NMS非极大值抑制
NMS非极大值抑制的功能:
筛选出一定区域内、属于同一种类、得分最大的框。
每个grid cell包含2个bounding box(每个bounding box包含4个box位置坐标和1个box置信度) 和20个类别的条件概率。
将box置信度和20个类别的条件概率分别相乘,得到一个全概率(20*1)。
因此每个bounding box有一个全概率,1个grid cell有2个全概率,总共输出有7*7*2=98个全概率
![]()
此图摘自:YOLOv1 前向推断后处理——NMS非极大值抑制_我的博客-CSDN博客
NMS的实现过程:
输出的大小为:[batch_size , all_anchors ,4+1+num_classes ]
第一个维度是图片的数量。
第二个维度是所有的预测框。
第三个维度是所有的预测框的预测结果:x,y,w,h,confidence,类别概率。
非极大抑制的执行过程如下所示:
1、对所有图片进行循环。
2、找出该图片中得分大于门限函数的框。在进行重合框筛选前就进行得分的筛选可以大幅度减少框的数量。
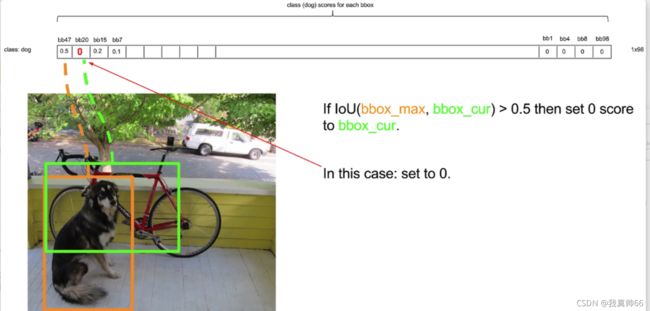
假设第一个类是狗,我们设一个阈值0.2,所有小于0.2的全设为0。
将所有全概率按狗的全概率重新按大到小进行排序。
非极大值抑制将多余的bounding box也设为0。
3、判断第2步中获得的框的种类与得分。取出预测结果中框的位置与之进行堆叠。此时最后一维度里面的内容由5+num_classes变成了4+1+2,四个参数代表框的位置,一个参数代表预测框是否包含物体,2分别代表种类的置信度和种类。
最左边的最大的bounding box和后面的bounding box分别计算ioU,设ioU阈值为0.5,如果ioU>0.5就将小的bounding box设为0,重合度大的剔除。
4、上一轮结束后,将第二大的bounding box分别和后面的计算,以此类推。
狗这一类结束后,重复操作猫类,飞机类等等,以上为NMS。
5、经过处理后,98个bounding box中有很多概率为0的类,分别对每个bounding box取最大值,如果最大值也是0就跳过这个bounding box,如果最大值大于0就记下这个概率以及对应的类,然后将这个bounding box中的(x,y,w,h)进行绘框,在框上写上刚刚记下的概率和类,对98个bounding box重复以上操作,至此前向推断完成。
def non_max_suppression(self, prediction, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果的格式转换成左上角右下角的格式。
#将原本框为中心点,宽高转化为左上角,右下角
# prediction [batch_size, num_anchors, 85]
#----------------------------------------------------------#
box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape)
#中心-宽高/2
box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
#中心+宽高/2
box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4]
output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))]
for i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 对种类预测部分取max。
# class_conf [num_anchors, 1] 种类置信度
# class_pred [num_anchors, 1] 种类
#----------------------------------------------------------#
class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] * class_conf[:, 0] >= conf_thres).squeeze()
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 根据置信度进行预测结果的筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask]
class_conf = class_conf[conf_mask]
class_pred = class_pred[conf_mask]
if not image_pred.size(0):
continue
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# detections [num_anchors, 7]
# 7的内容为:x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1)
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测结果中包含的所有种类
#------------------------------------------#
unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique()
if prediction.is_cuda:
unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda()
detections = detections.cuda()
for c in unique_labels:
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得某一类得分筛选后全部的预测结果
#------------------------------------------#
detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c]
# #------------------------------------------#
# # 使用官方自带的非极大抑制会速度更快一些!
# #------------------------------------------#
# keep = nms(
# detections_class[:, :4],
# detections_class[:, 4] * detections_class[:, 5],
# nms_thres
# )
# max_detections = detections_class[keep]
# 按照存在物体的置信度排序
_, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4]*detections_class[:, 5], descending=True)
detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index]
# 进行非极大抑制
max_detections = []
while detections_class.size(0):
# 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉
max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0))
if len(detections_class) == 1:
break
ious = self.bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:])
detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres]
# 堆叠
max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data
# Add max detections to outputs
output[i] = max_detections if output[i] is None else torch.cat((output[i], max_detections))
if output[i] is not None:
output[i] = output[i].cpu().numpy()
box_xy, box_wh = (output[i][:, 0:2] + output[i][:, 2:4])/2, output[i][:, 2:4] - output[i][:, 0:2]
output[i][:, :4] = self.yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image)
return output
参考:
睿智的目标检测31——非极大抑制NMS与Soft-NMS_Bubbliiiing的学习小课堂-CSDN博客
YOLOv1 前向推断后处理——NMS非极大值抑制_我的博客-CSDN博客