Spring Data JPA分页与排序
1、认识JPA的分页接口和排序类
在项目的开发中,需要经常对数据表进行分页和排序查询。下面将介绍如何使用Spring Data JPA对数据进行分页和排序。
1.1 分页排序接口 PagingAndSortingRepository
PagingAndSortingRepository 接口继承自 CrudRepository 接口提供的分页和排序方法。其关键代码如下:
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository extends CrudRepository
{
Iterable findAll(Sort var1);
Page findAll(Pageable var1);
} 其方法有如下两种:
Iterable
Page
1.2 分页接口 Pageable 和 Page
Pageable 接口用于构造分页查询,返回 Page 对象。Page 从0开始分页。
例如:可以通过以下代码来构建查询用户信息的分页查询参数。
//排序
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id");
//分页
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageIndex, pageSize, sort);
//分页查询
Page userPage = userDao.findAll(pageable); 1.3 排序类 Sort
Sort 类专门用来处理排序。最简单的排序就是先传入一个属性列,然后根据属性列的值进行排序。默认情况下是升序排列。它还可以根据提供的多个字段属性值进行排序。例如以下代码是通过Sort.Order对象的List集合来创建Sort对象的:
//排序
List orders = new ArrayList();
orders.add(new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id"));
orders.add(new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.ASC,"createTime"));
//分页
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageIndex, pageSize, Sort.by(orders));
//分页获取
Page userPage = userDao.findAll(pageable); Sort排序的方法还有下面几种:
- 直接创建Sort对象, 适合对单一属性做排序。
- 通过Sort.Order对象创建Sort对象,适合对单一属性做排序。
- 通过属性的List集合创建Sort对象,适合对多个属性采取同一种排序方式的排序。
- 通过Sort.Order对象的List集合创建Sort对象,适合所有情况,比较容易设排序方式。
- 忽略大小写排序。
- 使用JapSort.unsafe进行排序。
- 使用聚合函数进行排序。
2、使用Pageable和Page接口进行分页
【示例】使用Pageable和Page接口进行分页查询用户列表,并显示分页信息。
(1)创建数据库表
在MySQL数据库中创建用户信息表(tb_user),并添加数据。
-- 判断数据表是否存在,存在则删除
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tb_user;
-- 创建“用户信息”数据表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tb_user
(
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '用户编号',
user_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户姓名',
province VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '省份',
create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '注册时间'
) COMMENT = '用户信息表';
-- 添加数据
INSERT INTO tb_user(user_name,province) VALUES
('pan_junbiao的博客_01','广东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_02','黑龙江省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_03','山东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_04','安徽省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_05','黑龙江省'),
('pan_junbiao的博客_06','江苏省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_07','黑龙江省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_08','广东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_09','陕西省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_10','广东省'),
('pan_junbiao的博客_11','广东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_12','江苏省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_13','陕西省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_14','安徽省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_15','山东省'),
('pan_junbiao的博客_16','陕西省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_17','安徽省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_18','江苏省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_19','黑龙江省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_20','安徽省'),
('pan_junbiao的博客_21','江苏省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_22','广东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_23','安徽省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_24','陕西省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_25','广东省'),
('pan_junbiao的博客_26','广东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_27','安徽省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_28','山东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_29','山东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_30','黑龙江省'),
('pan_junbiao的博客_31','广东省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_32','江苏省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_33','陕西省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_34','安徽省'),('pan_junbiao的博客_35','山东省');(2)编写实体类(Entity层)
创建User类(用户信息的持久化类)。
package com.pjb.jpapage.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 用户信息的持久化类
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
@Entity
@Table(name = "tb_user")
public class User
{
//用户编号
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
//用户姓名
@Column(name = "user_name")
private String userName;
//省份
@Column(name = "province")
private String province;
//注册时间
@Column(name = "create_time")
private Date createTime;
public int getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName()
{
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getProvince()
{
return province;
}
public void setProvince(String province)
{
this.province = province;
}
public Date getCreateTime()
{
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime)
{
this.createTime = createTime;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "编号:" + this.id +" 姓名:" + this.userName + " 省份:" + this.province;
}
}(3)实现数据库访问接口层(Dao层)
创建UserDao(用户信息数据库访问接口),并继承JpaRepository接口。
package com.pjb.jpapage.dao;
import com.pjb.jpapage.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 用户信息数据库访问接口
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
@Repository
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository
{
/**
* 根据用户姓名,分页查询用户列表(使用原生SQL语句)
*/
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM tb_user WHERE user_name LIKE %:name%", nativeQuery = true)
public Page getUserPageByNameSQL(@Param("name")String userName,Pageable pageable);
/**
* 根据用户姓名,分页查询用户列表(使用JPQL语句)
*/
@Query("SELECT u FROM User u WHERE u.userName LIKE %:name%")
public Page getUserPageByNameJPQL(@Param("name")String userName,Pageable pageable);
} (4)编写测试方法(Test层)
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 分页与排序
* 使用JPA的分页接口和排序类
* @author pan_junbiao
*/
@Test
public void getUserPageable()
{
int pageIndex = 0; //当前页码(注意:第一页是从0开始)
int pageSize = 10; //分页大小
//排序
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.ASC, "id");
//分页
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageIndex, pageSize, sort);
//测试1:分页查询所有用户
//Page userPage = userDao.findAll(pageable);
//测试2:根据用户姓名,分页查询用户列表(使用原生SQL语句)
//Page userPage = userDao.getUserPageByNameSQL("pan_junbiao的博客", pageable);
//测试3:根据用户姓名,分页查询用户列表(使用JPQL语句)
Page userPage = userDao.getUserPageByNameJPQL("pan_junbiao的博客", pageable);
//数据列表
List userList = userPage.getContent();
for (User user : userList)
{
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
//分页信息
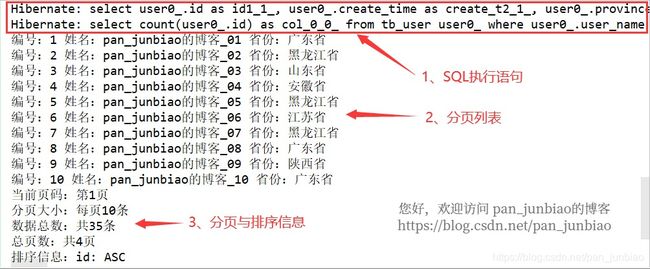
System.out.println("当前页码:第" + (userPage.getNumber() + 1) + "页");
System.out.println("分页大小:每页" + userPage.getSize() + "条");
System.out.println("数据总数:共" + userPage.getTotalElements() + "条");
System.out.println("总页数:共" + userPage.getTotalPages() + "页");
System.out.println("排序信息:" + userPage.getSort().toString());
} 执行结果:
3、使用Specification动态分页查询
3.1 使用Specification构造分页查询
使用Specification构建动态分页查询,需要在数据库访问层(Dao层)中的类中继承JpaSpecificationExecutor接口。
【示例】使用Specification构建动态分页查询用户列表,并显示分页信息。
(1)实现数据库访问接口层(Dao层)
创建UserDao(用户信息数据库访问接口),并继承JpaRepository接口和JpaSpecificationExecutor接口。
package com.pjb.jpapage.dao;
import com.pjb.jpapage.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 用户信息数据库访问接口
* @author pan_junbiao
**/
@Repository
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository, JpaSpecificationExecutor
{
}
(2)编写测试方法(Test层)
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 分页与排序
* 使用Specification进行查询
* @author pan_junbiao
*/
@Test
public void getUserSpecification()
{
int pageIndex = 0; //当前页码(注意:第一页是从0开始)
int pageSize = 10; //分页大小
//排序
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.ASC, "Id");
//分页
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageIndex, pageSize, sort);
//使用Specification的匿名内部类
Specification specification = new Specification()
{
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root root, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder)
{
//根据用户编号
Path path_id = root.get("id");
//gt是大于的意思,这里代表id大于8
Predicate predicate_id = criteriaBuilder.gt(path_id, 8);
//根据用户名称
Path path_userName = root.get("userName");
//根据用户姓名,模糊查询
Predicate predicate_userName = criteriaBuilder.like(path_userName, "%pan_junbiao的博客%");
//根据省份
Path path_province = root.get("province");
Predicate predicate_province = criteriaBuilder.equal(path_province.as(String.class), "广东省");
//构建组合的Predicate
Predicate predicate = criteriaBuilder.and(predicate_id, predicate_userName, predicate_province);
return predicate;
}
};
//执行查询
Page userPage = userDao.findAll(specification, pageable);
//数据列表
List userList = userPage.getContent();
for (User user : userList)
{
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
//分页信息
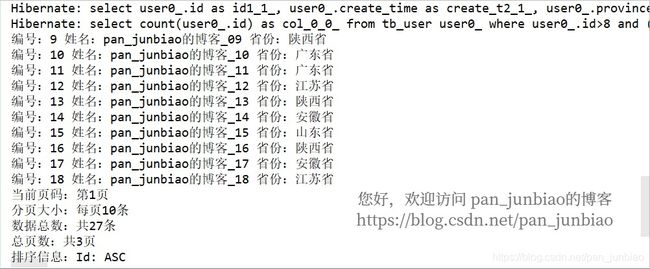
System.out.println("当前页码:第" + (userPage.getNumber() + 1) + "页");
System.out.println("分页大小:每页" + userPage.getSize() + "条");
System.out.println("数据总数:共" + userPage.getTotalElements() + "条");
System.out.println("总页数:共" + userPage.getTotalPages() + "页");
System.out.println("排序信息:" + userPage.getSort().toString());
} 执行结果:
3.2 使用Specification实现多条件组合的分页查询
【示例】根据不同查询条件进行的组合,进行分页查询。
/**
* 分页与排序
* 使用Specification实现多条件组合的分页查询
* @author pan_junbiao
*/
@Test
public void getAssemblySpecification()
{
int pageIndex = 0; //当前页码(注意:第一页是从0开始)
int pageSize = 10; //分页大小
//排序
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.ASC, "Id");
//分页
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageIndex, pageSize, sort);
//创建查询条件类
User userParam = new User();
userParam.setId(8);
userParam.setUserName("pan_junbiao的博客");
//userParam.setProvince("广东省");
//使用Specification的匿名内部类
Specification specification = new Specification()
{
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root root, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder)
{
List predicateList = new ArrayList();
//根据用户编号
if(userParam.getId()>0)
{
Path path_id = root.get("id");
//gt是大于的意思
Predicate predicate_id = criteriaBuilder.gt(path_id, userParam.getId());
predicateList.add(predicate_id);
}
//根据用户名称
if(userParam.getUserName()!=null && userParam.getUserName().length()>0)
{
Path path_userName = root.get("userName");
//根据用户姓名,模糊查询
Predicate predicate_userName = criteriaBuilder.like(path_userName, "%"+ userParam.getUserName() +"%");
predicateList.add(predicate_userName);
}
//根据省份
if(userParam.getProvince()!=null && userParam.getProvince().length()>0)
{
Path path_province = root.get("province");
Predicate predicate_province = criteriaBuilder.equal(path_province.as(String.class), userParam.getProvince());
predicateList.add(predicate_province);
}
//构建组合的Predicate
Predicate[] arrayPredicates = new Predicate[predicateList.size()];
return criteriaBuilder.and(predicateList.toArray(arrayPredicates));
}
};
//执行查询
Page userPage = userDao.findAll(specification, pageable);
//数据列表
List userList = userPage.getContent();
for (User user : userList)
{
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
//分页信息
System.out.println("当前页码:第" + (userPage.getNumber() + 1) + "页");
System.out.println("分页大小:每页" + userPage.getSize() + "条");
System.out.println("数据总数:共" + userPage.getTotalElements() + "条");
System.out.println("总页数:共" + userPage.getTotalPages() + "页");
System.out.println("排序信息:" + userPage.getSort().toString());
} 执行结果:
3.3 关联字段的处理
使用Specification时,当查询的字段为关联字段,如下是实体类中的关联部门信息的字段(一对一关联)。
当需要以部门实体类中的部门编号(departmentCode)为查询字段时,写法如下:
踩坑经验:
使用Specification进行查询时,一开始我把User实体类中的字段写成了Id(首字母大写),
发现执行提示错误:Unable to locate Attribute with the the given name [id] on this ManagedType
原来实体类声明字段大小写敏感,我把该字段改成id,就可以了。