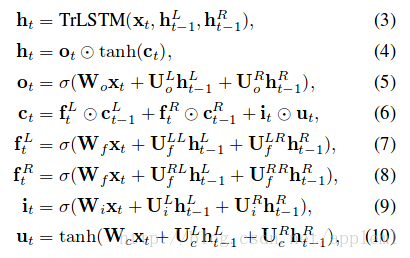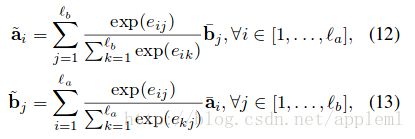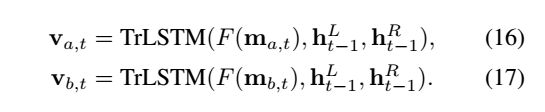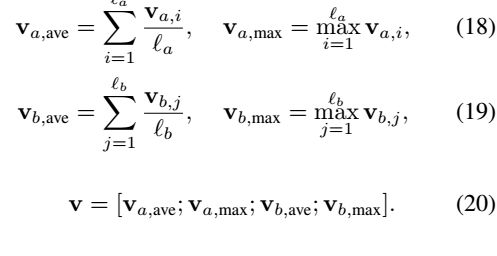解决的问题
自然语言推理,判断a是否可以推理出b。简单讲就是判断2个句子ab是否有相同的含义。
方法
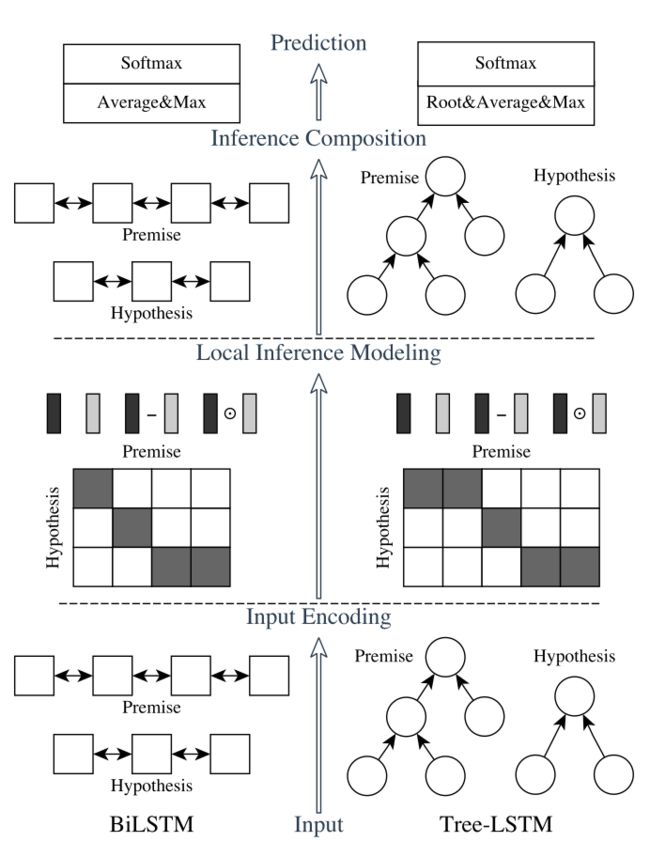
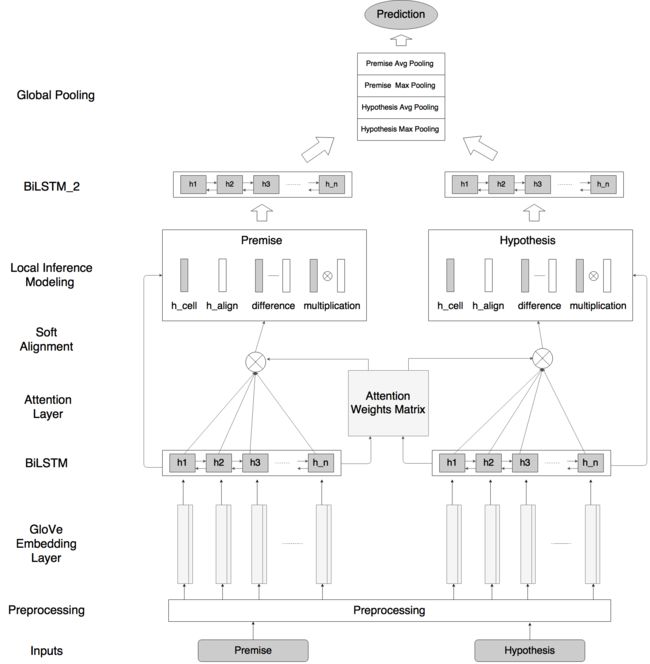
我们的自然语言推理网络由以下部分组成:输入编码(Input Encoding ),局部推理模型(Local Inference Modeling ),和推理合成(inference composition)。结构图如下所示:
垂直来看,上图显示了系统的三个主要组成部分;水平来看,左边代表称为ESIM的序列NLI模型,右边代表包含了句法解析信息的树形LSTM网络。
输入编码
1 # Based on arXiv:1609.06038 2 q1 = Input(name='q1', shape=(maxlen,)) 3 q2 = Input(name='q2', shape=(maxlen,)) 4 5 # Embedding 6 embedding = create_pretrained_embedding( 7 pretrained_embedding, mask_zero=False) 8 bn = BatchNormalization(axis=2) 9 q1_embed = bn(embedding(q1)) 10 q2_embed = bn(embedding(q2)) 11 12 # Encode 13 encode = Bidirectional(LSTM(lstm_dim, return_sequences=True)) 14 q1_encoded = encode(q1_embed) 15 q2_encoded = encode(q2_embed)
有2种lstm:
句子中的每个词都有了包含周围信息的 word representation
树中的每个节点(短语或字句)有了向量表示 htt
关于tree-LSTM 的介绍需要看文章:
[1] Improved semantic representations from tree-structured long short-term memory networks
[2] Natural Language inference by tree-based convolution and heuristic matching
[3] Long short-term memory over recursive structures
局部推理(Local Inference Modeling )
个人感觉就是一个attention的过程,取了个名字叫局部推理。
A: sequential model
1 def soft_attention_alignment(input_1, input_2): 2 "Align text representation with neural soft attention" 3 attention = Dot(axes=-1)([input_1, input_2]) 4 5 #计算两个tensor中样本的张量乘积。例如,如果两个张量a和b的shape都为(batch_size, n), 6 #则输出为形如(batch_size,1)的张量,结果张量每个batch的数据都是a[i,:]和b[i,:]的矩阵(向量)点积。 7 8 w_att_1 = Lambda(lambda x: softmax(x, axis=1), 9 output_shape=unchanged_shape)(attention) 10 w_att_2 = Permute((2, 1))(Lambda(lambda x: softmax(x, axis=2), 11 output_shape=unchanged_shape)(attention)) 12 #Permute层将输入的维度按照给定模式进行重排,例如,当需要将RNN和CNN网络连接时,可能会用到该层。 13 #dims:整数tuple,指定重排的模式,不包含样本数的维度。重拍模式的下标从1开始。 14 #例如(2,1)代表将输入的第二个维度重拍到输出的第一个维度,而将输入的第一个维度重排到第二个维度 15 16 in1_aligned = Dot(axes=1)([w_att_1, input_1]) 17 in2_aligned = Dot(axes=1)([w_att_2, input_2]) 18 return in1_aligned, in2_aligned
两句话相似或相反的对应
B: Tree-LSTM model
待续
推理合成(inference composition)
a是上层局部推理得到的。
ma 输入LSTM
对 lstm 每个time step 的结果进行pooling.
# Compare q1_combined = Concatenate()( [q1_encoded, q2_aligned, submult(q1_encoded, q2_aligned)]) q2_combined = Concatenate()( [q2_encoded, q1_aligned, submult(q2_encoded, q1_aligned)]) compare_layers = [ Dense(compare_dim, activation=activation), Dropout(compare_dropout), Dense(compare_dim, activation=activation), Dropout(compare_dropout), ] q1_compare = time_distributed(q1_combined, compare_layers) q2_compare = time_distributed(q2_combined, compare_layers) # Aggregate q1_rep = apply_multiple(q1_compare, [GlobalAvgPool1D(), GlobalMaxPool1D()]) q2_rep = apply_multiple(q2_compare, [GlobalAvgPool1D(), GlobalMaxPool1D()])