TensorFlow基础10-(误差反向传播算法以及实现多层神经网络)
记录TensorFlow听课笔记
文章目录
- 记录TensorFlow听课笔记
- 一,误差反向传播算法
- 二,链式求导法则
- 三,隐含层有多个神经元的误差反向传播
- 四,激活函数
- 五,实现多层神经网络
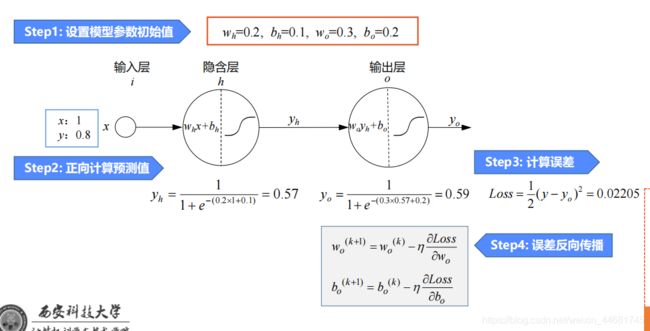
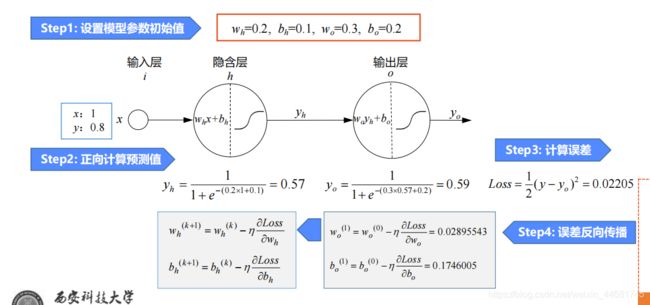
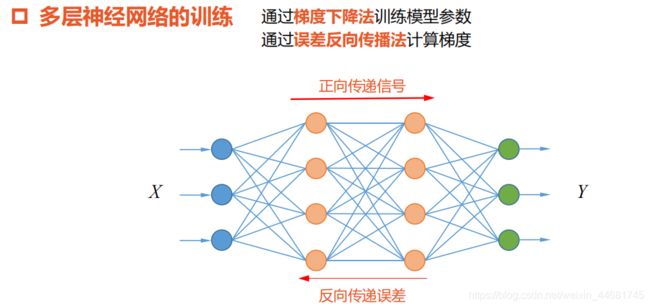
一,误差反向传播算法
利用链式法则,反向传播损失函数的梯度信息,
计算出损失函数对网络中所有模型参数的梯度。
神经网络的训练
使用误差反向传播算法计算梯度
使用梯度下降法学习模型参数
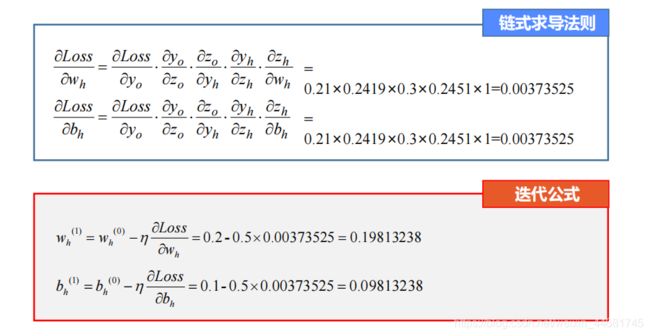
二,链式求导法则
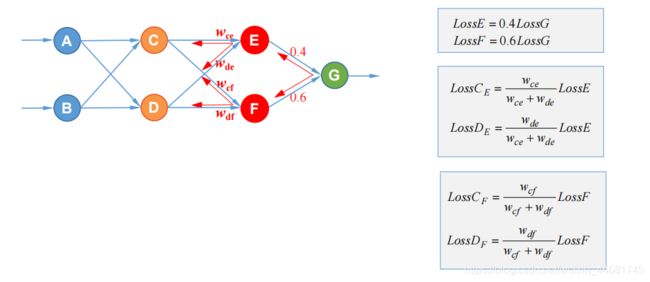
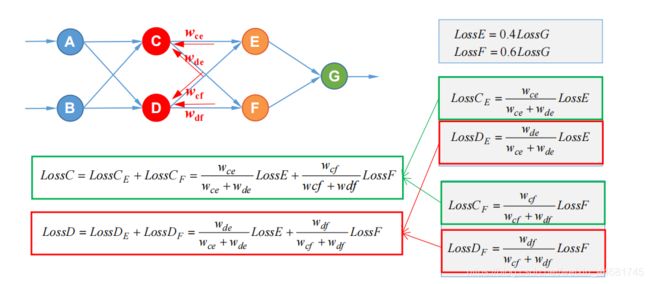
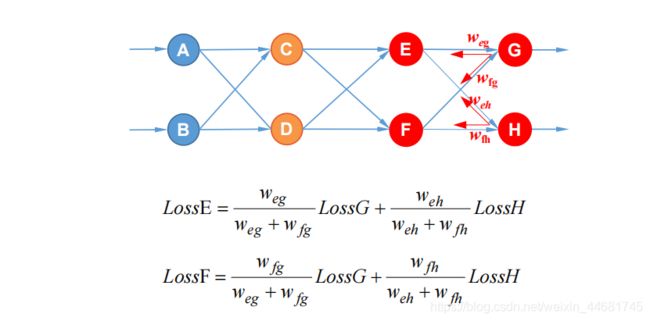
三,隐含层有多个神经元的误差反向传播
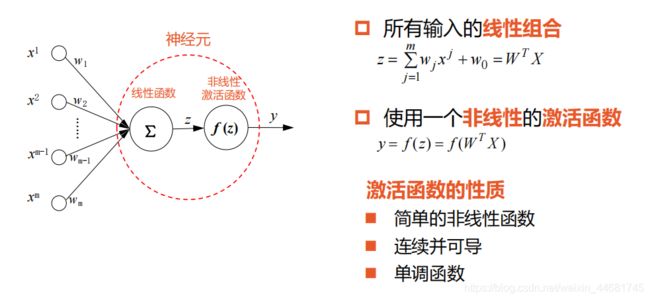
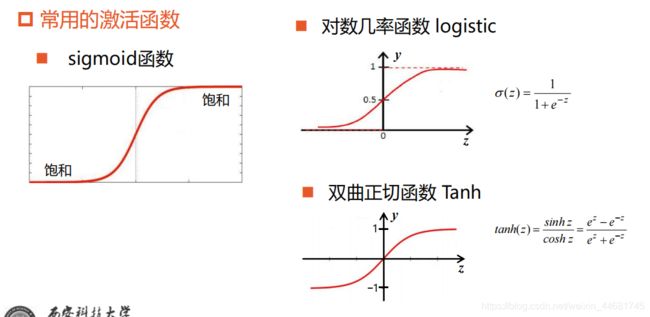
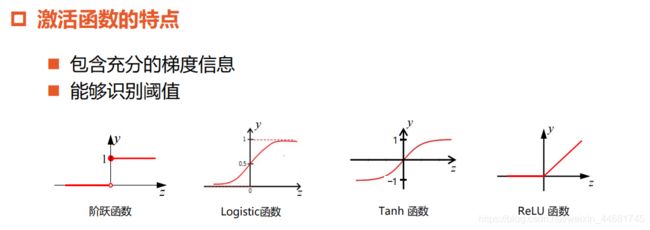
四,激活函数
激活函数的性质
简单的非线性函数
连续并可导
单调函数
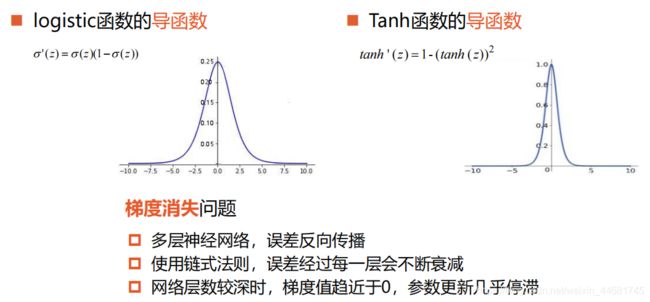
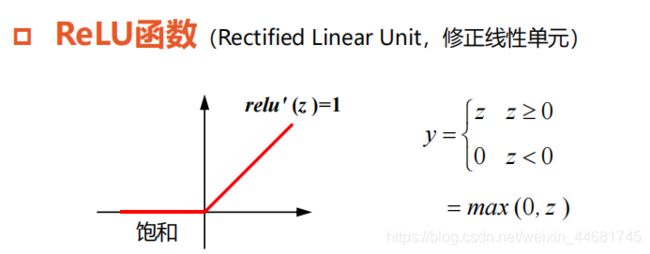
z>0时,导数等于1,缓解了梯度消失问题
不存在幂运算,计算速度快
导数恒等于1,训练模型收敛速度快
输出不是以0为均值的,会影响收敛的速度
z<0时,梯度为0,神经元死亡
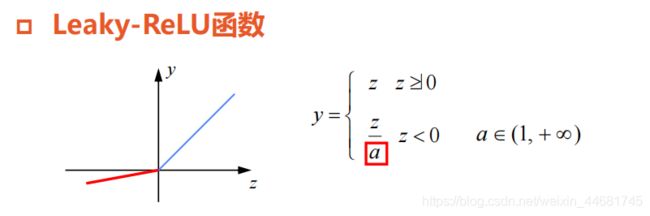
避免了ReLU神经元死亡
神经网络的计算和训练速度快
超参数a需要人工调整
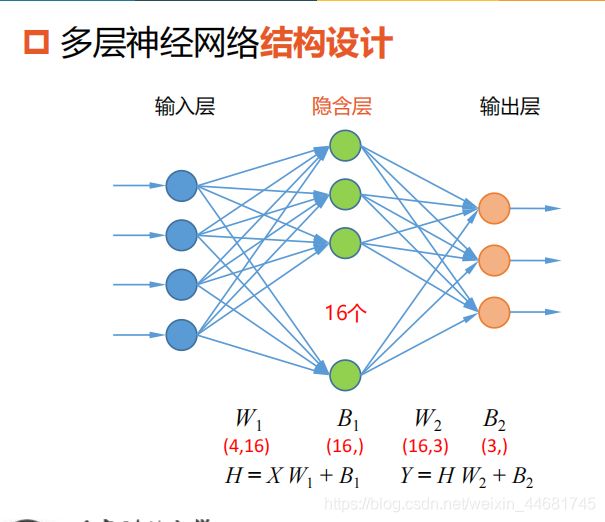
五,实现多层神经网络
隐含层激活函数 relu函数
输出层激活函数 softmax函数 损
失函数 交叉熵损失函数
实现过程
导入库,设置GPU模式
加载数据,转换为NumPy数组
数据预处理
设置超参数和显示间隔
设置模型参数初始值
训练模型
结果可视化
#增加隐藏层的多层神经网络
import tensorflow as tf
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#下载鸢尾花数据集
TRAIN_URL="http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_training.csv"
train_path=tf.keras.utils.get_file(TRAIN_URL.split('/')[-1],TRAIN_URL)
TEST_URL="http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_test.csv"
test_path=tf.keras.utils.get_file(TRAIN_URL.split('/')[-1],TEST_URL)
#读取数据集
df_iris_train=pd.read_csv(train_path,header=0)
df_iris_test=pd.read_csv(test_path,header=0)
#将数据集变为np数组
iris_train=np.array(df_iris_train)
iris_test=np.array(df_iris_test)
#取出数据集前四列特征以及第五列标签
x_train=iris_train[:,0:4]
y_train=iris_train[:,4]
x_test=iris_test[:,0:4]
y_test=iris_test[:,4]
#归一化中心化
x_train=x_train-np.mean(x_train,axis=0)
x_test=x_test-np.mean(x_test,axis=0)
#转换数据类型并标签独热编码
X_train=tf.cast(x_train,tf.float32)
Y_train=tf.one_hot(tf.constant(y_train,dtype=tf.int32),3)
X_test=tf.cast(x_test,tf.float32)
Y_test=tf.one_hot(tf.constant(y_test,dtype=tf.int32),3)
#设置超参数和显示间隔
learn_rate=0.5
iter=50
display_step=10
#设置模型参数初始值
np.random.seed(612)
W1=tf.Variable(np.random.randn(4,16),dtype=tf.float32)
B1=tf.Variable(np.zeros([16]),dtype=tf.float32)
W2=tf.Variable(np.random.randn(16,3),dtype=tf.float32) #隐藏层权重和偏置
B2=tf.Variable(np.zeros([3]),dtype=tf.float32)
#训练模型
acc_train=[] #训练准确率
acc_test=[]
cce_train=[] #训练交叉熵
cce_test=[]
for i in range(0,iter+1):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
Hidden_train=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X_train,W1)+B1)
PRED_train=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(Hidden_train,W2)+B2)
Loss_train=tf.reduce_mean(tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true=Y_train,y_pred=PRED_train))
Hidden_test=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X_test,W1)+B1)
PRED_test=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(Hidden_test,W2)+B2)
Loss_test=tf.reduce_mean(tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_true=Y_test,y_pred=PRED_test))
Accuracy_train=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(PRED_train.numpy(),axis=1),y_train),tf.float32))
Accuracy_test=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(PRED_test.numpy(),axis=1),y_test),tf.float32))
acc_train.append(Accuracy_train)
acc_test.append(Accuracy_test)
cce_train.append(Loss_train)
cce_test.append(Loss_test)
grads=tape.gradient(Loss_train,[W1,B1,W2,B2])
W1.assign_sub(learn_rate*grads[0])
B1.assign_sub(learn_rate*grads[1])
W2.assign_sub(learn_rate*grads[2])
B2.assign_sub(learn_rate*grads[3])
if i % display_step == 0:
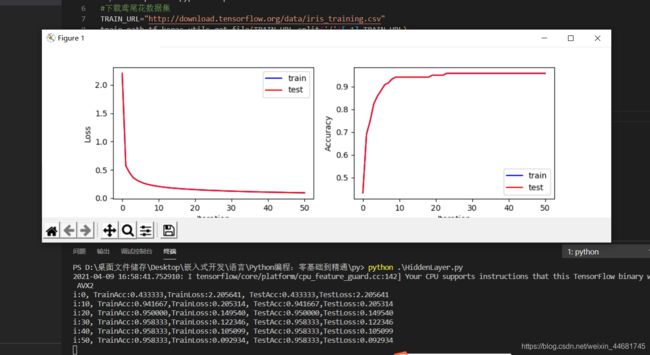
print("i:%i, TrainAcc:%f,TrainLoss:%f, TestAcc:%f,TestLoss:%f"%(i,Accuracy_train,Loss_train,Accuracy_test,Loss_test))
#损失函数和准确率可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(cce_train,color="blue",label="train")
plt.plot(cce_test,color="red",label="test")
plt.xlabel("Iteration")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(acc_train,color="blue",label="train")
plt.plot(acc_test,color="red",label="test")
plt.xlabel("Iteration")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.legend()
plt.show()