Inception-Resnet-V2 Pre-train 总结
工作之后有点小忙碌,一直都没来得及更新博客。这是工作之后的第一篇博客。Mark一下自己,快要一个月了,快要发工资了,R神很高兴啊。
今天在工作培训中,需要运用InceptionV4-Resnet-V2进行图片的分类。
由于InceptionV4的网络很深,所以直接训练是很不理智的,于是下载了Pre-train的模型。
网络文章地址:http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07261
源代码地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_41153216/10591023
如果需要Pretrain模型可以去Github上下载。
代码的主程序如下
def main():
ImageInform = SaveFile()
#print(ImageInform[0])
Train_Set, Test_Set = TrTsSet(ImageInform)
Train_Num = len(Train_Set)
#Create the log directory here. Must be done here otherwise import will activate this unneededly.
if not os.path.exists(log_dir):
os.mkdir(log_dir)
# ------- Training Process --------
with tf.Graph().as_default() as graph:
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO) #Set the verbosity to INFO level
x, y_ = inputs()
#Create the model inference
with slim.arg_scope(inception_resnet_v2_arg_scope()):
logits, end_points = inception_resnet_v2(x, num_classes = num_classes, is_training = True)
#Define the scopes that you want to exclude for restoration
exclude = ['InceptionResnetV2/Logits', 'InceptionResnetV2/AuxLogits']
variables_to_restore = slim.get_variables_to_restore(exclude = exclude)
#Performs the equivalent to tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits but enhanced with checks
loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(onehot_labels = y_, logits = logits)
total_loss = tf.losses.get_total_loss() #obtain the regularization losses as well
#Create the global step for monitoring the learning_rate and training.
global_step = get_or_create_global_step()
lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate = initial_learning_rate,
global_step = global_step, decay_steps = decay_steps,
decay_rate = learning_rate_decay_factor, staircase = True)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr)
#Create the train_op.
train_op = slim.learning.create_train_op(total_loss, optimizer)
#State the metrics that you want to predict. We get a predictions that is not one_hot_encoded.
predictions = tf.argmax(end_points['Predictions'], 1)
probabilities = end_points['Predictions']
real_label = tf.argmax(y_, 1)
accuracy, accuracy_update = tf.contrib.metrics.streaming_accuracy(predictions, real_label)
metrics_op = tf.group(accuracy_update, probabilities)
#Now finally create all the summaries you need to monitor and group them into one summary op.
tf.summary.scalar('losses/Total_Loss', total_loss)
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', lr)
my_summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
#Now we need to create a training step function that runs both the train_op, metrics_op and updates the global_step concurrently.
def train_step(sess, train_op, global_step,batch_x,batch_y):
'''
Simply runs a session for the three arguments provided and gives a logging on the time elapsed for each global step
'''
#Check the time for each sess run
start_time = time.time()
total_loss, global_step_count, _ = sess.run([train_op, global_step, metrics_op],feed_dict={x:batch_x,y_:batch_y})
time_elapsed = time.time() - start_time
#Run the logging to print some results
logging.info('global step %s: loss: %.4f (%.2f sec/step)', global_step_count, total_loss, time_elapsed)
return total_loss, global_step_count
#Now we create a saver function that actually restores the variables from a checkpoint file in a sess
saver = tf.train.Saver(variables_to_restore)
def restore_fn(sess):
return saver.restore(sess, checkpoint_file)
#Define your supervisor for running a managed session. Do not run the summary_op automatically or else it will consume too much memory
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(logdir = log_dir, summary_op = None, init_fn = restore_fn)
#print('I have done')
#Run the managed session
with sv.managed_session() as sess:
for step in range(num_steps):
if ((step*batch_size)%Train_Num == 0):
permutation = np.zeros((Train_Num,1))
permutation = np.random.permutation(Train_Num)
Batch = permutation[(step%15)*batch_size:((step%15)+1)*batch_size]
#import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
batch_x, batch_y = ANB(Batch,Train_Set)
#At the start of every epoch, show the vital information:
if step % display_step == 0:
logging.info('Steps: %s', step)
learning_rate_value, accuracy_value = sess.run([lr, accuracy],feed_dict={x:batch_x,y_:batch_y})
#logging.info('Current Learning Rate: %s', learning_rate_value)
logging.info('Current Streaming Accuracy: %s', accuracy_value)
# optionally, print your logits and predictions for a sanity check that things are going fine.
logits_value, probabilities_value, predictions_value, labels_value = \
sess.run([logits, probabilities, predictions, real_label],feed_dict={x:batch_x,y_:batch_y})
#print('logits:', logits_value)
#print('Probabilities:', probabilities_value)
#print('predictions:', predictions_value)
#print('Labels:', labels_value)
loss, _ = train_step(sess, train_op, sv.global_step,batch_x,batch_y)
summaries = sess.run(my_summary_op,feed_dict={x:batch_x,y_:batch_y})
sv.summary_computed(sess, summaries)
#If not, simply run the training step
else:
loss, _ = train_step(sess, train_op, sv.global_step,batch_x,batch_y)
# 测试,每隔几部存入一个数据
'''
if (step%1) == 0:
sv.saver.save(sess, sv.save_path, global_step = sv.global_step)
'''
#We log the final training loss and accuracy
logging.info('Final Loss: %s', loss)
logging.info('Final Accuracy: %s', sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:batch_x,y_:batch_y}))
#Once all the training has been done, save the log files and checkpoint model
logging.info('Finished training! Saving model to disk now.')
saver.save(sess, "./sc15_model.ckpt")
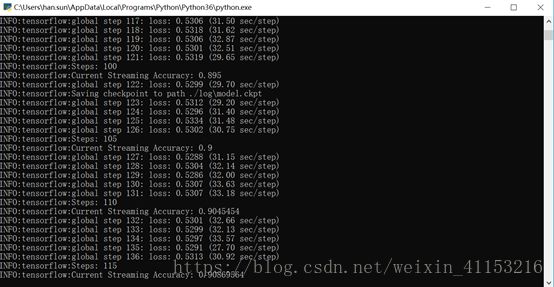
#sv.saver.save(sess, sv.save_path, global_step = sv.global_step)实验结果如下:
图中的正确率是对于训练集的。
在调试过程中的总结:
从图中可以看出,经过115个batch_size的训练,正确率可以达到90.86%。但是Loss已经不变了,可以考虑更改初始学习率。
每一步的训练大概需要30 s,这样的话,训练过程就会比较久。
改进方法,从服务器端运行。
如何从checkpoint的地方读入数据?
网络中的模型是自动存储的,每隔10分钟,存储4个文件。Checkpoint文件会进行覆盖,其它三个文件就是模型,然后下次每次都从上次的checkpoint开始训练。
模型的载入和读取,参考:https://blog.csdn.net/lwplwf/article/details/62419087 网络模型的保存和读取