MNE-Python | 使用 ICLabel 模型进行 ICA 并自动修复样本
本文涵盖了使用 ICA 和 ICLabel 模型 1 自动修复信号,该模型源自 EEGLab。 有关 ICA 的概念背景,请参阅此 scikit-learn 教程。 有关如何使用 ICA 删除工件的基本了解,请参阅 MNE-Python 中的教程。
ICLabel 旨在对配备最大信号 ICA 分解算法的独立成分(IC)进行分类,该算法需要 EEG 数据集采用平均值作为重参考并在 [1,100] Hz 之间进行滤波处理。 也可以在不符合这些规范的数据集上运行 ICLabel,但分类性能可能会受到负面影响。 此外,ICLabel 论文没有研究这些预处理步骤的影响。
同样的我们需要导入必要的 Python 模块并加载一些示例数据。 因为 ICA 的计算量很大,可以将数据裁剪为 60 秒; 为了避免重复预处理(mne.preprocessing),我们将直接从该子模块导入一些函数和类。
import mne
from mne.preprocessing import ICA
from mne_icalabel import label_components
sample_data_folder = mne.datasets.sample.data_path() / "MEG" / "sample"
sample_data_raw_file = sample_data_folder / "sample_audvis_raw.fif"
raw = mne.io.read_raw_fif(sample_data_raw_file)
# 我们裁剪 60 秒的信号段,并删除 MEG 通道
raw.crop(tmax=60.0).pick_types(eeg=True, stim=True, eog=True)
raw.load_data()输出为:
Opening raw data file C:\Users\Mathieu\mne_data\MNE-sample-data\MEG\sample\sample_audvis_raw.fif...
Read a total of 3 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) idle
Range : 25800 ... 192599 = 42.956 ... 320.670 secs
Ready.
Removing projector
Removing projector
Removing projector
Reading 0 ... 36037 = 0.000 ... 60.000 secs... | Measurement date | December 03, 2002 19:01:10 GMT |
|---|---|
| Experimenter | MEG |
| Participant | Unknown |
| Digitized points | 146 points |
| Good channels | 9 Stimulus, 59 EEG, 1 EOG |
| Bad channels | None |
| EOG channels | EOG 061 |
| ECG channels | Not available |
| Sampling frequency | 600.61 Hz |
| Highpass | 0.10 Hz |
| Lowpass | 172.18 Hz |
| Filenames | sample_audvis_raw.fif |
| Duration | 00:01:00 (HH:MM:SS) |
滤波去除缓慢低频漂移
在运行 ICA 之前,一个重要的步骤是对数据的低频漂移进行过滤,低频漂移会对 ICA 拟合的质量产生负面影响。 缓慢漂移的问题在于它们降低了假定为独立来源相互之间的独立性(例如,在缓慢向上漂移期间,神经、心跳、眨眼和其他肌电信号都会呈现出更高的值),使得算法更难找到准确的解。所以建议使用截止频率为 1 Hz 的高通滤波器。 但是,由于滤波是线性操作,从滤波后的信号中找到的 ICA 解可以应用于未滤波的信号,参考以下文献:
Irene Winkler, Stefan Debener, Klaus-Robert Müller, and Michael Tangermann. On the influence of high-pass filtering on ICA-based artifact reduction in EEG-ERP. In Proceedings of EMBC-2015, 4101–4105. Milan, 2015. IEEE. doi:10.1109/EMBC.2015.7319296.
因此我们将保留未滤波的原始对象的副本,以便我们可以将 ICA 的解作用与原始数据。
filt_raw = raw.copy().filter(l_freq=1.0, h_freq=100.0)输出为:
Filtering raw data in 1 contiguous segment
Setting up band-pass filter from 1 - 1e+02 Hz
FIR filter parameters
---------------------
Designing a one-pass, zero-phase, non-causal bandpass filter:
- Windowed time-domain design (firwin) method
- Hamming window with 0.0194 passband ripple and 53 dB stopband attenuation
- Lower passband edge: 1.00
- Lower transition bandwidth: 1.00 Hz (-6 dB cutoff frequency: 0.50 Hz)
- Upper passband edge: 100.00 Hz
- Upper transition bandwidth: 25.00 Hz (-6 dB cutoff frequency: 112.50 Hz)
- Filter length: 1983 samples (3.302 sec)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Using backend SequentialBackend with 1 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 1 out of 1 | elapsed: 0.0s remaining: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 2 out of 2 | elapsed: 0.0s remaining: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 0.0s remaining: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 4 out of 4 | elapsed: 0.0s remaining: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 59 out of 59 | elapsed: 0.0s finished拟合并绘制ICA解
现在即可准备开始建立并拟合ICA。通过观察原始数据可以知道 EOG 和 ECG 的伪影影响很强,所以我们预计这些伪影将在 ICA 之前发生的 PCA 分解的前几个维度中被捕获。因此可能不需要大量的成分来区分数据(尽管有时需要更多的成分来获得更准确的解)。首先可以做尝试,我们将使用n_components=15 运行 ICA(仅使用前 15 个 PCA 成分来计算 ICA 分解)——考虑到我们的数据有 59 个良好的 EEG 通道,成分数量相对较小,但其优势在于它可以快速运行,我们将能够轻松判断它是否有效(因为我们已经知道 EOG / ECG 伪影应该是什么样子)。
ICA 拟合具有不确定性(例如,提取出的成分可能会在不同的计算中出现符号翻转,或者可能并不总是以相同的顺序返回),因此我们还将指定一个随机种子,以便每次本教程都获得相同的结果由我们的网络服务器构建。
在拟合 ICA 之前,我们将应用一个共同的平均重参考,以符合 ICLabel 的要求。
filt_raw = filt_raw.set_eeg_reference("average")输出为:
EEG channel type selected for re-referencing
Applying average reference.
Applying a custom ('EEG',) reference.我们将使用 “extended infomax” 方法来拟合 ICA,以符合 ICLabel 要求。 ICLabel 未与其他 ICA 分解算法进行测试,但其性能和准确性不应受算法影响。
ica = ICA(
n_components=15,
max_iter="auto",
method="infomax",
random_state=97,
fit_params=dict(extended=True),
)
ica.fit(filt_raw)
ica输出为
Fitting ICA to data using 59 channels (please be patient, this may take a while)
Selecting by number: 15 components
Computing Extended Infomax ICA
Fitting ICA took 3.3s.| Method | infomax |
|---|---|
| Fit | 500 iterations on raw data (36038 samples) |
| ICA components | 15 |
| Explained variance | 91.0 % |
| Available PCA components | 59 |
| Channel types | eeg |
| ICA components marked for exclusion | — |
我们可以传递给 fit函数 方法的一些可选参数包括 decim(在计算 IC 时仅使用每第 N 个样本,可提升快速性)和reject(拒绝每种通道类型提供最大可接受幅值范围的区间)。
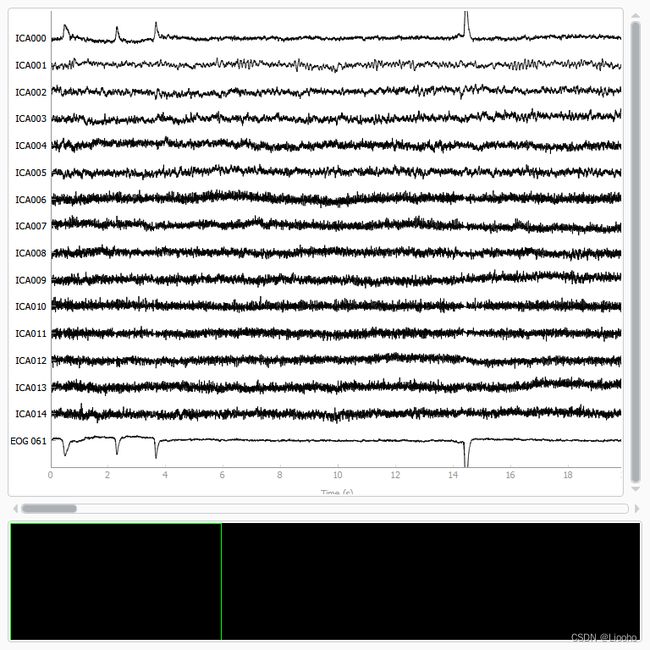
现在我们可以查看 IC 以查看它们捕获的内容。 plot_sources 将显示 IC 的时间序列。 请注意,在我们对 plot_sources 的调用中,我们可以使用原始的、未过滤的 Raw 对象:
raw.load_data()
ica.plot_sources(raw, show_scrollbars=False, show=True)输出为:
Creating RawArray with float64 data, n_channels=16, n_times=36038
Range : 25800 ... 61837 = 42.956 ... 102.956 secs
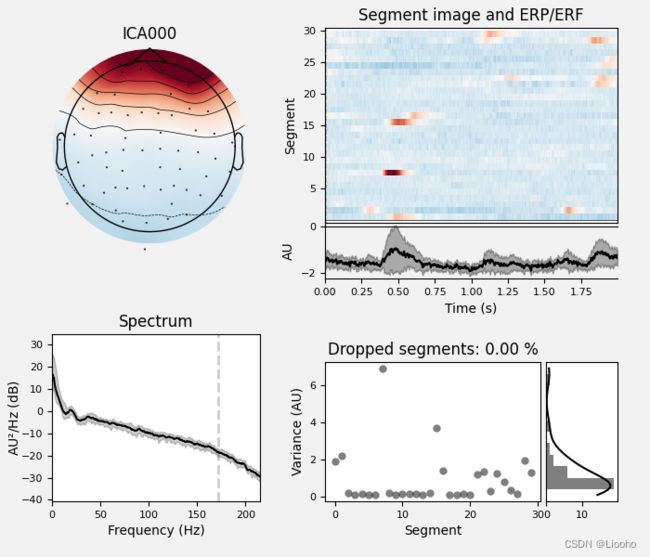
Ready.我们可以很清楚地看到第一个成分 (ICA000) 捕获了 EOG 信号。 我们可以用plot_components 可视化每个组件的头皮场分布。 这些是基于 ICA 混合矩阵中的值进行插值的:
ica.plot_components()
# blinks
ica.plot_overlay(raw, exclude=[0], picks="eeg")输出为:
Applying ICA to Raw instance
Transforming to ICA space (15 components)
Zeroing out 1 ICA component
Projecting back using 59 PCA components我们还可以使用 plot_properties 单独绘制 IC 图:
ica.plot_properties(raw, picks=[0])输出为:
Using multitaper spectrum estimation with 7 DPSS windows
Not setting metadata
30 matching events found
No baseline correction applied
0 projection items activated自动选择 ICA 成分
我们可以应用自动 ICA 标记算法,该算法将输出以下七个成分的概率值:
-
brain
-
muscle artifact
-
eye blink
-
heart beat
-
line noise
-
channel noise
-
other
ICLabel label_components 函数的输出按顺序为这些类中的每一个生成预测概率值。详见文献:
Luca Pion-Tonachini, Ken Kreutz-Delgado, and Scott Makeig. Iclabel: an automated electroencephalographic independent component classifier, dataset, and website. NeuroImage, 198:181–197, 2019. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811919304185, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.026.
ic_labels = label_components(filt_raw, ica, method="iclabel")
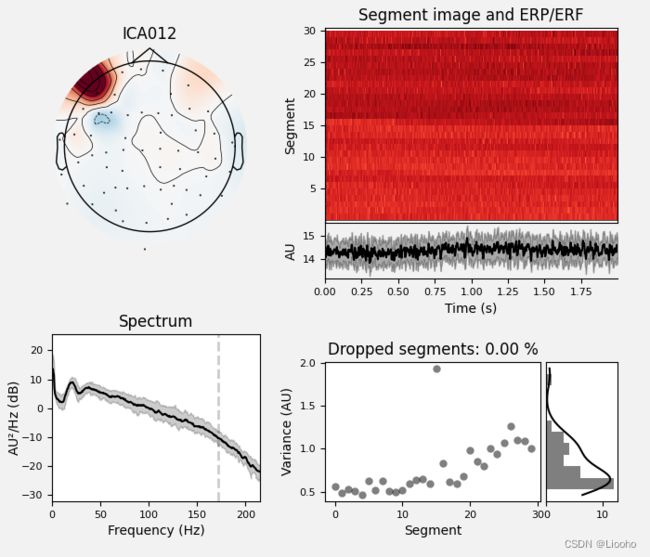
# 例如:ICA0 可以准确地识别为眨眼,ICA12 被归为肌肉伪影。
print(ic_labels["labels"])
ica.plot_properties(raw, picks=[0, 12], verbose=False)print输出结果:
['eye blink', 'brain', 'brain', 'brain', 'brain', 'brain', 'muscle artifact', 'muscle artifact', 'other', 'brain', 'muscle artifact', 'muscle artifact', 'muscle artifact', 'muscle artifact', 'eye blink']提取标签并重构原始数据
我们可以提取出所有不属于大脑的成分,保留“大脑”和“其他”。 “其他”是不可分类的成分。 保险起见,并假设我们不能盲目地删除这些成分。
labels = ic_labels["labels"]
exclude_idx = [idx for idx, label in enumerate(labels) if label not in ["brain", "other"]]
print(f"Excluding these ICA components: {exclude_idx}")输出为:
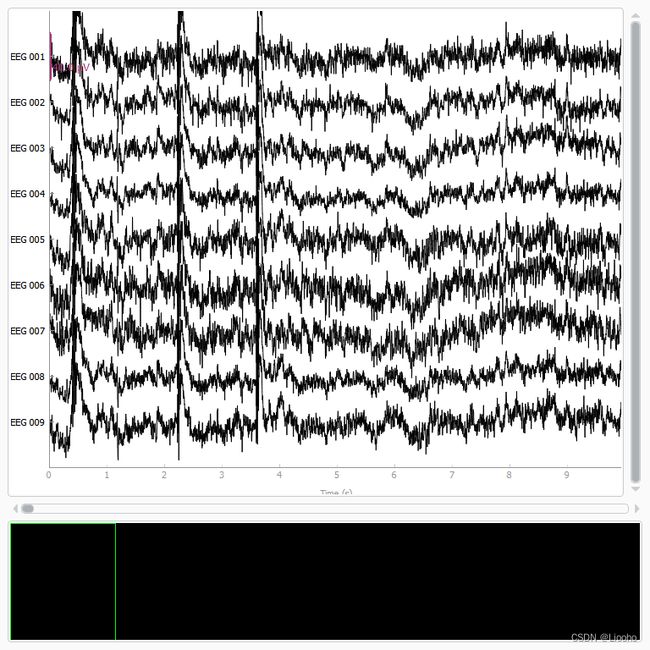
Excluding these ICA components: [0, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]现在我们有了需要被剔除的成分,可以用 mne.apply 去除每个通道上信号的伪影,需要注意的是,我们要将对于过滤后的数据得到的 ICA 解决方案作用于原始未滤波的信号。将原始的数据与重构后的数据一同绘制,心跳和眨眼的伪影已得到修复。
# ica.apply() changes the Raw object in-place, so let's make a copy first:
reconst_raw = raw.copy()
ica.apply(reconst_raw, exclude=exclude_idx)
raw.plot(order=artifact_picks, n_channels=len(artifact_picks), show_scrollbars=False)
reconst_raw.plot(order=artifact_picks, n_channels=len(artifact_picks), show_scrollbars=False)
del reconst_raw输出为:
Applying ICA to Raw instance
Transforming to ICA space (15 components)
Zeroing out 8 ICA components
Projecting back using 59 PCA components