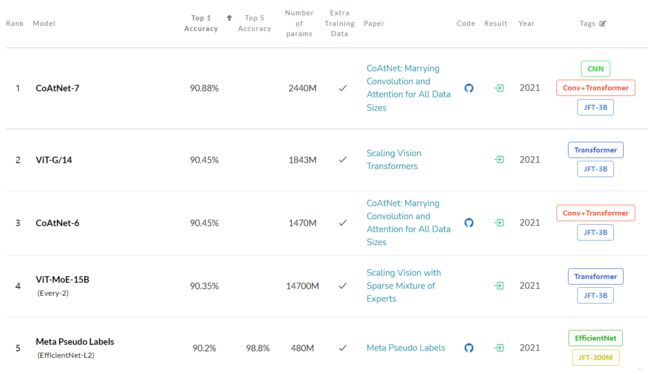
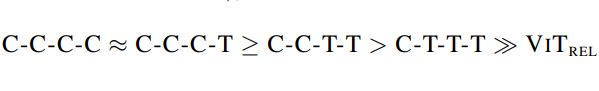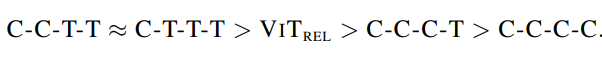CoAtNet: 90.88% Paperwithcode榜单第一,层层深入考虑模型设计
【GiantPandaCV导语】CoAt=Convolution + Attention,paperwithcode榜单第一名,通过结合卷积与Transformer实现性能上的突破,方法部分设计非常规整,层层深入考虑模型的架构设计。
引言
Transformer模型的容量大,由于缺乏正确的归纳偏置,泛化能力要比卷积网络差。
提出了CoAtNets模型族:
- 深度可分离卷积与self-attention能够通过简单的相对注意力来统一化。
- 叠加卷积层和注意层在提高泛化能力和效率方面具有惊人的效果
方法
这部分主要关注如何将conv与transformer以一种最优的方式结合:
- 在基础的计算块中,如果合并卷积与自注意力操作。
- 如何组织不同的计算模块来构建整个网络。
合并卷积与自注意力
卷积方面谷歌使用的是经典的MBConv, 使用深度可分离卷积来捕获空间之间的交互。
卷积操作的表示: L ( i ) \mathcal{L}(i) L(i)代表i周边的位置,也即卷积处理的感受野。
y i = ∑ j ∈ L ( i ) w i − j ⊙ x j (depthwise convolution) y_{i}=\sum_{j \in \mathcal{L}(i)} w_{i-j} \odot x_{j} \quad \text { (depthwise convolution) } yi=j∈L(i)∑wi−j⊙xj (depthwise convolution)
自注意力表示: G \mathcal{G} G表示全局空间感受野。
y i = ∑ j ∈ G exp ( x i ⊤ x j ) ∑ k ∈ G exp ( x i ⊤ x k ) ⏟ A i , j x j (self-attention) y_{i}=\sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}} \underbrace{\frac{\exp \left(x_{i}^{\top} x_{j}\right)}{\sum_{k \in \mathcal{G}} \exp \left(x_{i}^{\top} x_{k}\right)}}_{A_{i, j}} x_{j} \quad \text { (self-attention) } yi=j∈G∑Ai,j ∑k∈Gexp(xi⊤xk)exp(xi⊤xj)xj (self-attention)
融合方法一:先求和,再softmax
y i post = ∑ j ∈ G ( exp ( x i ⊤ x j ) ∑ k ∈ G exp ( x i ⊤ x k ) + w i − j ) x j y_{i}^{\text {post }}=\sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}}\left(\frac{\exp \left(x_{i}^{\top} x_{j}\right)}{\sum_{k \in \mathcal{G}} \exp \left(x_{i}^{\top} x_{k}\right)}+w_{i-j}\right) x_{j} yipost =j∈G∑(∑k∈Gexp(xi⊤xk)exp(xi⊤xj)+wi−j)xj
融合方法二:先softmax,再求和
y i pre = ∑ j ∈ G exp ( x i ⊤ x j + w i − j ) ∑ k ∈ G exp ( x i ⊤ x k + w i − k ) x j y_{i}^{\text {pre }}=\sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}} \frac{\exp \left(x_{i}^{\top} x_{j}+w_{i-j}\right)}{\sum_{k \in \mathcal{G}} \exp \left(x_{i}^{\top} x_{k}+w_{i-k}\right)} x_{j} yipre =j∈G∑∑k∈Gexp(xi⊤xk+wi−k)exp(xi⊤xj+wi−j)xj
出于参数量、计算两方面的考虑,论文打算采用第二种融合方法。
垂直布局设计
决定好合并卷积与注意力的方式后应该考虑如何构建网络整体架构,主要有三个方面的考量:
- 使用降采样降低空间维度大小,然后使用global relative attention。
- 使用局部注意力,强制全局感受野限制在一定范围内。典型代表有:
- Scaling local self-attention for parameter efficient visual backbone
- Swin Transformer
- 使用某种线性注意力方法来取代二次的softmax attention。典型代表有:
- Efficient Attention
- Transformers are rnns
- Rethinking attention with performers
第二种方法实现效率不够高,第三种方法性能不够好,因此采用第一种方法,如何设计降采样的方式也有几种方案:
- 使用卷积配合stride进行降采样。
- 使用pooling操作完成降采样,构建multi-stage网络范式。
- 根据第一种方案提出 V i T R E L ViT_{REL} ViTREL, 即使用ViT Stem,直接堆叠L层Transformer block使用relative attention。
- 根据第二种方案,采用multi-stage方案提出模型组: S 0 , . . . , S 4 S_0,...,S_4 S0,...,S4,如下图所示:
S o − S 2 S_o-S_2 So−S2采用卷积以及MBConv,从 S 2 − S 4 S_2-S_4 S2−S4的几个模块采用Transformer 结构。具体Transformer内部有以下几个变体:C代表卷积,T代表Transformer
- C-C-C-C
- C-C-C-T
- C-C-T-T
- C-T-T-T
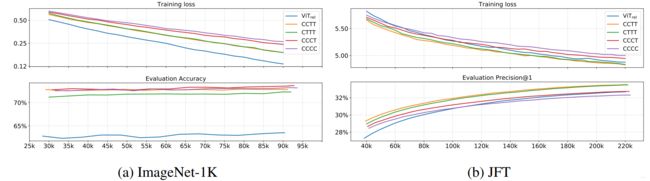
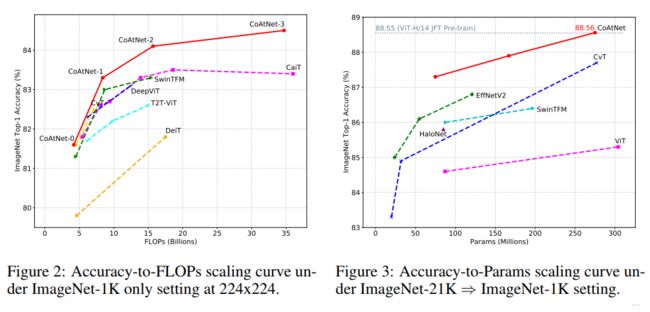
初步测试模型泛化能力
泛化能力排序为:(证明架构中还是需要存在想当比例的卷积操作)
初步测试模型容量
主要是从JFT以及ImageNet-1k上不同的表现来判定的,排序结果为:
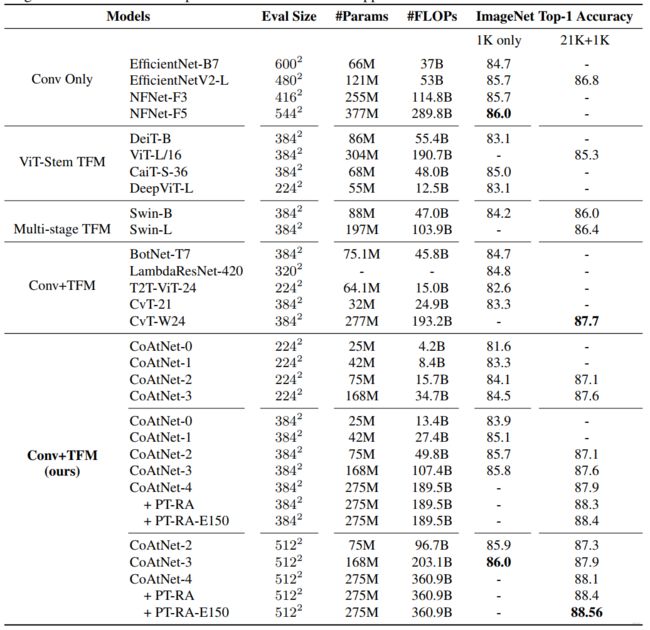
测试模型迁移能力
为了进一步比较CCTT与CTTT,进行了迁移能力测试,发现CCTT能够超越CTTT。
最终CCTT胜出!
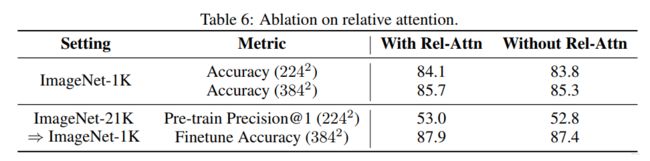
实验
与SOTA模型比较结果:
实验结果:
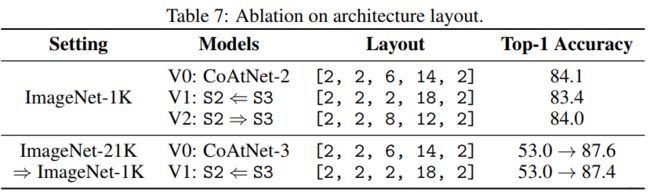
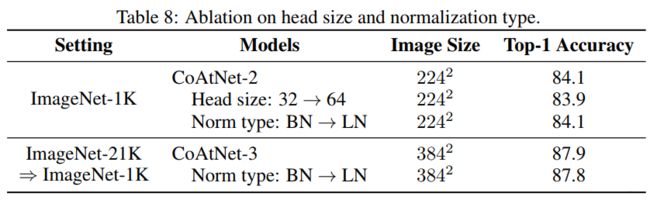
消融实验:
代码
浅层使用的MBConv模块如下:
class MBConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, image_size, downsample=False, expansion=4):
super().__init__()
self.downsample = downsample
stride = 1 if self.downsample == False else 2
hidden_dim = int(inp * expansion)
if self.downsample:
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
if expansion == 1:
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# dw
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, 3, stride,
1, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
# pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
else:
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
# pw
# down-sample in the first conv
nn.Conv2d(inp, hidden_dim, 1, stride, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
# dw
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, 3, 1, 1,
groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
SE(inp, hidden_dim),
# pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
)
self.conv = PreNorm(inp, self.conv, nn.BatchNorm2d)
def forward(self, x):
if self.downsample:
return self.proj(self.pool(x)) + self.conv(x)
else:
return x + self.conv(x)
主要关注Attention Block设计,引入Relative Position:
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, image_size, heads=8, dim_head=32, dropout=0.):
super().__init__()
inner_dim = dim_head * heads
project_out = not (heads == 1 and dim_head == inp)
self.ih, self.iw = image_size
self.heads = heads
self.scale = dim_head ** -0.5
# parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * self.ih - 1) * (2 * self.iw - 1), heads))
coords = torch.meshgrid((torch.arange(self.ih), torch.arange(self.iw)))
coords = torch.flatten(torch.stack(coords), 1)
relative_coords = coords[:, :, None] - coords[:, None, :]
relative_coords[0] += self.ih - 1
relative_coords[1] += self.iw - 1
relative_coords[0] *= 2 * self.iw - 1
relative_coords = rearrange(relative_coords, 'c h w -> h w c')
relative_index = relative_coords.sum(-1).flatten().unsqueeze(1)
self.register_buffer("relative_index", relative_index)
self.attend = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
self.to_qkv = nn.Linear(inp, inner_dim * 3, bias=False)
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(inner_dim, oup),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
) if project_out else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim=-1)
q, k, v = map(lambda t: rearrange(
t, 'b n (h d) -> b h n d', h=self.heads), qkv)
dots = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-1, -2)) * self.scale
# Use "gather" for more efficiency on GPUs
relative_bias = self.relative_bias_table.gather(
0, self.relative_index.repeat(1, self.heads))
relative_bias = rearrange(
relative_bias, '(h w) c -> 1 c h w', h=self.ih*self.iw, w=self.ih*self.iw)
dots = dots + relative_bias
attn = self.attend(dots)
out = torch.matmul(attn, v)
out = rearrange(out, 'b h n d -> b n (h d)')
out = self.to_out(out)
return out
参考
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.04803.pdf
https://github.com/chinhsuanwu/coatnet-pytorch