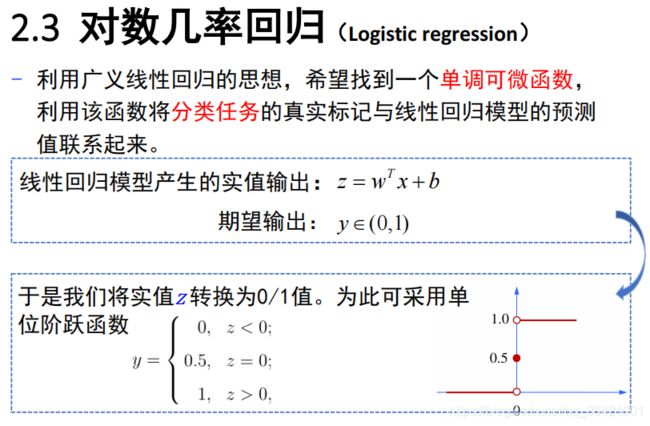
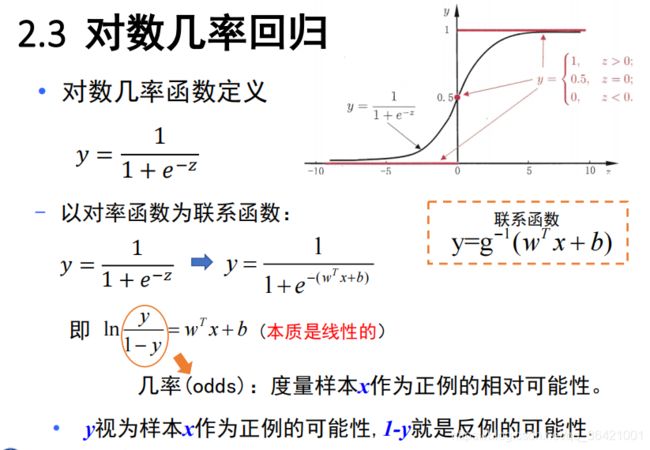
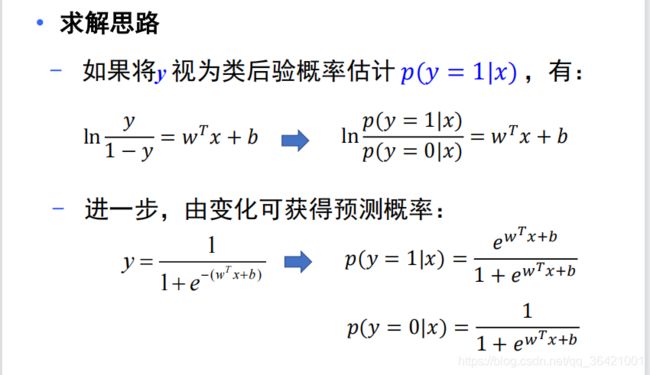
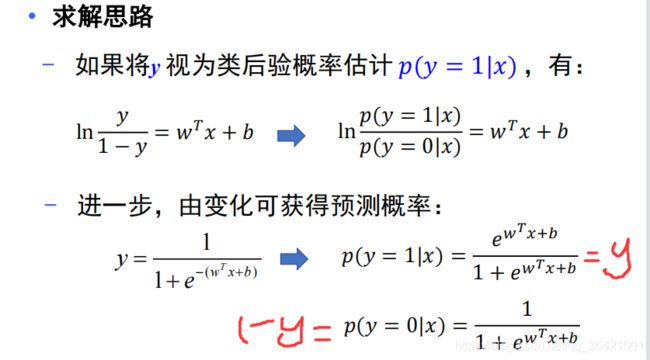
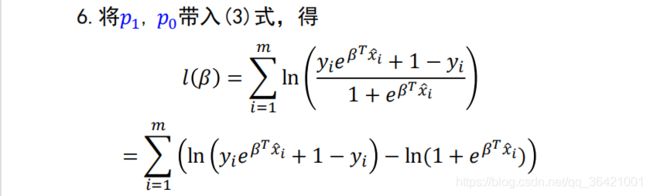逻辑回归,也叫对数几率回归:




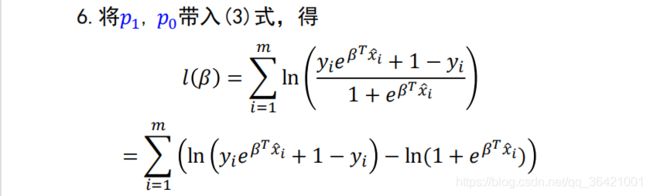



import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets._samples_generator import make_classification
class logistic_regression():
def __init__(self):
pass
def sigmoid(self,x):
z = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return z
def initialize_param(self,dims):
w = np.zeros((dims, 1))
b = 0
return w, b
def logistic(self,x, y, w, b):
num_train = x.shape[0]
num_feature = x.shape[1]
a = self.sigmoid(np.dot(x, w) + b)
cost = -1 / num_train * np.sum(y * np.log(a) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - a))
dw = np.dot(x.T, (a - y)) / num_train
db = np.sum(a - y) / num_train
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
return a, cost, dw, db
def logistic_train(self,x, y, learning_rate, epochs):
w, b = self.initialize_param(x.shape[1])
cost_list = []
for i in range(epochs):
a, cost, dw, db = self.logistic(x, y, w, b)
w = w - learning_rate * dw
b = b - learning_rate * db
if i % 100 == 0:
cost_list.append(cost)
print('epoch %d cost %f' % (i, cost))
params = {
'w': w,
'b': b
}
grads = {
'dw': dw,
'db': db
}
return cost_list, params, grads
def predict(self,x, params):
y_prediction = self.sigmoid(np.dot(x, params['w']) + params['b'])
for i in range(len(y_prediction)):
if y_prediction[i] > 0.5:
y_prediction[i] = 1
else:
y_prediction[i] = 0
return y_prediction
def accuracy(self,y_test, y_pred):
correct_count = 0
for i in range(len(y_test)):
for j in range(len(y_pred)):
if y_test[i] == y_pred[j] and i == j:
correct_count += 1
accuracy_score = correct_count / len(y_test)
return accuracy_score
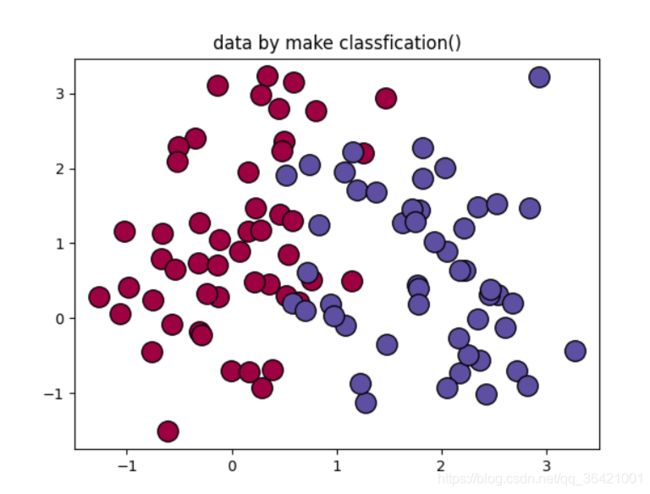
def create_data(self):
x, labels = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2, random_state=1,
n_clusters_per_class=2)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
x += 2 * rng.uniform(size=x.shape)
unique_label = set(labels)
colors = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, len(unique_label)))
for k, col in zip(unique_label, colors):
x_k = x[labels == k]
plt.plot(x_k[:, 0], x_k[:, 1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col, markeredgecolor='k', markersize=14)
plt.title('data by make classfication()')
offset = int(x.shape[0] * 0.9)
x_train, y_train = x[:offset], labels[:offset]
x_test, y_test = x[offset:], labels[offset:]
y_train = y_train.reshape((-1, 1))
y_test = y_test.reshape((-1, 1))
print("x_train=", x_train.shape)
print("x_test=", x_test.shape)
print("y_train=", y_train.shape)
print("y_test=", y_test.shape)
return x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test
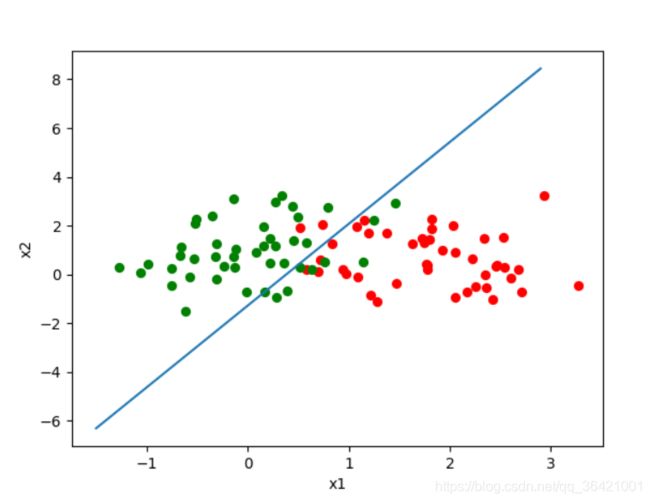
def plot_logistic(self,x_train, y_train, params):
n = x_train.shape[0]
xcord1 = []
ycord1 = []
xcord2 = []
ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if y_train[i] == 1:
xcord1.append(x_train[i][0])
ycord1.append(x_train[i][1])
else:
xcord2.append(x_train[i][0])
ycord2.append(x_train[i][1])
fig = plt.figure(2)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=32, c='red')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=32, c='green')
x = np.arange(-1.5, 3, 0.1)
y = (-params['b'] - params['w'][0] * x) / params['w'][1]
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
model=logistic_regression()
x_train,y_train,x_test,y_test=model.create_data()
cost_list, params, grads = model.logistic_train(x_train, y_train, 0.01, 1000)
print(params)
y_prediction = model.predict(x_test, params)
print(y_prediction)
y_train_pred = model.predict(x_train, params)
accuracy_score_train = model.accuracy(y_train, y_train_pred)
print('train accuracy is:',accuracy_score_train)
y_test_pred = model.predict(x_test, params)
accuracy_score_test = model.accuracy(y_test, y_test_pred)
print('test accuracy is:',accuracy_score_test)
model.plot_logistic(x_train, y_train, params)