computer security 复习
conclusion合集
最惨莫过于全过了一遍ppt结果到头来往年真题还是不会
好抽象的概念啊救命
就算不考过一遍总归没错
3:
对称加密的保密性:对称加密,对称块加密算法,流密码
消息认证和哈希函数:使用对称加密进行身份验证,没有消息加密的消息认证,安全哈希函数,哈希函数的其他应用
4:
公钥加密:结构,公钥密码系统的应用,公钥密码学要求,非对称加密算法
数字签名和密钥管理:电子签名,公钥证书,使用公钥加密的对称密钥交换,数字信封
随机和伪随机数:随机数的使用,随机与伪随机
实际应用:存储数据的加密
5:
数字用户认证原则:数字用户验证模型,认证方式,用户验证的风险评估
基于密码的验证:密码的脆弱性,散列密码的使用,用户密码破解-选择的密码,密码文件访问控制,密码选择策略
基于token的验证:智能卡,智能手机,电子身份证
生物识别的验证:生物识别应用中使用的物理特性,生物特征认证系统的操作,生物识别准确度
6:
访问控制矩阵:访问控制列表,能力清单
自主访问控制
Unix 访问控制示例
基于角色的访问控制
基于属性的访问控制:使用主体、客体和环境的属性来提供非常有表现力的安全策略,适用于复杂的网络服务,使用扩展访问控制标记语言
7:
对数据库安全的需求
数据库管理系统
关系数据库:关系数据库系统的元素,结构化查询语言
SQL注入攻击:典型的 SQLi 攻击,注入技术,SQLi 攻击途径和类型,SQLi 对策
数据库访问控制:基于SQL 的访问定义,级联授权,基于角色的访问控制
8:
恶意软件的类型:恶意软件的广泛分类,攻击套件,攻击源
高级持续威胁
利用蠕虫传播漏洞:目标发现,蠕虫传播模型,莫里斯蠕虫,蠕虫攻击简史,蠕虫技术现状,手机密码,手机蠕虫,客户端漏洞,路过式下载,点击劫持
有效负载隐身后门、rootkit :Backdoor,Rootkit,Kernel mode rootkits,Virtual machine and other external rootkits
传播-社会工程-跨度电子邮件,木马:垃圾邮件,木马,手机木马
有效负载系统损坏:数据破坏,现实世界损坏 ,逻辑爆炸
有效载荷-攻击代理-僵尸:机器人,机器人的使用,远程控制设施
有效负载信息盗窃键盘记录器、网络钓鱼、间谍软件:凭据盗窃、键盘记录器和间谍软件,网络钓鱼和身份盗窃,侦察、间谍活动和数据泄露
对策:恶意软件对策方法,基于主机的扫描仪,基于签名的防病毒,周界扫描方法,分布式情报收集方法
9:
软件安全问题:常见的软件漏洞利用,引入软件安全和防御性规划
处理程序输入:输入大小和缓冲区溢出,解释计划输入,验证输入语法
写安全计划代码:正确的算法实现,正确地解释数据值
10:
SSL 和 TLS:TLS架构,TLS 协议,TLS 攻击,SSL/TLS 攻击
HTTPS:连接机构,连接关闭
11:
拒绝服务攻击:拒绝服务攻击的性质,经典的拒绝服务攻击,源地址欺骗,SYN 欺骗
洪水攻击:ICMP洪水,UDP洪水,TCP SYN 洪水
防御dos攻击
分布式dos攻击
基于应用的带宽攻击:SIP洪水,基于HTTP的攻击
反射器和放大器攻击:反射攻击,放大攻击,DNS 放大攻击
响应拒绝服务攻击
12:
对防火墙的需求
防火墙特性和访问政策
防火墙的类型:包过滤防火墙,状态检测防火墙,应用级网关,电路级网关
防火墙基础:堡垒主机,基于主机的防火墙,个人防火墙
防火墙位置和配置:DMZ 网络,虚拟专用网络,分布式防火墙,防火墙位置和拓扑
13:
IP 安全:封装安全负载,安全关联,IPSEC 模式
VPNs
入侵检测系统 (IDS):异常检测,启发式和签名检测
入侵防御系统:基于主机,基于网络
Honeypots
14:
信息安全管理
组织情境和安全政策
安全风险评估:基线方法,非正式的方法,详细的风险分析,组合方法
详细的安全风险分析:上下文和系统表征,识别威胁/风险/漏洞,分析风险,评估风险,处理风险
15:
网络犯罪和计算机犯罪:计算机犯罪的类型,执法挑战,与执法部门合作,英国计算机滥用法
知识产权:知识产权类型,与网络和计算机安全相关的知识产权,英国版权设计和专利法,数字千年版权法案,数字版权管理
隐私:隐私法律法规,GDPR 和数据保护法,组织反应,电脑使用隐私,隐私、数据监控、大数据和社交媒体
16:
cookie: 第一方和第三方方法,GDPR 合规性,新方法
洋葱路由器: Tor 项目,技术实施,Tor 服务,分布式哈希表
物联网: 定义,修补漏洞
17:
攻击面
攻击树
渗透测试基础
渗透测试与漏洞评估
为什么要进行渗透测试?
白帽黑客与黑帽黑客
白盒、黑盒、灰盒测试
渗透测试方法
NIST 方法:计划、发现、攻击和报告阶段。
18:
数字现金
交易
公共交易记录——区块链
加密交易印章
比特币区块链详情
默克尔树
工作量证明和挖矿
比特币网络
问题
1,2
五个网络安全基本要求
机密性,完整性,可用性,真实性,问责制
Confidentiality :Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary information
Integrity:Guarding against improper information modification or destruction, including ensuring information nonrepudiation and uthenticity
Availability: Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information
Authenticity :The property of being genuine and being able to be verified and trusted; confidence in the validity of a transmission, message or message originator. Requires verifying users checking the origin of each input
Accountability: Providing the capability of actions being traced to their originator. Supports nonrepudiation, deterrence, fault isolation, intrusion detection and prevention. Records are kept to provide post-attack analysis and meet legal requirements
Vulnerabilities, Threats and Attacks 漏洞、威胁和攻击
Categories of vulnerabilities
•Corrupted (loss of integrity)
•Leaky (loss of confidentiality)
•Unavailable or very slow (loss of availability)
Threats
•Capable of exploiting vulnerabilities
•Represent potential security harm to an asset
Attacks (threats carried out)
•Passive – attempt to learn or make use of information from the system
that does not affect system resources
•Active – attempt to alter system resources or affect their operation
•Insider – initiated by an entity inside the security parameter
•Outsider – initiated from outside the perimete
Countermeasures 对策
May itself introduce new vulnerabilities
Residual vulnerabilities may remain
Goal is to minimize residual level of risk to the assets
目标是将资产的剩余风险水平降至最低
Means used to deal with security attacks
•Prevent
•Detect
•Recove
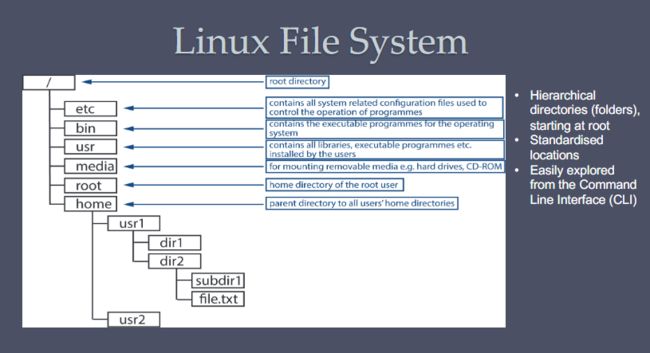
linux
Linux is a clone of Unix
Unix was one of the first multitasking operating systems from Bell in 1969
•Open Source operating system providing full multitasking across multiple architectures
•Created in 1991 by Linus Torvald and supported by a very large community
•It is free, unlike Windows, MacOs, and iOS (Android offshoot of Linux)
Available in a wide variety of distributions
- A distribution is a chosen Linux kernel, a package management system and a set of
applications - Some are commercially backed: RedHat, openSUSE
- Others community managed: Debian, Gentoo…
- We’ll be using Ubuntu, commercially managed by Canonical Ltd, based on Debian and very stable
Virtual Machines
- An operating system abstracts the hardware so multiple processes can run
- Machine virtualization is an abstraction of hardware so that multiple operating systems can run concurrently
- A hypervisor provides the interface abstractions for this to happen
- Commonly used by cloud providers to deliver multiple instances on a single server
- A full copy of the OS is installed on every VM
Containers
Rather than packaging the whole OS, software can provide namespace management within a Process to isolate applications (rebasing the apps view of the directory structure, and catching and redirecting the signals)
Applications can be packaged with the other applications and services needed and run in a user space process
docker是最有名的container
Docker
A Docker container image is a lightweight, standalone, executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an
application: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries and settings.
An image becomes a container when it runs on a container runtime eg Docker Engine
3-symmetric-cryptography
Symmetric Cryptography 对称密码学 p3
为传输或存储的数据提供机密性的通用技术
也称为常规加密 conventional encryption 或单密钥加密single-key encryption
安全使用的两个要求:
- 需要强大的加密算法
- 发送方和接收方必须以安全的方式获得密钥的副本,并且必须保证密钥的安全
明文 Plaintext: The original message fed into the algorithm
加密算法 Encryption algorithm: The rules for substituting and transforming the plaintext
密钥 Secret Key: The sequence of bytes that guides the encryption algorithm
密文 Ciphertext: The scrambled message out of the algorithm
解密算法 Decryption algorithm: The rules for substituting and transforming the ciphertext to return the plaintext
Attacking Symmetric Encryption 攻击对称加密 p5
密码分析攻击Cryptanalytic Attacks
基于:算法性质, 明文一般特征的一些知识,一些示例明文-密文对
蛮力攻击Brute-Force Attacks
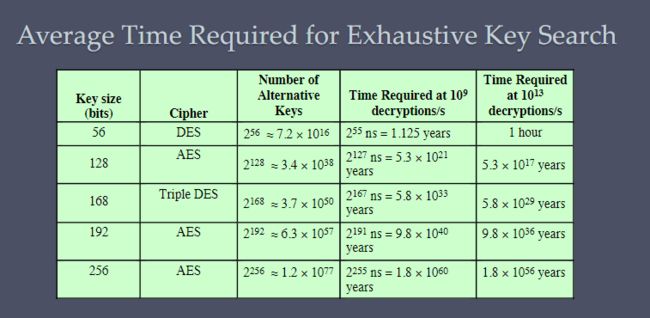
Data Encryption Standard (DES) 数据加密标准 p6
第一个广泛使用的加密方案
使用 64 位明文块和 56 位密钥生成 64 位密文块
强度问题:
- 对算法本身的担忧
DES 是现有研究最多的加密算法 - 关于使用 56 位密钥的担忧
商用现成处理器的速度使这成为长度严重不足关键
Triple DES (3DES) p7
使用两个或三个唯一密钥重复基本 DES 算法三次
优点:
- 168位密钥长度克服了DES暴力破解的脆弱性
- 底层加密算法与DES相同
缺点: - 算法在软件上迟钝
使用64位块大小
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) p8
安全强度等于或比 3DE 好
对称密码块
128 位数据128/192/256 位码
比较
Block & Stream Ciphers 块和流密码 p12
Block Cipher
• 一次处理输入的一个元素块
• 为每个输入块生成一个输出块
• 相同的块生成相同的输出
• 比较普遍
Cipher Block Chaining
• 一次处理一个区块
• 使用当前块的输出与下一个块的输入异或
• 相同的块生成不同的输出
Stream Cipher
• 连续处理输入元素
• 一次生成一个元素
• 主要优势是它们几乎总是更快并且使用更少的代码
• 一次加密一个字节的明文
• 伪随机流是一种在不了解 th 的情况下不可预测的流。
Message Authentication p14
防止主动攻击
验证收到消息的完整性和真实性
可以使用常规加密
- 消息加密本身不提供安全的身份验证形式
- 通过加密消息及其身份验证标签,可以在单个算法中结合身份验证和机密性
- 通常,消息身份验证是作为与消息加密不同的功能提供的
- 无需保密的消息身份验证可能更可取的情况包括:
有许多应用程序将相同的消息广播到多个目的地
一种交换,其中一方负载很重,无法承担解密所有传入消息的时间
明文形式的计算机程序认证是一项有吸引力的服务 - 因此,身份验证和加密都可以满足安全要求
哈希函数 p19
hash function H 必须有以下属性:
Can be applied to a block of data of any size
Produces a fixed-length output
H(x) is relatively easy to compute for any given x
One-way or pre-image resistant
Computationally infeasible to find x such that H(x) = h
Computationally infeasible to find y ≠ x such that H(y) = H(x)
Collision resistant or strong collision resistance
Computationally infeasible to find any pair (x,y) such that H(x) =H(y)
Security of Hash Functions
- 密码分析Exploit logical weaknesses in the algoritm
- 暴力攻击Strength of hash function depends solely on the length of the hash code produced by the algorithm
SHA 是使用最广泛的哈希算法
其他应用:
- 密码Hash of a password is stored by an operating system
- 入侵检测Store H(F) for each file on a system and secure the hash values
4-public-key-cryptography
Public-key encryption 公钥加密 p3
非对称的,基于数学方程
用两个单独的钥匙:公钥和私钥
用户用私钥加密数据
任何知道相应公钥的人都可以解密该消息 p5
一些需求:
以计算方式轻松创建密钥对
秘钥应可用于每个人
接收者容易计算私钥来解密密文
发件人容易计算公钥来加密消息
对手不能够以其他方式恢复原始消息
对手不能够从公钥中确定私钥
对称加密算法 p7
RSA (Rivest, Shamir, Adleman)
Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm
Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC)
Digital Signatures 数字签名 p8
The result of a cryptographic transformation of data that,when properly implemented, provides a mechanism for verifying origin authentication, data integrity and signatory non-repudiation.
三种数字签名算法:
Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA)
RSA Digital Signature Algorithm
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA)
一些应用:p12
随机数 p13
公钥算法的密钥
对称流密码的流密钥
用作临时会话密钥或用于创建数字信封的对称密钥
握手以防止重放攻击
会话密钥
要求:p14
随机性和不可预测性
随机和伪随机 :p15
伪随机数是:
• 生成的序列满足统计随机性测试
• 可能是可预测的
True random number generator (TRNG):
一些应用: p16
存储数据
5-user-authentication
System Identity and Authentication 系统标识和认证 p4
An identity on a system 通常是唯一的
系统上的所有操作都与至少一个标识相关联
Access Control:此标识符将用于检查用户可以执行哪些操作
Accountability:此标识符将与日志文件中的记录相关联
User Authentication:用户与身份相关联的过程
To authenticate, the user is typically required to show evidence that they are who they claim, This evidence is the factor.
User identity attributes 用户标识属性 p5
用户认证风险评估
- Assurance Level 保证级别 p8
四个等级 - Potential impact 潜在影响 p9
low moderate high
每个保证级别的最大潜在影响 p10 - Areas of risk 风险领域
Password-Based Authentication 基于密码的认证 p11
没啥可说
Password Storage 密码存储 p12
密码需要保存在系统中但不应明文保存
字典攻击:Attacker 获取字典,并对每个条目应用哈希函数,大多数密码都是单个单词,因此攻击者可以搜索密码文件以匹配条目,Attacker 可以应用常见的密码添加规则来生成进一步的匹配可能性,例如
数字在末尾,标点在末尾
使用盐值:在密码上使用随机数前缀会降低字典攻击的有效性
Password Cracking 密码破解p17
Dictionary attacks
•Develop a large dictionary of possible passwords and try each against the password file
•Each password must be hashed using each salt value and then compared to stored hash values
Rainbow table attacks
•Pre-compute tables of hash values for all salts
•A mammoth table of hash values
•Can be countered by using a sufficiently large salt value and a sufficiently large hash length
短密码更容易破解
John the Ripper
•Open-source password cracker first developed in 1996
•Uses a combination of brute-force and dictionary technique
现代用的方法:p18
复杂的密码策略
密码选择策略:p20
教用户用厉害的,计算机生成的密码,反应式密码检查,复杂的密码策略
Memory Cards储存卡 p22
可以存储但不处理数据
•最常见的是磁条卡
•可以包括内部电子存储器
•可单独用于物理访问比如:酒店房间,自动取款机
• 结合使用可提供更高的安全性密码或PIN
存储卡的缺点包括:需要特殊阅读器,令牌丢失,用户不满
Smart Tokens,Smart Cards, SmartPhones p23,24,27
smart card Contain:An entire microprocessor:Processor, Memory ,I/O ports
通常包括三种类型的内存:ROM,RAM,EEPROM
Electronic Identity Cards (eID) 电子身份证 p25
使用smart card作为身份证
Biometric Authentication 生物认证 p28
尝试根据独特的身体特征对个人进行身份验证
Based on pattern recognition
Physical characteristics used include:
- Facial characteristics
- Fingerprints
- Hand geometry
- Retinal pattern 视网膜
- Iris 虹膜
- Signature
- Voice
6-access-control
Access Control p4
Access Control 定义p4 原则p5
Access Control Policies策略 p7
Discretionary access control (DAC) 自主访问控制 p9
根据请求者的身份和访问规则(授权)控制访问,说明请求者可以(或不允许)做什么
通常使用访问控制矩阵提供:一个维度由已识别的可能尝试访问资源的数据的主体组成,另一个维度列出了可以访问的对象
Mandatory access control (MAC) 强制访问控制
基于安全标签与安全许可的比较来控制访问
Role-based access control (RBAC) 基于角色的访问控制 p17
Controls access based on the roles that users have within the system and on rules stating what accesses are allowed to users in given roles
need define roles then define the security policy
Attribute-based access control (ABAC) 基于属性的访问控制 p22
Subjects, Objects 和对应的 Access Rights
its flexibility and expressive power is strength
subject 属性:
A subject is an active entity that causes information to flow among objects or changes the system state
Attributes define the identity and characteristics of the subject
object 属性:
An object (or resource) is a passive information system-related entity containing or receiving information
Objects have attributes that can be leverages to make access control decisions
Environment 属性:
Describe the operational, technical, and even situational environment or context in which the information access occurs
These attributes have so far been largely ignored in most access control policies
策略:p26
UNIX File Access Control p12
Unique user identification number (user ID)
Member of a primary group identified by a group ID
Access Control Lists (ACLs) p15
FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Linux, Solaris
Constraints p21
7-databases
数据库
介绍p3
相关p6
Structured Query Language (SQL)p8
Database Security p11
SQL Injection Attacks (SQLi) p12
o修改或删除数据
o执行任意操作的系统命令
o启动DoS攻击
SQLi Attack Avenues攻击途径 p15
Inband Attacks p16
使用相同的通信渠道注入 SQL 代码和检索结果
包括:Tautology,End-of-line comment,Piggybacked queries
tautology 例子:用and 或or语句跳过密码检查
Piggybacked queries例子:使用分号来执行额外的查询语句
Inferential Attack p19
没有实际的数据传输,但攻击者能够通过发送特定请求并观察网站/数据库服务器的结果行为来重建信息
包括:Illegal/logically incorrect queries,Blind SQL injection
out-of-band attack p22
使用不同的通道检索数据
SQL注入对策 p23
Defensive coding
- Manual defensive coding practices
- Parameterized query insertion
- SQL DOM
Detection - Signature based
- Anomaly based
- Code analysis
Run-time prevention
Check queries at runtime to see if they conform to a model of expected queries
database access control p24
Centralized administration
Ownership-based administration
Decentralized administration
SQL Access Controls p25
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) p26
8-malicious Software 恶意软件
malware
定义p4
广泛意义上可以按如何传播和如何执行进行分类 p6
Based first on how it spreads or propagates to reach the desired targets
Then on the actions or payloadsit performs once a target is reached
比如是否需要host program,是否独立,是否会复制(trojans ,spam e-mail不会复制;viruses and worms 会复制)
传播机制可以分为:
• 现有内容被病毒感染,随后传播到其他系统
• 通过蠕虫或驱动下载利用软件漏洞来允许恶意软件复制
• 诱使用户绕过安全机制安装木马或响应网络钓鱼攻击的社会工程攻击
如何执行:
• 系统或数据文件损坏
• 盗窃服务/使系统成为僵尸网络攻击的僵尸代理
• 从系统/键盘记录中窃取信息
• 隐藏/隐藏其在系统中的存在
Attack Kits p7
Attack Sources p8
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) p9
特征:Advanced, Persistent 持久,Threats p10
APT Attacks p11
Viruses p12
容易通过网络环境传播且会复制并继续感染其他内容
component p13
感染机制 Infection mechanism/ infection vector
触发器 Trigger / logic bomb
阶段p14
Dormant phase,Triggering phase,Propagation phase,Execution phase
休眠阶段、触发阶段、传播阶段、执行阶段
分类 p17
Classification by target
• Boot sector infector
• File infector
• Macro virus
• Multipartite virus
Classification by concealment strategy隐藏策略
• Encrypted virus
• Stealth virus
• Polymorphic virus
• Metamorphic virus
Worms p18
利用客户端或服务器程序中的软件漏洞
Can use network connections to spread from system to system
Spreads through shared media (USB drives, CD, DVD data disks)
Morris Worm p22
Mobile Phone Worms p27
其他
Watering-Hole Attacks p29
Clickjacking p31
payload
Payload System Corruption p33
Ransomware p35 勒索软件
Attack Agents Bots p36
Remote Control Facility p37
Information Theft Keyloggers and Spyware p38 信息盗窃键盘记录器和间谍软件
Information Theft Phishing p39 网络信息钓鱼
Stealthing Backdoor p40
Stealthing Rootkit p41
Malware Countermeasure Approaches p44
预防的四大要素:政策,意识,漏洞缓解,威胁缓解
杀毒软件的迭代:simple scanners - heuristic scanners - activity traps - full-featured protection
著名的Sandbox Analysis p46
9-softwareExploits
Security Flaws漏洞 p3
包含五点
•Unvalidated input
•Cross-site scripting
•Buffer overflow
•Injection flaws
•Improper error handling
救,,不想看了
软件安全性,质量和可靠性 p5
Input Size & Buffer Overflow p11
Interpretation of Program Input
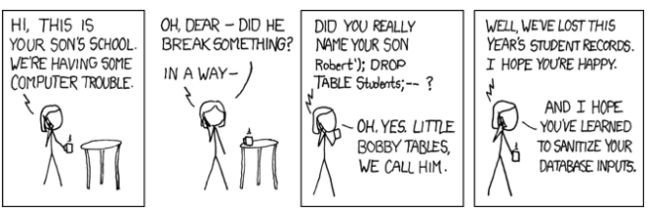
sql注入 p14
Robert'); DROP TABLE STUDENTS; --
用PDO:
$dsn = "mysql:host=localhost;dbname=myDatabase;charset=utf8mb4";
try {
$pdo = new PDO($dsn, "username", "password", $options);
} catch (Exception $e) {
error_log($e->getMessage());
exit('Something weird happened'); //something a user can understand
}
//select
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=?");
$stmt->execute([$id]);
$user = $stmt->fetch();
//insert
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("INSERT INTO myTable (name, age) VALUES (?, ?)");
$stmt->execute([$_POST['name'], 29]);
$stmt = null;
//update
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("UPDATE myTable SET name = ? WHERE id = ?")->execute([$_POST['name'], $_SESSION['id']]);
$stmt = null;
//delete
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("DELETE FROM myTable WHERE id = ?");
$stmt->execute([$_SESSION['id']]);
$stmt = null;
用mysql:
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// prepare and bind
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO MyGuests (firstname, lastname, email) VALUES (?, ?, ?)");
$stmt->bind_param("sss", $firstname, $lastname, $email);
xss攻击 p16
怎么写安全代码和处理程序输入
Validating Input Syntax p18
Alternate Encodings p19
Correct Algorithm Implementation p21
一些安全问题:
•正确的算法实现
•纠正算法的机器指令
•有效操作数据
10-secureWeb
Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange p3
第一个公开的公钥算法
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
两种执行方式:作为底层协议套件的一部分提供,嵌入特定包中
TLS概念 p9:
session 是 between a client and a server
由握手协议创建
Define a set of 密码安全参数
Used to avoid the expensive negotiation of new security parameters for each connection
TLS Connection是对等关系Peer-to-peer relationships
Handshake Protocol 握手协议 p12
TLS 中最复杂的部分
首先认证双方,接着协商加密和 MAC 算法,最后商议要用的秘钥
有四个阶段:

Alert Protocol警报协议 p15
传达 TLS 相关的实体警报,警报消息是压缩和加密的
每条消息包括两个字节:
第一个字节取值警告(1)或致命(2)来传达消息的严重性
第二个字节包含一个代码表示特定警报
Heartbeat Protocol 心跳协议 p16
A periodic signal generated by hardware or software to indicate normal operation or to synchronize other parts of a system
通常用于监控协议实体的可用性
在 TLS 记录协议之上运行,在握手协议的第 1 阶段建立使用
每个peer表示是否支持心跳
有两个目的:
• 向发件人保证收件人还活着
• 在空闲期间通过连接生成活动
SSL/TLS Attacks p17
Four general categories:
对握手协议的攻击
对记录和应用程序数据协议的攻击
对 PKI 的攻击
其他攻击
HTTPS p19
HTTP over SSL
结合HTTP和SSL实现安全Web 浏览器和 Web 服务器之间的通信
充当 HTTP 客户端的代理也充当 TLS 客户端
有点绕口令的Connection closure
Closure of an HTTPS connection requires that TLS close the connection with the peer TLS entity on the remote side, which will involve closing the underlying TCP connection
关闭 HTTPS 连接需要 TLS 关闭与远程端对等 TLS 实体的连接,这将涉及关闭底层 TCP 连接
11-DoSAttacks
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack p3
对某些服务可用性的一种攻击形式
可能受到攻击的资源类别有:Network bandwidth,System resources,Application resources p4
Flooding ping command p6
第一代 DoS 攻击
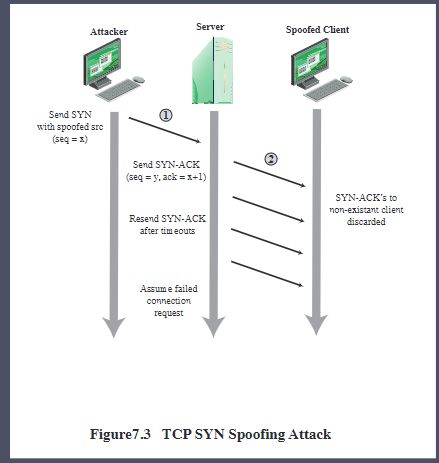
Source Address Spoofing p7
Use forged source addresses
TCP Three-way handshake p8
SYN Spoofing欺骗 p9
TCP 连接从交换设置了 SYN 标志的数据包开始
是常见的DoS攻击
ATTACKS
Flooding Attacks(p11)
根据使用的网络协议分类:
ICMP flood
UDP flood
TCP SYN flood
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks p12
使用多个系统生成攻击
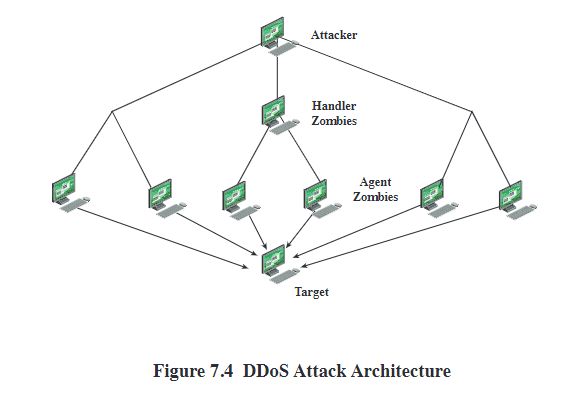
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Based Attacks P15
通过http请求攻击
Reflection Attacks P16
“Reflects” the attack off the intermediary (reflector)
Domain Name System (DNS) Reflection Attack P17
DNS Amplification Attacks P18
攻击者创建一系列包含欺骗源的 DNS 请求目标系统地址
利用 DNS 行为将小请求数据包转换为更大的响应数据包(放大)
DoS Attack Defenses p20
这些攻击不能完全阻止
防御 DDoS 攻击的四道防线:
Attack prevention and preemption (Before attack)
Attack detection and filtering (During the attack)
Attack source traceback and identification (During and after the attack)
Attack reaction (After the attack)
Prevention:
• Block spoofed source addresses
• Filters may be used to ensure path back to the claimed source address is the one being used by the current packet
• Use modified TCP connection handling code
• Block IP directed broadcasts
• Block suspicious services and combinations
• Manage application attacks with a form of graphical puzzle (captcha) to distinguish legitimate human requests
• Good general system security practices
• Use mirrored and replicated servers when high-performance and reliability is required
Responding to DoS Attacks 响应攻击 p22
有计划:
• 有关如何联系 ISP 技术人员的详细信息
• 需要对上游实施流量过滤
• 如何应对攻击的详细信息
实施反欺骗、定向广播和速率限制过滤器
最好有网络监视器和 IDS 来检测和通知异常流量模式
识别攻击类型
•捕获和分析数据包
•设计过滤器以阻止上游的攻击流量
•或识别并纠正系统/应用程序错误
让 ISP 跟踪数据包流回源
• 可能困难且耗时
•如果计划采取法律行动是必要的
实施应急计划
•切换到备用备份服务器
•在具有新地址的新站点上调试新服务器
更新事件响应计划
•分析攻击和响应以供将来处理
12-firewalls
为什么需要防火墙:保护局域网的有效方法,在家庭网络和互联网之间建立受控链接,用作外围防御
防火墙特性:Design goals
防火墙访问策略p5
Filter Characteristics p6
能力:
• 定义单个阻塞点
• 提供监控安全的位置事件
• 方便的与安全无关的多种互联网平台功能
• 可作为IPSec 的平台
限制:
• 无法防御绕过防火墙的攻击
• 可能无法完全抵御内部威胁
• 可以从组织外部访问不适当保护的无线 LAN
• 笔记本电脑、PDA 或便携式存储设备可能在公司网络之外被感染,然后在内部使用
Packet Filtering Firewall p9
将规则应用于每个传入和传出的 IP 数据包
• 通常是基于 IP 或 TCP 标头中的匹配的规则列表
•根据规则匹配转发或丢弃数据包
两个默认策略:
Discard - 除非明确允许,否则禁止
•更保守、可控、对用户可见
Forward - 除非明确禁止,否则允许
•更易于管理和使用,但安全性较低
优点p11
•简单
•通常对用户透明且速度非常快
弱点
•无法阻止利用应用程序特定漏洞的攻击或功能
•有限的日志记录功能
•不支持高级用户认证
• 易受 TCP/IP 协议漏洞攻击
•不正确的配置可能导致违规
Stateful Inspection Firewall p12
各种网关
Application-Level Gateway p14
Also called an application proxy
Circuit-Level Gateway p15
SOCKS Circuit-Level Gateway p16
堡垒主机 bastion host p17
Host-Based Firewalls p18
好处:
•过滤规则可以根据主机环境定制
•提供独立于拓扑的保护
•提供额外的保护层
Personal Firewall p19
控制个人计算机或工作站与 Internet 或企业网络之间的流量
适合家庭或公司使用
通常比基于服务器或独立的防火墙简单得多
主要作用是拒绝未经授权的远程访问
还可以监控传出流量以检测和阻止蠕虫和恶意软件活动
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) p21
Firewall Topologies p22
Host-resident firewall
•Includes personal firewall software and firewall software on servers
Screening router
•Single router between internal and external networks with stateless or full packet filtering
Single bastion inline
•Single firewall device between an internal and external router
Single bastion T
•Has a third network interface on bastion to a DMZ where externally visible servers are placed
Double bastion inline
•DMZ is sandwiched between bastion firewalls
Double bastion T
•DMZ is on a separate network interface on the bastion firewall
Distributed firewall configuration
•Used by large businesses and government organizations
13-IPSEC-VPN-IDS
IP Security (IPsec) p3
有多种应用程序安全机制
•S/MIME、Kerberos、SSL/HTTPS
Benefits of IPsec p4
•当在防火墙或路由器中实施时,它为穿过边界的所有流量提供强大的安全性
•在防火墙中,它可以抵抗绕过
• 在传输层之下,因此对应用程序透明
•可以对最终用户透明
•可为个人用户提供安全保障
•安全的路由架构
The Scope of IPsec p5
两个主要功能:
组合认证/加密功能 Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
密钥交换功能
还有一个仅认证功能, implemented using an Authentication Header (AH)
Security Associations 安全协会 p6
由 3 个参数定义:
Security Parameter Index (SPI)
IP Destination Address
Protocol Identifier
Transport and Tunnel Modes p8
传输模式:
扩展到 IP 数据包的有效负载
通常用于端到端两台主机之间的通信
隧道模式:
为整个 IP 数据包提供保护
VPN p9
在防火墙上实施 IPSEC,
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)入侵侦测系统 p10
Host-based IDS (HIDS)
Network-based IDS (NIDS)
Distributed or hybrid IDS
三个逻辑组件:
Sensors - collect data
Analyzers - determine if intrusion has occurred
User interface - view output or control system behavior
IDS 需求: p11
分析方法:p12
Anomaly detection p13
有Statistical,Knowledge based,Machine-learning
Signature/Heuristic detection p14
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)入侵防御系统 p15
是 IDS 的扩展,包括尝试阻止或阻止检测到的恶意活动的能力
Can be host-based, network-based, or distributed/hybrid
Host-Based IPS(HIPS) p16
HIPS作用p18
Network-Based IPS(NIPS) P19
Honeypots P20
Decoy systems
分类:LOW,HIGH
14-informationTechnologySecurity
Information Technology (IT) Security Management Overview信息技术安全管理
IT 安全管理:用于实现和维护适当级别的机密性、完整性、可用性、责任性、真实性和可靠性的过程。
IT 安全管理功能包括:p4八点
流程p5
IT 安全是一个持续的过程,Plan - Do - Check - Act 模型
组织背景和安全政策p7
Security Policy p8
需要解决:
• 范围和目的,包括目标与业务、法律、法规要求
• IT 安全要求
• 职责分配
• 风险管理方法
• 安全意识和培训
• 一般人事问题和任何法律制裁
• 将安全性集成到系统开发中
• 信息分类方案
• 应急和业务连续性计划
• 事件检测和处理流程
• 政策审查的方式和时间,以及对政策的变更控制
组织情境p7
Management Support p9
安全风险评估 p10
approach
Baseline Approach p11
informal approach p12
Detailed Risk Analysis p13
Combined Approach p14
asset ,threat,vulnereability,risk
确定要检查的资产
资产,威胁,漏洞,风险的定义:
Asset: A system resource or capability of value to its owner that requires protection
Threat: A potential for a threat source to exploit a vulnerability in some asset, which if it occurs may compromise the security of the asset and cause harm to the asset’s owner
Vulnerability: A flaw or weakness in an asset’s design, implementation, or operation and management that could be exploited by some threat
Risk: The potential for loss computed as the combination of the likelihood that a given threat exploits some ulnerability to an asset, and the magnitude of harmful consequence that results to the asset’s owner
Asset Identification p19
Threat Identification p21
Threat Sources p22
Vulnerability Identification p23
Analyze Risks p24
风险 = 发生威胁的概率 x 组织成本
Analyze Existing Controls p25
risk
风险相似度p26
风险结果p27
风险等级(E,H,M,L)P28
风险处理方案P31
15-lawEthics
Computer Crime
type p4:
Computers as targets
Computers as storage devices
Computers as communications tools
法律 p7:
网络犯罪分子p8
受害者p9
英国计算机滥用法(1990)p11
知识产权Intellectual property
知识产权p12
版权p13
专利p15
商标p16
US Digital Millennium Copyright Act 1998 (DMCA) p18
数字版权管理DRM P20
隐私
隐私权p22
欧盟数据保护指令 p23
隐私通用标准p25:Anonymity: Pseudonymity,Unlinkability,Unobservability
隐私保护p27
16-privacyTechnology
cookie p3
cookie 是服务器发送到浏览器并存储在浏览器中的一小段信息。
第三方 Cookie p4
存在浏览器中
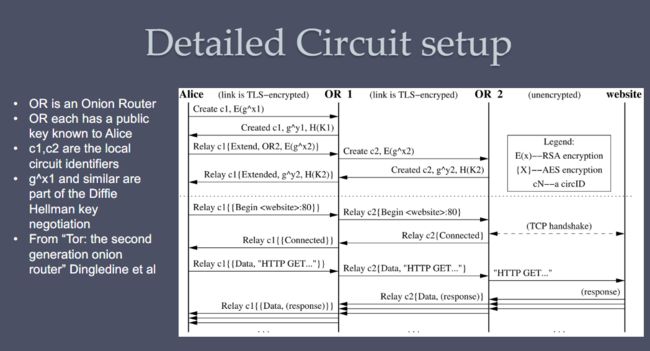
The Onion Router (TOR) p6
洋葱路由器 (TOR)旨在允许匿名浏览互联网,它也是访问暗网的关键工具
数据包通过 OR1 密钥加密发送,OR2 密钥加密密文,OR3 密钥加密实际 GET 请求
洋葱服务标识符是带有洋葱后缀的字符串,例如abc123467.onion
The identifier is used to lookup the public key and the IP address of a Tor node that will accept connections in a distributed hash table (DHT)
DHT是一种分布式结构通过互联网允许插入、查找和删除键值对
通常通过散列字符串来创建密钥
The Internet of Things p11
物联网是一个术语,指的是智能设备的扩展互连,从电器到微型传感器
Information technology to Operational technology to Personal technology再到最后的Sensor/actuator technology 也就是物联网
Patching Vulnerability p14 关于物联网的安全
17-penetrationTesting
攻击面Attack Surface :由系统中可触及和可利用的漏洞组成
类别:Network attack Surface,Software Attack Surface,Human Attack Surface
攻击树attack tree p5
Penetration Testing 渗透测试 p7
公开和利用目标系统中的漏洞的授权和合法尝试
Computer system, web application, networks, IoT,…
目标系统安全性分析评估
报告:
o目录潜在威胁
o确定网络攻击的可行性
o评估成功的网络攻击对企业的潜在影响
why? p9
使计算机系统、网络系统和网络应用程序更安全
● 旨在在攻击者利用之前发现并缓解系统中的安全漏洞
● 基本原理:渗透测试提供了一定程度的保证,任何恶意用户都无法侵入系统
Who needs ?p10
未来,大型组织可能会被立法要求聘请网络/数字安全专家
hacker p11
White hat hacker
Malicious hackers (black hats)
渗透测试方法:黑盒,白盒,灰盒
约束:
道德黑客(经常)受时间限制
恶意黑客受到隐身的限制
渗透测试仪往往很吵
Not concerned about triggering IDS and firewalls
Not realistic attack simulation
风险:
测试可能会减慢响应时间
系统可能在渗透测试过程中损坏
经验丰富的渗透测试人员可以降低风险
渗透测试方法:
NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology (p15)
https://www.nist.gov/
PTES – Penetration Testing Execution Standard
http://www.pentest-standard.org/index.php/Main_Page
Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/
OWASP – Open Web Application Security Project
https://owasp.org/ Web applications only
18-cryptocurrency加密货币
货币身份可以是数据库表中的键
在加密货币中,身份对应于非对称密钥对
加密货币将交易记录在公共记录上——区块链
交易输出具有:
o一定数量的比特币(以 Satoshis 为单位)
o锁定脚本或产权负担,使用所有者的公钥提供金额的加密封印
交易输入具有:
o指向先前交易的未使用输出的指针,作为哈希交易
o输出索引指向上一次交易
o解锁脚本,当应用于产权负担时,可验证所有者的私钥是产权中的公钥对
比特币交易:区块链交易包含由前所有者使用其私钥解锁并锁定到新所有者的公钥的输入
当交易达成一致时,交易链被发送到网络
● 矿工收集尚未进入区块链的交易并尝试构建block
● Block 是一种数据结构
block头包含指向前一个block的链接
•比特币是点对点网络
典型的比特币网络
• 各个节点相互连接,以促进交易和区块的分配
• 节点度通常为 5 或更多