关于ViT(Vision Transformer)的算法解读
这个我需要做一个详细的了解,因为后边的所有模型都基于此去修改。
代码出处:https://github.com/lucidrains/vit-pytorch
论文自行百度。
话不多说,先上图:
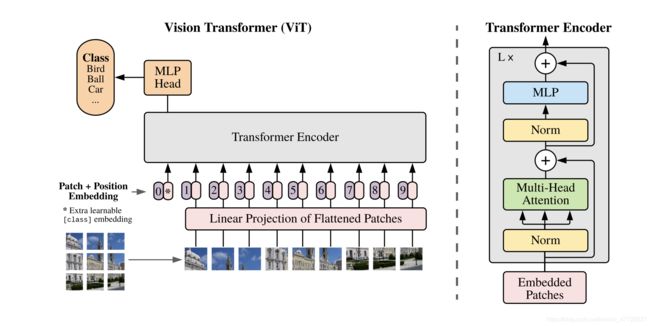
看下代码的实现:
1.参数的了解
v = ViT(
image_size = 256,
patch_size = 32,
num_classes = 1000,
dim = 1024, # 每个向量的维度
depth = 6, # 就是上右图的L,就是用了几次这个Transformer Encoder
heads = 16, # 多头注意力机制的 多头
mlp_dim = 2048, # mlp的维度
dropout = 0.1, # 防止过拟合用的
emb_dropout = 0.1
)
【注】关于Linear Projection of Flattened Patches
其实我刚开始一直在搜索 什么叫Linear Projection of Flattened Patches?然后都没有这个内容的讲解,其实这个东西就叫patch embeddings 大家可以看下原论文的描述,关键的我标黄了。

2.patch embeddings
就是把这个patch展平,然后压缩到dim维(对于论文中的D),我也不知道为什么要压缩到1024维,但是肯定是效果好(像传统的transformer做NLP一般用的是64维)。
image_height, image_width = pair(image_size) # 原图大小 比如说 256 图块大小 32
patch_height, patch_width = pair(patch_size) # 图块大小
assert image_height % patch_height == 0 and image_width % patch_width == 0, 'Image dimensions must be divisible by the patch size.'
num_patches = (image_height // patch_height) * (image_width // patch_width) # (256/32)*(256/32)也就是64块
patch_dim = channels * patch_height * patch_width # 图块拉成 3 * 32 * 32 变成一维的长度
self.to_patch_embedding = nn.Sequential(
Rearrange('b c (h p1) (w p2) -> b (h w) (p1 p2 c)', p1 = patch_height, p2 = patch_width),
nn.Linear(patch_dim, dim), # 通过线性函数 把32*32*3 -> 1024
)
2. class(cls_token) + position embeddings
和上面代码一直,我分成了64块图片,加入位置信息,并且,多加了一个class维度,用来做分类,我的理解是,它可以整合我这64块图片的信息,最终判断这是个什么类。
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, dim)) # shape [1, 64, 1024]
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, dim)) # shape [1, 1, 1024]
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(emb_dropout)
3. Transformer
Transformer的一个结构 向前的过程就是实现了一个残差的过程。
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, depth, heads, dim_head, mlp_dim, dropout = 0.):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([])
for _ in range(depth):
self.layers.append(nn.ModuleList([
PreNorm(dim, Attention(dim, heads = heads, dim_head = dim_head, dropout = dropout)),
PreNorm(dim, FeedForward(dim, mlp_dim, dropout = dropout))
]))
def forward(self, x):
for attn, ff in self.layers:
x = attn(x) + x
x = ff(x) + x
return x
我们把Transformer拿出来看看,然后我后面做了注释
(transformer): Transformer(
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): ModuleList(
(0): PreNorm(
(norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(fn): Attention( # 多头注意力Attention
(attend): Softmax(dim=-1)
(to_qkv): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=3072, bias=False) # 定义 qkv
(to_out): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(1): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(1): PreNorm(
(norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(fn): FeedForward( # MLP
(net): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(1): GELU()
(2): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(4): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
这个就是多头注意力机制 在前向传递的时候的过程。具体的函数einsum,其实就是个矩阵乘法。
# Attention 的 forward
def forward(self, x):
b, n, _, h = *x.shape, self.heads
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim = -1)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h = h), qkv)
dots = einsum('b h i d, b h j d -> b h i j', q, k) * self.scale
attn = self.attend(dots)
out = einsum('b h i j, b h j d -> b h i d', attn, v)
out = rearrange(out, 'b h n d -> b n (h d)')
return self.to_out(out)
4. MLP分类
就是一个简单MLP的简单分类了
self.mlp_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
)
解读就到这里了。