi(Mat src_log, Mat & dst,int size, double sigma)
{
Mat gauss, gray;
GaussianBlur(src_log, gauss, Size(3, 3), 0.8, 0.8);
cvtColor(gauss, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
double N = (size - 1) / 2;
double C = -1.0 / (CV_PI*pow(sigma,4));
Mat kernel = (Mat_<double>(5, 5) << -2, -4, -4, -4, -2,
-4, 0, 8, 0, -4,
-4, 8, 24, 8, -4,
-4, 0, 8, 0, -4,
-2, -4, -4, -4, -2);
// double theta = 0.0;
// for (int y = 0;y
// {
// double* ptr = kernel.ptr(y);
//
// for (int x = 0; x < size; x++)
// {
//
// ptr[x] = C*(1.0- (pow((double)x - N, 2) + pow((double)y - N, 2)) / 2.0*sigma*sigma)*exp(-(pow((double)x - N, 2) + pow((double)y - N, 2))/2.0*sigma*sigma);
// theta += ptr[x];
//
//
// }
//
//
// }
// for (int y = 0; y < size; y++)
// {
// double* ptr = kernel.ptr(y);
//
// for (int x = 0; x < size; x++)
// {
//
// ptr[x] /= theta;
//
//
//
// }
//
//
// }
filter2D(gray, dst, -1, kernel);
}
void Canny(Mat src_canny, Mat & dst_canny,int value_low,int value_high)
{
Mat gauss, gray,dst;
//第一步噪声处理
GaussianBlur(src_canny, gauss, Size(3, 3), 1, 1);
cvtColor(gauss, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat dst_x(src_canny.rows,src_canny.cols,CV_32FC1), dst_y(src_canny.rows, src_canny.cols, CV_32FC1);
Mat out(Size(gray.size()), gray.type());
dst = out;
dst_canny = cv::Mat::zeros(src_canny.rows,src_canny.cols,CV_8UC1);
//第二步Sobel算子检测边缘
Mat kernel_x = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0 / 5, 0, -1.0 / 3, 2.0 / 5, 0, -2.0 / 5, 1.0 / 3, 0, -1.0 / 3);
Mat kernel_y = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0 / 5, 2.0 / 5, 1.0 / 5, 0, 0, 0, -1.0 / 5, -2.0 / 5, -1.0 / 5);
filter2D(gray, dst_x, -1, kernel_x);
filter2D(gray, dst_y, -1, kernel_y);
for (int i = 0; i < src_canny.rows; i++)
{
uchar* ptr_x = dst_x.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_y = dst_y.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* ptr_dst = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src_canny.cols; j++)
{
ptr_dst[j] = sqrt(ptr_x[j] * ptr_x[j] + ptr_y[j] * ptr_y[j]);
}
}
dst_x.convertTo(dst_x, CV_32FC1, 1.0 / 255);
dst_y.convertTo(dst_y, CV_32FC1, 1.0 / 255);
Mat mag, angle;
//计算梯度幅度与梯度方向
//转极坐标函数,可计算r与theta
cartToPolar(dst_x, dst_y, mag, angle, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < src_canny.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < src_canny.cols; j++)
{
double value = angle.at<float>(i, j);
if ((value <= 22.5 && value> -22.5) || (value >= 157.5 && value < -157.5))
{
angle.at<float>(i, j) = 0;//0度
}
if ((value <= 67.5 && value > 22.5) || (value < -112.5 && value >= -157.5))
{
angle.at<float>(i, j) = 45;//45度
}
if ((value > 67.5 && value <= 112.5) || (value < -67.5 && value >= -112.5))
{
angle.at<float>(i, j) = 90;//90度
}
if ((value > 112.5 && value < 157.5) || (value < -112.5 && value >= -157.5))
{
angle.at<float>(i, j) = 135;//135度
}
}
}
//简单讨论一下四个梯度方向的非极大值抑制
for (int i = 1; i < src_canny.rows-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < src_canny.cols-1; j++)
{
uchar t = dst.at<uchar>(i, j);
uchar a = dst.at<uchar>(i-1, j);
uchar b = dst.at<uchar>(i+1, j);
uchar c = dst.at<uchar>(i, j-1);
uchar d = dst.at<uchar>(i, j+1);
uchar e = dst.at<uchar>(i + 1, j+1);
uchar f = dst.at<uchar>(i - 1, j - 1);
uchar g = dst.at<uchar>(i - 1, j + 1);
uchar h = dst.at<uchar>(i + 1, j - 1);
double value = angle.at<float>(i, j);
if (dst.at<uchar>(i, j) <= value_low)
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) = 0;
}
// if (dst.at(i, j) >= value_low )
// {
// if (dst.at(i, j) <= value_high)//弱边
// {
if (value == 135 && t == std::max(std::max(t, g), h))//梯度方向为135度
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i,j) = t;
}
if (value == 90 && t == std::max(std::max(t, a), b))//梯度方向为90度
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) = t;
}
if (value == 45 && t == std::max(std::max(t, e), f))//梯度方向为45度
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) = t;
}
if (value == 0 && t == std::max(std::max(t, c), d))//梯度方向为0度
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) = t;
}
/*}*/
/*}*/
}
}
//双阈值处理有点问题
for (int i = 0 ; i< src_canny.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < src_canny.cols; j++)
{
uchar t = dst.at<uchar>(i, j);
if (dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) >= value_low)
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) = 255;
// if (dst_canny.at(i, j) >= value_high)//强边
// {
//
// for (int n = 3 ;n > 0 ;n--)
// {
// for (int m = 3; m > 0; m--)
// {
// if ((i > 0 && j > 0) && (i
// {
//
// uchar k = dst_canny.at(i - n + 2, j - m + 2);
// if (k >= 0 && k < value_high)
// {
// dst_canny.at(i - n + 2, j - m + 2) = 255;
// }
// }
// }
//
// }
//
// }
// // if (dst_canny.at(i, j) <= value_high)//弱边
// // {
// // dst_canny.at(i, j) = 127;
// //
// // }
}
else
{
dst_canny.at<uchar>(i, j) = 0;
}
}
}
}