二叉树题目总结
文章目录
-
-
- 1.二叉树的递归遍历
- 2.二叉树的迭代遍历
- 3.二叉树的层序遍历
- 4.翻转二叉树
- 5.对称二叉树
- 6.二叉树的最大深度
- 7. N叉树的最大深度
- 8. 二叉树的最小深度
- 9.完全二叉树的节点个数
-
1.二叉树的递归遍历
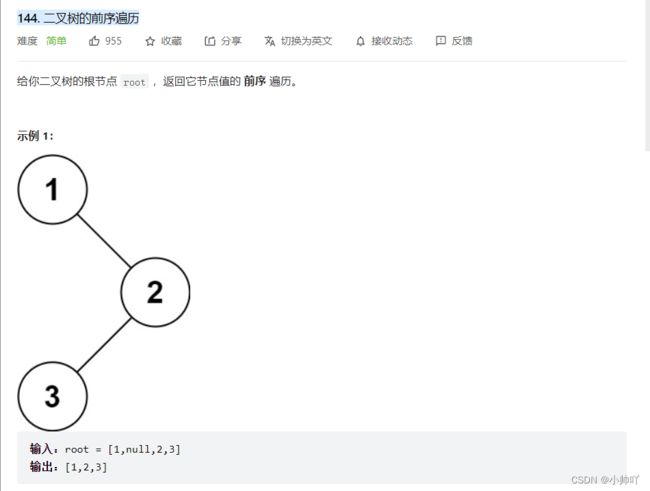
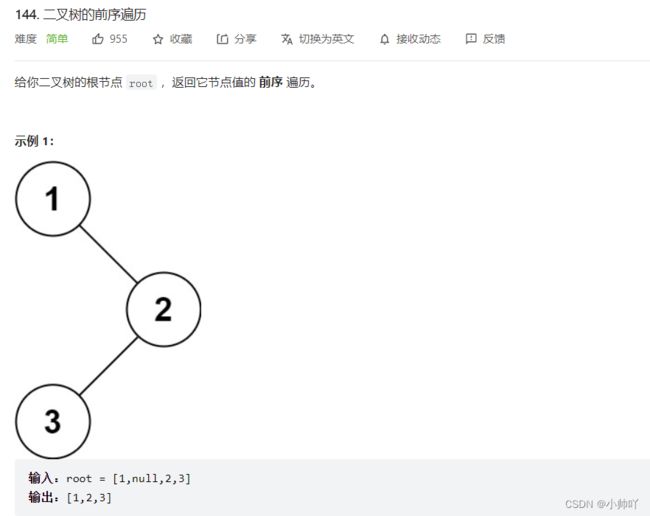
二叉树的前序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root,vector<int> &vec)
{
if(root==nullptr) return;
vec.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root->left,vec);
traversal(root->right,vec);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root,res);
return res;
}
};
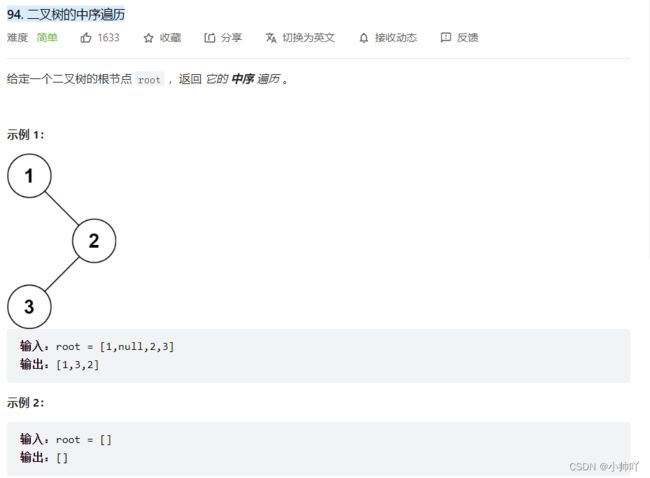
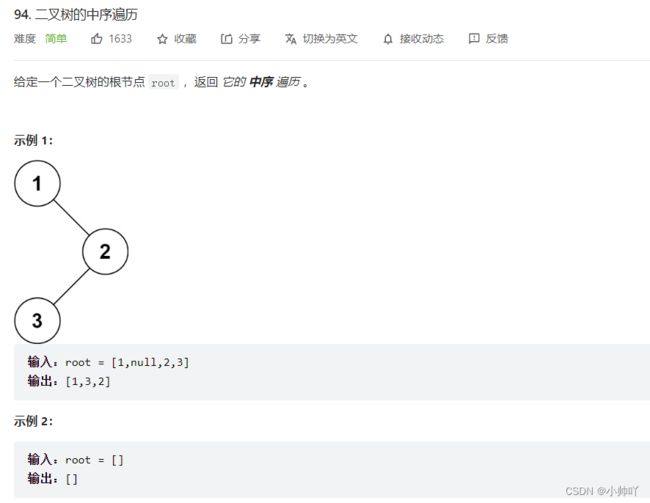
二叉树的中序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root,vector<int> &vec)
{
if(root==nullptr) return;
traversal(root->left,vec);
vec.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root->right,vec);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root,res);
return res;
}
};
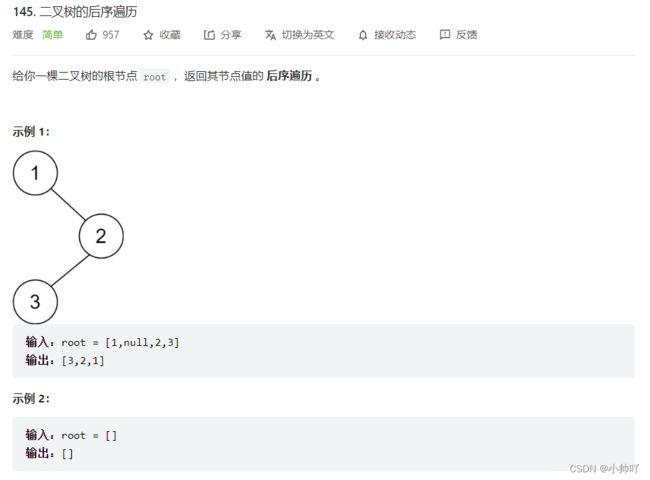
二叉树的后序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root,vector<int> &vec)
{
if(root==nullptr) return;
traversal(root->left,vec);
traversal(root->right,vec);
vec.push_back(root->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root,res);
return res;
}
};
2.二叉树的迭代遍历
//定义一个栈其中存储节点指针,如果root节点不为空,root入栈
//当栈不为空,出栈一个节点,然后将其右节点,左节点入栈
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> sk;
if(root!=nullptr) sk.push(root);
while(!sk.empty())`在这里插入代码片`
{
TreeNode* node = sk.top();
sk.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->right!=nullptr)
sk.push(node->right);
if(node->left!=nullptr)
sk.push(node->left);
}
return res;
}
};
//前序遍历是根左右,而后续遍历是左右根,可以看出来只要更改前序遍历时左右节点入栈的顺序就可以实现根右左
//将根右左反转一下,即得到左右根,即得到后续遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> sk;
sk.push(root);
while(!sk.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = sk.top();
sk.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left!=nullptr)
sk.push(node->left);
if(node->right!=nullptr)
sk.push(node->right);
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> sk;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(cur!=nullptr||!sk.empty())
{
if(cur!=nullptr)
{
sk.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else
{
cur = sk.top();
res.push_back(cur->val);
sk.pop();
cur = cur->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
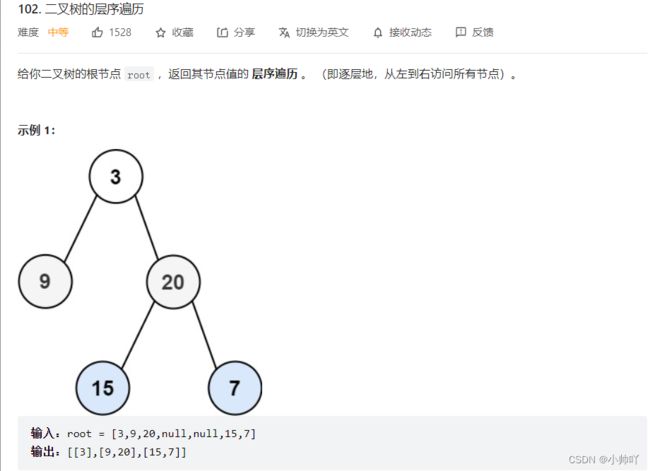
3.二叉树的层序遍历
//定义一个变量存每层的节点数量来实现对每层的遍历和存储
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root!=nullptr) q.push(root);
else return res;
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector<int> out;
TreeNode* cur = nullptr;
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
cur = q.front();
q.pop();
out.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur->left!=nullptr) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right!=nullptr) q.push(cur->right);
}
res.push_back(out);
}
return res;
}
};
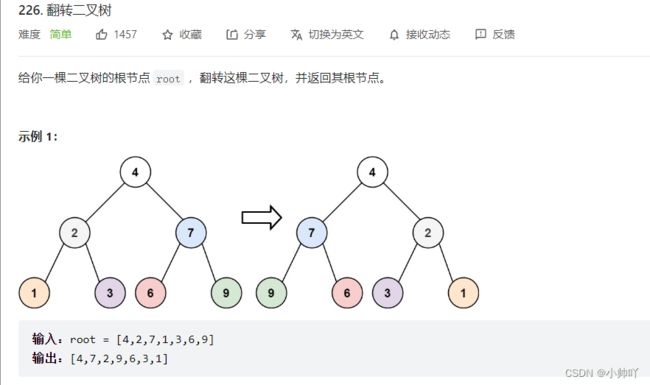
4.翻转二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return root;
swap(root->left,root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return root;
stack<TreeNode*> sk;
sk.push(root);
while(!sk.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = sk.top();
sk.pop();
swap(node->left,node->right);
if(node->right!=nullptr) sk.push(node->right);
if(node->left!=nullptr) sk.push(node->left);
}
return root;
}
};
层序遍历迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return root;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
swap(cur->left,cur->right);
if(cur->left!=nullptr) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right!=nullptr) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
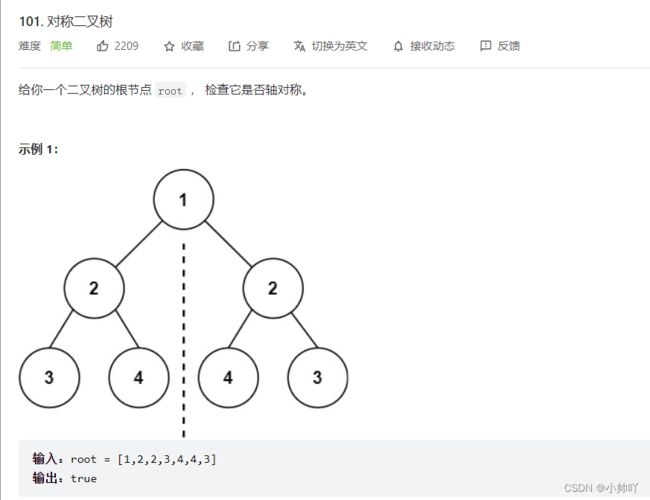
5.对称二叉树
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left,TreeNode* right)
{
if(left!=nullptr&&right==nullptr) return false;
else if(left==nullptr&&right!=nullptr) return false;
else if(left==nullptr&&right==nullptr) return true;
else if(left->val!=right->val) return false;
bool out = compare(left->left,right->right);
bool in = compare(left->right,right->left);
if(out==true&&in==true) return true;
else return false;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return true;
return compare(root->left,root->right);
}
};
迭代法:
//通过队列,每次两个出队列
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return true;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root->left);
q.push(root->right);
while(!q.empty())
{
TreeNode* left = q.front();
q.pop();
TreeNode* right = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!left&&!right) continue;
if(!left||!right||(left->val!=right->val)) return false;
q.push(left->left);
q.push(right->right);
q.push(left->right);
q.push(right->left);
}
return true;
}
};
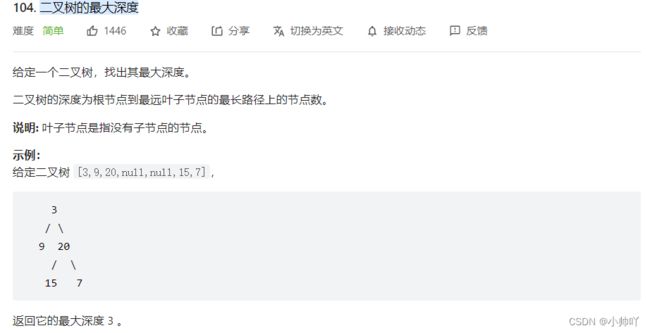
6.二叉树的最大深度
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right))+1;
}
};
迭代法:
//通过层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
int res = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
res++;
}
return res;
}
};
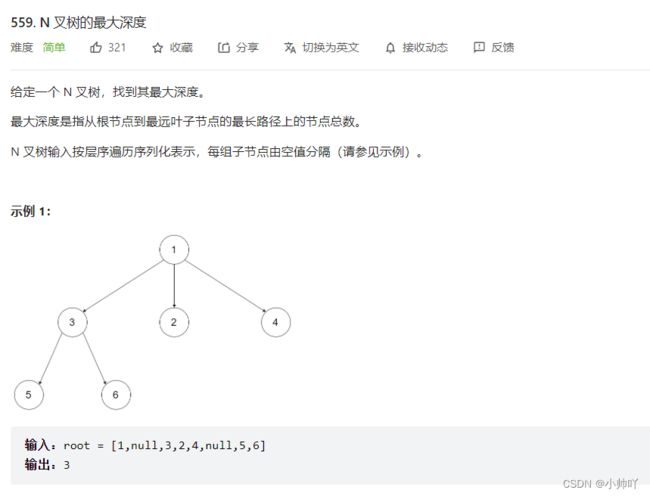
7. N叉树的最大深度
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<root->children.size();i++)
{
res = max(res,maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
res++;
return res;
}
};
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
int res = 0;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int s = q.size();
for(int i =0;i<s;i++)
{
Node* node = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i =0;i<node->children.size();i++)
{
q.push(node->children[i]);
}
}
res++;
}
return res;
}
};
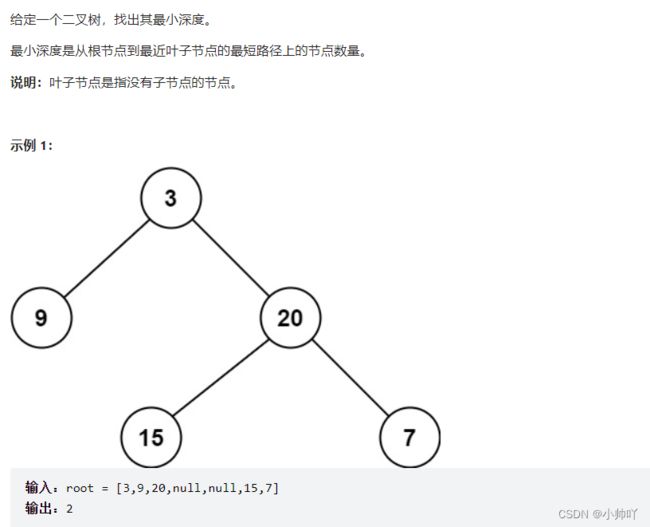
8. 二叉树的最小深度
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
if(!root->left&&root->right) return minDepth(root->right)+1;
else if(root->left&&!root->right) return minDepth(root->left)+1;
else if(root->left&&root->right) return min(minDepth(root->left),minDepth(root->right))+1;
else return 1;
}
};
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int res =0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int s = q.size();
res++;
for(int i =0;i<s;i++)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
if(!cur->left&&!cur->right) return res;
}
}
return res;
}
};
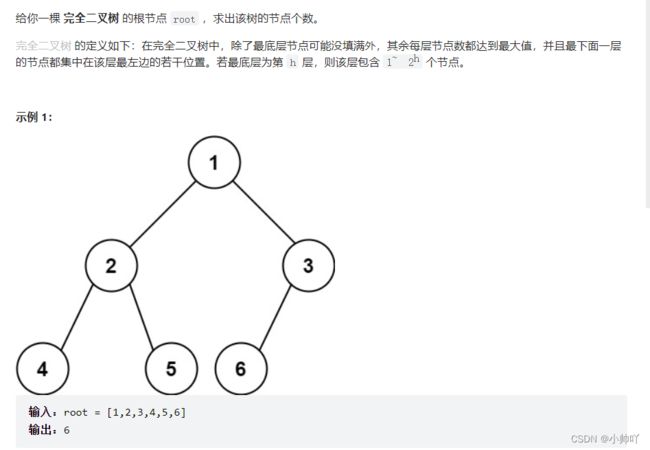
9.完全二叉树的节点个数
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
return countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right)+1;
}
};
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
if(!root) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int s = q.size();
res+=s;
for(int i = 0;i<s;i++)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};