数据结构——带头结点双向循环链表
相比较与单链表,双向循环链表每个结点多了一个prev指针域,用于指向该结点的前驱,并且链表的头尾结点也用指针域相连。所以对于带头结点的双向循环链表的判空条件为head->next=head;除此之外,双向循环链表的基本操作自然也与单链表有较大区别,接下来就让我们来逐步实现。
1.结构体定义
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
data为结点数据域,next指针指向当前结点的后继,prev指针指向当前结点的前驱。
2.基本操作实现
//测试函数
void Test_list();
//双链表判空
int ListEmpty(ListNode* pHead);
//动态申请一个结点data;
ListNode* buyDListNode(LTDataType data);
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate();
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);2.1动态申请结点
动态申请结点实现是后续实现链表的头结点创建和新结点插入的子功能,提前用函数封装好方便于后续操作函数的实现。具体实现:(1)通过malloc在堆上动态申请空间。(2)对新结点数据域对应赋值。(3)将结点前后指针域置空。
代码实现:
ListNode* buyDListNode(LTDataType data) {//动态申请结点
ListNode* newhead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newhead == NULL) {//申请失败
assert(0);
return NULL;
}
newhead->data = data;
newhead->next = NULL;
newhead->prev = NULL;
return newhead;
}2.2创建并返回链表头结点
通过动态申请结点函数创建头结点,头结点数据域初始化为0(或-1),初始状态下链表没有其余结点,所有将头结点的前后指针域都指向头结点本身。
代码实现:
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate() {
ListNode* pHead = buyDListNode(0);
pHead->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = pHead;
return pHead;
}2.3链表打印
通过简单循环便可实现:
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead) {
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}2.4链表尾插
对于双向链表的插入,我们只需注意要先将结点连接进链表再断开插入位置前后结点的联系即可,
实现也是比较简单,可以通过画图辅助,过程更加清晰:
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* node = buyDListNode(x);
//先不断开原链表,将新结点连接进去
node->prev = pHead->prev;
node->next = pHead;
node->prev->next = node;
pHead->prev = node;
}2.5链表头插
头插需注意的是是将结点插入在头结点之后,原理和尾插相同。
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* node = buyDListNode(x);
//先不断开原链表,将新结点连接进去
node->next = pHead->next;
node->prev = pHead;
pHead->next = node;
node->next->prev = node;
}2.6链表任意位置插入
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x) {
assert(pos);
ListNode* node = buyDListNode(x);
//先不断开原链表,将新结点连接进去
node->next = pos;
node->prev = pos->prev;
node->prev->next = node;
pos->prev = node;
}2.7链表删除
三种删除操作其操作也是相同的,只需理清结点指针域关系即可,通过画图即可清晰理清逻辑关系,所以这里直接给上代码:
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* delNode = NULL;
if (ListEmpty(pHead)) {
return;
}
delNode = pHead->prev;
delNode->prev->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = delNode->prev;
free(delNode);
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
if (ListEmpty(pHead)) {
return;
}
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
pHead->next = pHead->next->next;
pHead->next->prev = pHead;
free(cur);
}
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {
assert(pos);
if (pos == NULL) {
return;
}
ListNode* cur = pos;
cur->prev->next = cur->next;
cur->next->prev = cur->prev;
free(cur);
}
2.8链表查找
查找与打印主要都是遍历链表的过程,需注意的是循环条件不再是临时结点循环到NULL,而是结点遍历返回到头结点,即cur!=head:
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x) {
assert(pHead);
if (ListEmpty(pHead)) {
return NULL;
}
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead) {
if (cur->data == x) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
2.9链表销毁
链表销毁只需遍历链表逐步释放结点即可,在释放结点之前需临时保存下个结点,以免后续结点丢失:
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* head = pHead;
ListNode* cur = head->next;
while (cur != head) {
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(head);
head = NULL;
}3.功能测试
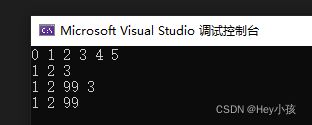
void Test_list() {
ListNode* list = ListCreate();
ListPushBack(list, 2);
ListPushBack(list, 3);
ListPushBack(list, 4);
ListPushBack(list, 5);
ListPushFront(list, 1);
ListPushFront(list, 0);
ListPrint(list);
ListPopBack(list);
ListPopBack(list);
ListPopFront(list);
ListPrint(list);
ListInsert(ListFind(list, 3), 99);
ListPrint(list);
ListErase(ListFind(list, 3));
ListPrint(list);
ListDestory(list);
}测试结果:
4.完整代码
#include
#include
#include
// 带头+双向+循环链表增删查改实现
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
//测试函数
void Test_list();
//双链表判空
int ListEmpty(ListNode* pHead);
//动态申请一个结点data;
ListNode* buyDListNode(LTDataType data);
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate();
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
int main() {
Test_list();
return 0;
}
void Test_list() {
ListNode* list = ListCreate();
ListPushBack(list, 2);
ListPushBack(list, 3);
ListPushBack(list, 4);
ListPushBack(list, 5);
ListPushFront(list, 1);
ListPushFront(list, 0);
ListPrint(list);
ListPopBack(list);
ListPopBack(list);
ListPopFront(list);
ListPrint(list);
ListInsert(ListFind(list, 3), 99);
ListPrint(list);
ListErase(ListFind(list, 3));
ListPrint(list);
ListDestory(list);
}
ListNode* buyDListNode(LTDataType data) {//动态申请结点
ListNode* newhead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newhead == NULL) {
assert(0);
return NULL;
}
newhead->data = data;
newhead->next = NULL;
newhead->prev = NULL;
return newhead;
}
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate() {
ListNode* pHead = buyDListNode(0);
pHead->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = pHead;
return pHead;
}
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* head = pHead;
ListNode* cur = head->next;
while (cur != head) {
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(head);
head = NULL;
}
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead) {
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* node = buyDListNode(x);
//先不断开原链表,将新结点连接进去
node->prev = pHead->prev;
node->next = pHead;
node->prev->next = node;
pHead->prev = node;
}
// 双向链表判空
int ListEmpty(ListNode* pHead) {//判空,空返回1,非空返回0
assert(pHead);
return pHead->next == pHead;
}
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* delNode = NULL;
if (ListEmpty(pHead)) {
return;
}
delNode = pHead->prev;
delNode->prev->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = delNode->prev;
free(delNode);
}
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x) {
assert(pHead);
ListNode* node = buyDListNode(x);
//先不断开原链表,将新结点连接进去
node->next = pHead->next;
node->prev = pHead;
pHead->next = node;
node->next->prev = node;
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead) {
assert(pHead);
if (ListEmpty(pHead)) {
return;
}
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
pHead->next = pHead->next->next;
pHead->next->prev = pHead;
free(cur);
}
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x) {
assert(pHead);
if (ListEmpty(pHead)) {
return NULL;
}
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead) {
if (cur->data == x) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x) {
assert(pos);
ListNode* node = buyDListNode(x);
//先不断开原链表,将新结点连接进去
node->next = pos;
node->prev = pos->prev;
node->prev->next = node;
pos->prev = node;
}
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {
assert(pos);
if (pos == NULL) {
return;
}
ListNode* cur = pos;
cur->prev->next = cur->next;
cur->next->prev = cur->prev;
free(cur);
}