高效推理网络:PeleeNet、VoVNet、DetNet
1. PeleeNet
参考代码:
- Caffe
- PyTorch
论文名称:
《PeleeNet:A Real-Time Object Detection System on Mobile Devices》
1.1 设计理念
在类MobileNet的轻量化网络中广泛采用深度可分离卷积用于减少参数量和计算量,但文章指出这样的结构在不同深度学习推理框架中效率却不高。对此文章全部采用传统卷积的形式在DenseNet的基础上进行改进得到名为PeleeNet的网络。相比MobileNet网络更加轻量化,运行的速度也更快。
相比原是的DenseNet网络文章从下面的角度对其进行改进:
- 1)Two-Way Dense Layer:这部分改进是参考InceptionNet系列网络,在原本的Dense Layer中再添加两个分支,从而可以增加网络对大目标的感知力与网络表达能力,改进前后的网络结构对比见下图所示:

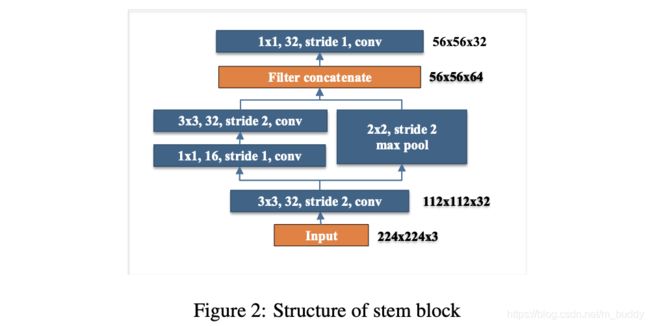
- 2)Stem Block:对于网络输入的初级文章使用多分枝的结构进行改进,避免直接采用增加初级channel数量的方式进行网络表达能力增强(开销大),其结构件下图所示:
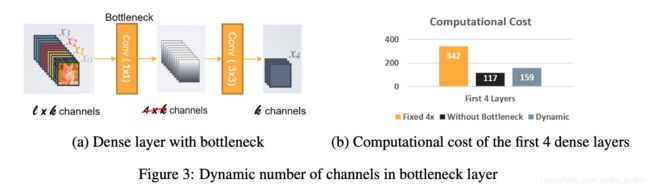
- 3)Dynamic Number of Channels in Bottleneck Layer :这里将DenseNet中的Bottleneck中的中间层channel变化倍率与输入特征图的分辨率进行关联,从而抛弃之前采用的固定倍率的方案。也就是大尺寸的特征图相应得到更小的倍率,从而减少计算量,参见下图:
- 4)Transition Layer without Compression:这里对transition层中的channel数量不做压缩,避免对特征表达带来损失;
- 5)Composite Function:采用Conv+BN+ReLU的形式而不是Conv+ReLU+BN的形式,从而方便进行网络折叠;
消融实验:

设计出的网络结构:

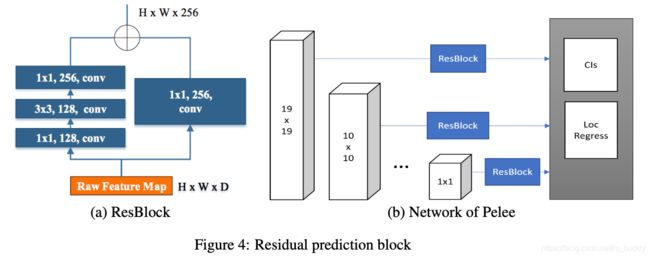
这篇文章提出的方法是建立在检测任务上的,这里采用检测算法头为SSD,对此文章在如下的方面进行调整:
- 1)检测特征选择:采用5个尺度的特征进行检测结果预测( 19 ∗ 19 , 10 ∗ 10 , 5 ∗ 5 , 3 ∗ 3 , 1 ∗ 1 19*19,10*10,5*5,3*3,1*1 19∗19,10∗10,5∗5,3∗3,1∗1);
- 2)预测头与特征图采用残差连接,同时进行特征抽取;
- 3)由于采用了残差连接的形式,预测头部分使用 1 ∗ 1 1*1 1∗1的卷积进行预测,从减少计算开销;
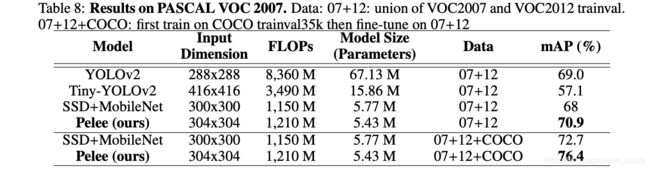
1.2 实验结果
2. VoVNet
参考代码:
vovnet-detectron2
论文名称:
《An Energy and GPU-Computation Efficient Backbone Network for Real-Time Object Detection》
2.1 设计理念
这篇文章在DenseNet的基础上从MAC(memory access cost)和GPU并行计算效率角度对DenseNet中的dense_block进行改进,从而得到兼顾性能和效率的OSA(one-shot aggregation)模块,并在此基础上构建了VoVNet。其在计算速度和功耗上均比相同级别的DenseNet具有较大改善。
MAC角度分析:
内存访问的时间在网络推理过程中是较为重要的因素,对于内存访问次数可以通过下面的计算方式进行计算:
M A C = h w ( c i + c o ) + k 2 c i c o MAC=hw(c_i+c_o)+k^2c_ic_o MAC=hw(ci+co)+k2cico
其中, h , w , c i , c o , k h,w,c_i,c_o,k h,w,ci,co,k分别代表特征图的高度宽度/输入输出的channel数量,以及卷积核的大小。而经常提到的FLOPs与真实的infer性能是并不直接关联的,将MAC与FLOPs进行比较可以建立如下关系:
M A C ≥ 2 h w B k 2 + B h w , B = k 2 h w c i c o MAC\ge2\sqrt{\frac{hwB}{k^2}}+\frac{B}{hw},B=k^2hwc_ic_o MAC≥2k2hwB+hwB,B=k2hwcico
对此,需要将算子输入和输出的channel数量尽量保持一致才能尽量减少MAC,而在愿DenseNet结构中是通过密集联机的方式,这样每个算子的输入输出是不相同的,对此文章提出使用最后concat连接的形式(OSA模块),将其与原模块进行对比见下图所示:
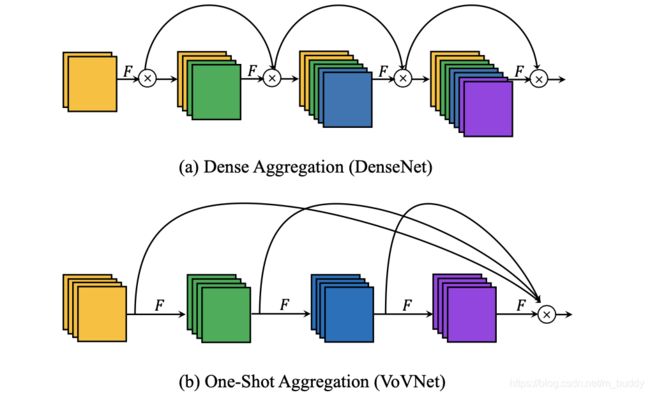
PS: 文章对于原DenseNet中的密集连接进行分析,结果发现密集中的部分layers其实是没有太大贡献的(对于其带来的开销性价比不高),因而直接采用最后concat连接的形式可以在性能相差不大的情况下,减少计算量。
GPU运算效率角度:
GPU的并行计算特性使得其对于大tensor是具有天然计算优势(相对于CPU)的。因而泰国细碎的网络层设计会使得GPU的运算效率变差。下面是原本的DenseNet中基础单元Bottleneck的结构:
# https://github.com/gpleiss/efficient_densenet_pytorch/blob/master/models/densenet.py#L21
class _DenseLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_input_features, growth_rate, bn_size, drop_rate, efficient=False):
super(_DenseLayer, self).__init__()
self.add_module('norm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_input_features)),
self.add_module('relu1', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
self.add_module('conv1', nn.Conv2d(num_input_features, bn_size * growth_rate,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)),
self.add_module('norm2', nn.BatchNorm2d(bn_size * growth_rate)),
self.add_module('relu2', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
self.add_module('conv2', nn.Conv2d(bn_size * growth_rate, growth_rate,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)),
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.efficient = efficient
由于密集连接引入了较多的层( 1 ∗ 1 1*1 1∗1和 3 ∗ 3 3*3 3∗3卷积层)使得总体的FLOP/s变小了,也就是整体计算效率变差。新提出的OSA模块没有采用密集连接的形式,从而简化了Bottleneck,减少了模块的碎片化程度。
构建的网络结构:
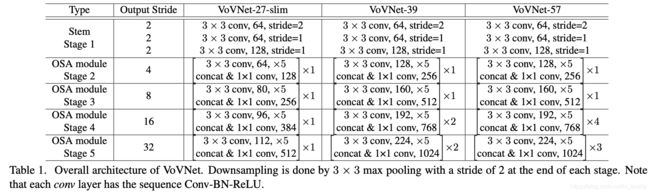
进一步改进:
在上述基础上对OSA模块进行了两个版本的改进,从而使用图c中的机构构建VoVNet-V2网络结构。
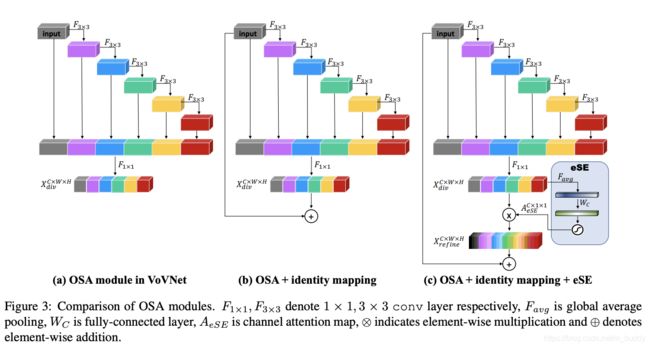
改进模块实现:
# https://github.com/youngwanLEE/vovnet-detectron2/blob/master/vovnet/vovnet.py#L186
class _OSA_module(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, in_ch, stage_ch, concat_ch, layer_per_block, module_name, SE=False, identity=False, depthwise=False
):
super(_OSA_module, self).__init__()
self.identity = identity
self.depthwise = depthwise
self.isReduced = False
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
in_channel = in_ch
if self.depthwise and in_channel != stage_ch:
self.isReduced = True
self.conv_reduction = nn.Sequential(
OrderedDict(conv1x1(in_channel, stage_ch,
"{}_reduction".format(module_name), "0")))
for i in range(layer_per_block):
if self.depthwise:
self.layers.append(
nn.Sequential(OrderedDict(dw_conv3x3(stage_ch, stage_ch, module_name, i))))
else:
self.layers.append(
nn.Sequential(OrderedDict(conv3x3(in_channel, stage_ch, module_name, i)))
)
in_channel = stage_ch
# feature aggregation
in_channel = in_ch + layer_per_block * stage_ch
self.concat = nn.Sequential(
OrderedDict(conv1x1(in_channel, concat_ch, module_name, "concat"))
)
self.ese = eSEModule(concat_ch)
def forward(self, x):
identity_feat = x
output = []
output.append(x)
if self.depthwise and self.isReduced:
x = self.conv_reduction(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x)
output.append(x)
x = torch.cat(output, dim=1)
xt = self.concat(x)
xt = self.ese(xt)
if self.identity:
xt = xt + identity_feat
return xt
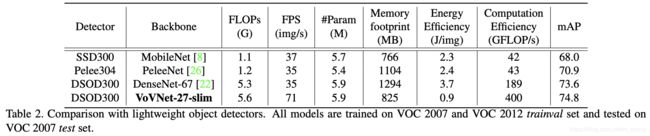
2.2 实验结果
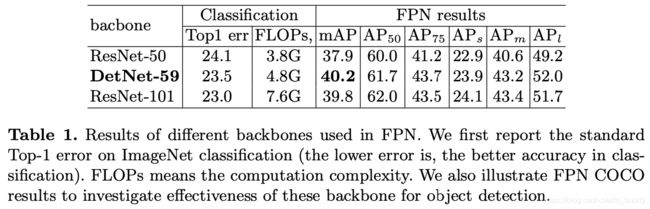
3. DetNet
参考代码:
DetNet_pytorch
论文名称:
《DetNet: A Backbone network for Object Detection》
3.1 设计理念
现有的很多检测网络都是使用ImageNet分类数据集上预训练网络构建检测backbone,但是在这其中存在ImageNet分类任务和检测任务并不一致的问题,一个显著的特点就是ImageNet分类网络通常采用较大的stride,但却正因为这个特点导致这样的网络并不适应于检测网络。对此,文章在ResNet的基础上进行改进得到针对与检测任务优化的backbone,文章将其取名为DetNet。
文章经过分析是得出较大的stride对检测性能具有阻碍作用,主要体现为如下两点:
- 1)对于大目标,经过大stride处理之后会使得大目标的位置预测变得模糊化;
- 2)对于小目标,较大stride的特征图天然对小目标表达能力就受限制;
对此文章从如下角度进行改进:
- 1)在stage 4之后保持网络中的特征图尺寸不变,之后的stage中会首先添加带有膨胀系数的bottleneck模块,用于增加感受野,将这种模块与其它类型的模块进行对比,见下图:
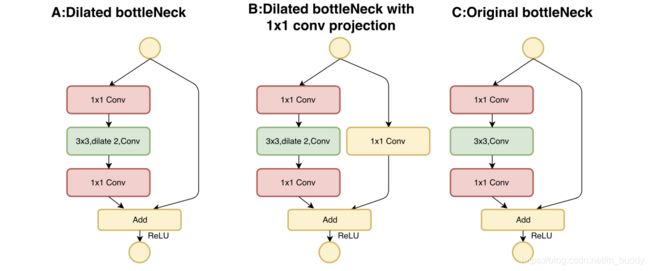
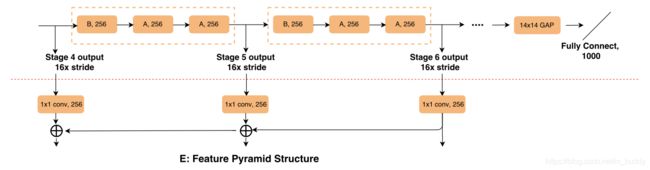
- 2)在后面stage5的基础上,参考传统的检测网络也添加了一个额外的stage。其结构见下图所示:
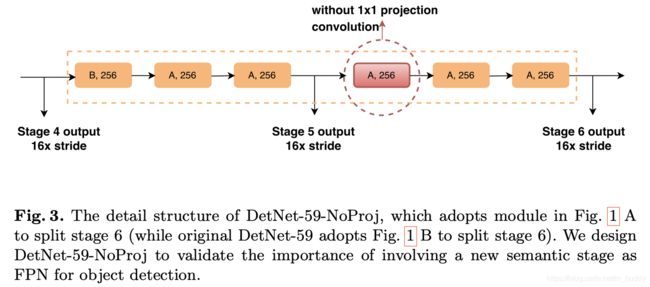
因而构建出来的基础网络部分见下图所示:

- 3)在基础网络上还通过引入FPN网络进行特征提取与优化,其结构见下图: