【回归预测-lssvm分类】基于最小二乘支持向量机lssvm实现数据分类代码
1 内容介绍
在信息爆炸的新时代,由于全球科技与经济迅猛发展,数据充斥在各行各业,数据的结构也变得多样化.其中对于数据的分类最常见,伴随着数据分类的同时出现两大处理难点,一个是非均衡问题,另一个就是高维问题.但是传统的数据方法在进行数据挖掘时,低维平衡数据被重点关注,传统分类方法有线性判别分析,Logistic判别模型,支持向量机算法,K近邻算法,决策树算法,随机森林算法,神经网络学习,等.但是目前各个领域充斥着大量高维非均衡数据,而传统方法对非均衡数据分类问题的关注比较缺失.目前对于非均衡数据分类时,由于数量本身的严重偏斜,分类器整体的分类准确度良好恰恰归功于多数类样本的正确分类.
2 仿真代码
%LS-SVM模型参数初始化
clc
clear
aa=xlsread('数据集.xlsx')
%% 重构矩阵
P=aa(:,1:2);
T=aa(:,3);
type = 'f';
kernel='RBF_kernel';
preprocess='original';
gam = 3;
sig2 = 0.6;
%进行模型训练
model = initlssvm(P,T,type,gam,sig2,kernel);
model = trainlssvm(model);
%回归预测
predictlabel = simlssvm(model,P);
%% 预测结果分析
[m,n]=size(predictlabel);
figure
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(1:m,predictlabel,'ob',1:m,T,'*r');
legend('预测值','实际值');
ylabel('分类','FontSize',12);
title('SVM')
grid on;
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(1:m,predictlabel-T,'-*r');
ylabel('error','FontSize',12);
legend('预测值error');
[M,b,r]=postreg(predictlabel,T)
clc
clear
aa=xlsread('数据集.xlsx')
%% 重构矩阵
P=aa(:,1:2);
T=aa(:,3);
type = 'f';
kernel='RBF_kernel';
preprocess='original';
gam = 3;
sig2 = 0.6;
%进行模型训练
model = initlssvm(P,T,type,gam,sig2,kernel);
model = trainlssvm(model);
%回归预测
predictlabel = simlssvm(model,P);
%% 预测结果分析
[m,n]=size(predictlabel);
figure
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(1:m,predictlabel,'ob',1:m,T,'*r');
legend('预测值','实际值');
ylabel('分类','FontSize',12);
title('SVM')
grid on;
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(1:m,predictlabel-T,'-*r');
ylabel('error','FontSize',12);
legend('预测值error');
[M,b,r]=postreg(predictlabel,T)
function [sig_e, bay,model] = bay_errorbar(model,Xt, type, nb, bay)
% Compute the error bars for a one dimensional regression problem
%
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2}, Xt)
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar(model, Xt)
%
% The computation takes into account the estimated noise variance
% and the uncertainty of the model parameters, estimated by
% Bayesian inference. sig_e is the estimated standard deviation of
% the error bars of the points Xt. A plot is obtained by replacing
% Xt by the string 'figure'.
%
%
% Full syntax
%
% 1. Using the functional interface:
%
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2,kernel,preprocess}, Xt)
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2,kernel,preprocess}, Xt, type)
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2,kernel,preprocess}, Xt, type, nb)
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2,kernel,preprocess}, 'figure')
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2,kernel,preprocess}, 'figure', type)
% >> sig_e = bay_errorbar({X,Y,'function',gam,sig2,kernel,preprocess}, 'figure', type, nb)
%
% Outputs
% sig_e : Nt x 1 vector with the [$ \sigma^2$] errorbands of the test data
% Inputs
% X : N x d matrix with the inputs of the training data
% Y : N x 1 vector with the inputs of the training data
% type : 'function estimation' ('f')
% gam : Regularization parameter
% sig2 : Kernel parameter
% kernel(*) : Kernel type (by default 'RBF_kernel')
% preprocess(*) : 'preprocess'(*) or 'original'
% Xt : Nt x d matrix with the inputs of the test data
% type(*) : 'svd'(*), 'eig', 'eigs' or 'eign'
% nb(*) : Number of eigenvalues/eigenvectors used in the eigenvalue decomposition approximation
%
% 2. Using the object oriented interface:
%
% >> [sig_e, bay, model] = bay_errorbar(model, Xt)
% >> [sig_e, bay, model] = bay_errorbar(model, Xt, type)
% >> [sig_e, bay, model] = bay_errorbar(model, Xt, type, nb)
% >> [sig_e, bay, model] = bay_errorbar(model, 'figure')
% >> [sig_e, bay, model] = bay_errorbar(model, 'figure', type)
% >> [sig_e, bay, model] = bay_errorbar(model, 'figure', type, nb)
%
% Outputs
% sig_e : Nt x 1 vector with the [$ \sigma^2$] errorbands of the test data
% model(*) : Object oriented representation of the LS-SVM model
% bay(*) : Object oriented representation of the results of the Bayesian inference
% Inputs
% model : Object oriented representation of the LS-SVM model
% Xt : Nt x d matrix with the inputs of the test data
% type(*) : 'svd'(*), 'eig', 'eigs' or 'eign'
% nb(*) : Number of eigenvalues/eigenvectors used in the eigenvalue decomposition approximation
%
% See also:
% bay_lssvm, bay_optimize, bay_modoutClass, plotlssvm
% Copyright (c) 2002, KULeuven-ESAT-SCD, License & help @ http://www.esat.kuleuven.ac.be/sista/lssvmlab
if iscell(model), model = initlssvm(model{:}); end
if model.type(1)~='f',
error(['confidence bounds only for function estimation. For' ...
' classification, use ''bay_modoutClass(...)'' instead;']);
end
eval('type;','type=''svd'';');
eval('nb;','nb=model.nb_data;');
if ~(strcmpi(type,'svd') | strcmpi(type,'eig') | strcmpi(type,'eigs') | strcmpi(type,'eign')),
error('Eigenvalue decomposition via ''svd'', ''eig'', ''eigs'' or ''eign''...');
end
if strcmpi(type,'eign')
warning('The resulting errorbars are most probably not very usefull...');
end
if ~isstr(Xt),
eval('[sig_e, bay] = bay_confb(model,Xt,type,nb,bay);',...
'[sig_e, bay] = bay_confb(model,Xt,type,nb);');
else
grid = 50;
[X,Y] = postlssvm(model,model.xtrain,model.ytrain);
eval('[sig_e, bay] = bay_confb(model,X,type,nb,bay);',...
'[sig_e, bay] = bay_confb(model,X,type,nb);');
% plot the curve including confidence bound
sige = sqrt(sig_e);
Yt = simlssvm(model,X);
figure;
hold on;
title(['LS-SVM_{\gamma=' num2str(model.gam(1)) ', \sigma^2=' num2str(model.kernel_pars(1)) ...
'}^{' model.kernel_type(1:3) '} and its 95% (2\sigma) error bands']);
if model.x_dim==1,
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
[~,si] = sort(X);
plot(X(si),Yt(si),'k'); hold on;
plot(X(si),Yt(si)+2.*sige(si),'-.r');
plot(X(si),Yt(si)-2.*sige(si),':r');
plot(X(si),Y(si),'k*'); hold off;
else
xlabel('time');
ylabel('Y');
plot(Yt,'k'); hold on;
plot(Yt+2.*sige,'-.r');
plot(Yt-2.*sige,':r');
plot(Y,'k*'); hold off;
end
end
function [sig_e, bay] = bay_confb(model,X,type,nb,bay)
% see formula's thesis TvG blz 126
nD = size(X,1);
%tol = .0001;
%
% calculate the eigenvalues
%
eval('bay;','[c1,c2,c3,bay] = bay_lssvm(model,1,type,nb);');
omega = kernel_matrix(model.xtrain(model.selector,1:model.x_dim), ...
model.kernel_type, model.kernel_pars);
oo = ones(1,model.nb_data)*omega;
% kernel values of X
theta = kernel_matrix(model.xtrain(model.selector, 1:model.x_dim), ...
model.kernel_type, model.kernel_pars, X);
for i=1:nD,
kxx(i,1) = feval(model.kernel_type, X(i,:),X(i,:), model.kernel_pars);
end
Zc = eye(model.nb_data) - ones(model.nb_data)./model.nb_data;
Hd = (Zc*bay.Rscores);
Hd = Hd*diag(1./bay.mu - (bay.mu+ bay.zeta*bay.eigvals).^-1)*Hd';
% forall x
for i=1:nD,
term1(i,1) = bay.zeta^-1 + kxx(i)/bay.mu - theta(:,i)'*Hd*theta(:,i);
term2(i,1) = 2/model.nb_data*sum(theta(:,i)'*Hd*omega) - 2/bay.mu/model.nb_data* sum(theta(:,i));
end
% once
term3 = 1/(bay.zeta*model.nb_data) ...
+ 1/(bay.mu*model.nb_data^2)* sum(oo) ...
-1/(model.nb_data^2)* oo*Hd*oo';
sig_e = term1+term2+term3;
function model = changelssvm(model,option, value)
% Change a field of the object oriented representation of the LS-SVM
%
%
% The different options of the fields are given in following table:
%
% 1. General options representing the kind of model:
%
% type: 'classifier' ,'function estimation'
% implementation: 'CMEX' ,'CFILE' ,'MATLAB'
% status: Status of this model ('trained' or 'changed' )
% alpha: Support values of the trained LS-SVM model
% b: Bias term of the trained LS-SVM model
% duration: Number of seconds the training lasts
% latent: Returning latent variables ('no' ,'yes' )
% x_delays: Number of delays of eXogeneous variables (by default 0 )
% y_delays: Number of delays of responses (by default 0 )
% steps: Number of steps to predict (by default 1 )
% gam: Regularisation parameter
% kernel_type: Kernel function
% kernel_pars: Extra parameters of the kernel function
%
%
% 2. Fields used to specify the used training data:
%
% x_dim: Dimension of input space
% y_dim: Dimension of responses
% nb_data: Number of training data
% xtrain: (preprocessed) inputs of training data
% ytrain: (preprocessed,coded) outputs of training data
% selector: Indexes of training data effectively used during training
%
%
% 3. Options used in the Conjugate Gradient (CG) algorithm:
%
% cga_max_itr: Maximum number of iterations in CG
% cga_eps: Stopcriterium of CG, largest allowed error
% cga_fi_bound: Stopcriterium of CG, smallest allowed improvement
% cga_show: Show the results of the CG algorithm (1 or 0)
% cga_startvalues: Starting values of the CG algorithm
%
%
% 4. Fields with the information for pre- and post-processing (only given if appropriate):
%
% preprocess: 'preprocess' or 'original'
% schemed: Status of the preprocessing
% ('coded' ,'original' or 'schemed' )
% pre_xscheme: Scheme used for preprocessing the input data
% pre_yscheme: Scheme used for preprocessing the output data
% pre_xmean: Mean of the input data
% pre_xstd: Standard deviation of the input data
% pre_ymean: Mean of the responses
% pre_ystd: Standard deviation of the reponses
%
%
% 5. The specifications of the used encoding (only given if appropriate):
%
% code: Status of the coding
% ('original' ,'changed' or 'encoded')
% codetype: Used function for constructing the encoding
% for multiclass classification (by default 'none')
% codetype_args: Arguments of the codetype function
% codedist_fct: Function used to calculate to which class a
% coded result belongs
% codedist_args: Arguments of the codedist function
% codebook2: Codebook of the new coding
% codebook1: Codebook of the original coding
%
% Full syntax
%
% >> model = changelssvm(model, field, value)
%
% Outputs
% model(*) : Obtained object oriented representation of the LS-SVM model
% Inputs
% model : Original object oriented representation of the LS-SVM model
% field : Field of the model one wants to change (e.g. 'preprocess')
% value : New value of the field of the model one wants to change
%
% See also:
% trainlssvm, initlssvm, simlssvm, plotlssvm.
% Copyright (c) 2010, KULeuven-ESAT-SCD, License & help @ http://www.esat.kuleuven.ac.be/sista/lssvmlab
%
% alias sigma^2
%
if (strcmpi(option,'sig2')) option = 'kernel_pars'; end
%
% selector -> nb_data
% nb_data -> selector
%
if strcmp(option,'selector'),
model.nb_data = length(value);
end
if strcmp(option,'nb_data'),
model.selector = 1:value;
end
%
% xtrain
%
if strcmp(option,'xtrain'),
[nb,model.x_dim] = size(value);
model.nb_data = nb;%min(nb,model.nb_data);
model.selector = 1:model.nb_data;
if length(model.gam)>model.y_dim & length(model.gam)~=size(value,1),
warning('Discarting different gamma''s...');
model.gam = max(model.gam);
end
eval('value=prelssvm(model,value);',...
'warning(''new trainings inputdata not comform with used preprocessing'');');
end
%
% ytrain
%
if strcmp(option,'ytrain'),
if size(value,2)~=size(model.ytrain,2),
model.y_dim = size(value,2);
end
eval('value = codelssvm(model,[],value);',...
'warning(''new trainings outputdata not comform with used encoding;'');');
eval('[ff,value] = prelssvm(model,[],value);',...
'warning(''new trainings outputdata not comform with used preprocessing;'');');
[nb,model.y_dim] = size(value);
model.nb_data = min(nb,model.nb_data);
model.selector = 1:model.nb_data;
end
%
% switch between preprocessing - original data
% model.prestatus = {'changed','ok'}
%
if (strcmpi(option,'preprocess')) & model.preprocess(1)~=value(1),
model.prestatus = 'changed';
end
%
% change coding
%
if strcmpi(option,'codetype') | strcmpi(option,'codebook2') | ...
strcmpi(option, 'codeargs') | strcmpi(option, 'codedistfct'),
model.code = 'changed';
elseif strcmpi(option,'codebook1'),
warning('change original format of the classifier; the toolbox will be unable to return results in the original format');
end
%
% final change
%
eval(['old_value = model.' lower(option) ';'],'old_value=[];');
eval(['model.' lower(option) '=value;']);
if (isempty(value) | isempty(old_value)),
different = 1;
else
eval('different = any(old_value~=value);','different=1;');
end
if different & ~strcmpi(option,'implementation'),
model.status = 'changed';
end
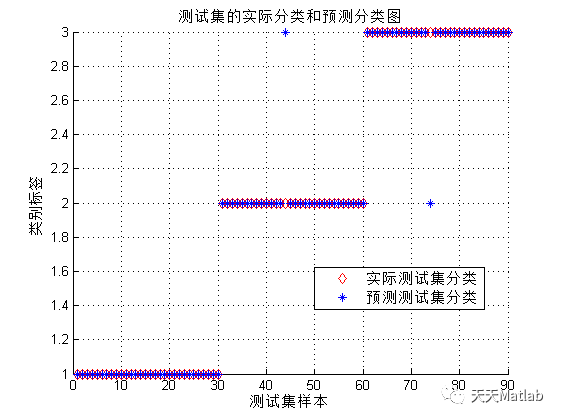
3 运行结果
4 参考文献
[1]李飞. 基于改进粒子群算法的支持向量机参数优化[D]. 河北工业大学.
[1]沈会. 基于最小二乘支持向量机方法的统计优化预测模型[D]. 武汉理工大学, 2018.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。