用Word2Vec建立你的私人购物助手
本练习项目是基于顾客消费历史,在电商网站上为其建立自动推荐特定数量商品的系统。代码和使用的数据集为:https://pan.baidu.com/s/17IZL65qK-yDutI1Xrp8wAg 提取码: 5l9g
启动Jupyter Notebook,快速导入所需库并载入数据集。
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport randomfrom tqdm import tqdmfrom gensim.models import Word2Vec import matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inline
import warnings;warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')df = pd.read_excel('Online Retail.xlsx')df.head()以下是对于该数据集某些领域的描述:
1. InvoiceNo: 发票号码,每次交易对应的唯一数字
2. StockCode: 产品/物品编码,每一唯一商品对应的唯一数字
3. Description:产品描述
4. Quantity:每次交易每种产品的数量
5. InvoiceDate: 每次交易生成的日期和时间
6. CustomerID:顾客ID,每位顾客对应的唯一数字。
df.shape输出: (541909, 8)
该数据集包含541909次交易。这是一个搭建模型的极佳数字。
处理缺失数据
# check for missing valuesdf.isnull().sum()已有充足数据,接下来去除所有含缺失值的行。
# remove missing valuesdf.dropna(inplace=True)数据准备
将产品编码转换为线性数据:
df['StockCode']= df['StockCode'].astype(str)查看数据集中唯一顾客的数量:
customers = df["CustomerID"].unique().tolist()len(customers)输出:4372
数据集中有4372个顾客。对于每一个顾客,提取其购买历史。换句话说,有4372个购买顺序。
从数据集中保留一小部分用以验证是很好的做法。因此,将使用90%的顾客数据创建word2vec嵌入。将数据分割。
# shuffle customer ID'srandom.shuffle(customers)
# extract 90% of customer ID'scustomers_train = [customers[i] for i in range(round(0.9*len(customers)))]
# split data into train and validation settrain_df = df[df['CustomerID'].isin(customers_train)]validation_df = df[~df['CustomerID'].isin(customers_train)]将对于数据集中的顾客创建购买顺序,兼顾训练和验证的目的。
# list to capture purchase history of the customerspurchases_train = []
# populate the list with the product codesfor i in tqdm(customers_train): temp = train_df[train_df["CustomerID"] == i]["StockCode"].tolist() purchases_train.append(temp)# list to capture purchase history of the customerspurchases_val = []
# populate the list with the product codesfor i in tqdm(validation_df['CustomerID'].unique()): temp = validation_df[validation_df["CustomerID"] == i]["StockCode"].tolist() purchases_val.append(temp)为产品创建word2vec词嵌入
# train word2vec modelmodel = Word2Vec(window = 10, sg = 1, hs = 0, negative = 10, # for negative sampling alpha=0.03, min_alpha=0.0007, seed = 14)
model.build_vocab(purchases_train, progress_per=200)
model.train(purchases_train, total_examples = model.corpus_count, epochs=10, report_delay=1)因为不再需要训练模型,呼叫 init_sims( )。这会使得模型记忆能力更强。
model.init_sims(replace=True)查看模型总结:
print(model)输出:word2vec(词汇=3151,规格=100,透明度=0.03)
本模型有3151个唯一单词,其规格向量各自为100。接下来,提取词汇表中所有单词的向量,将其存储以便取用。
# extract all vectorsX = model[model.wv.vocab]
X.shape输出:(3151,100)
视觉化word2vec词嵌入
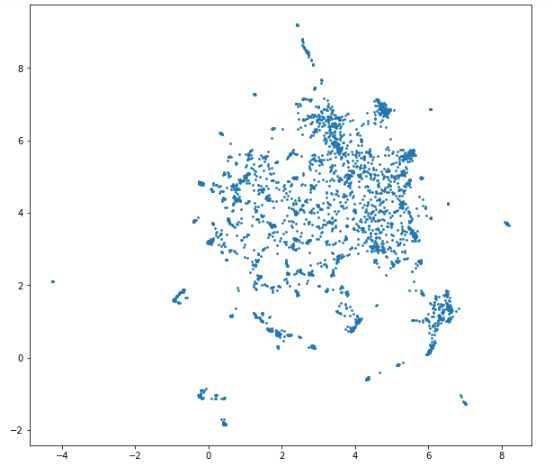
视觉化呈现已创建的嵌入总是很有帮助。此处有100个维度的嵌入。我们连4维都不能视觉化呈现,更别提100维了。那究竟该怎么办呢?
将通过UMAP算法把产品嵌入维度从100减少至2。这在维度减少中的应用十分常见。
import umap
cluster_embedding = umap.UMAP(n_neighbors=30, min_dist=0.0, n_components=2, random_state=42).fit_transform(X)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,9))plt.scatter(cluster_embedding[:, 0], cluster_embedding[:, 1], s=3, cmap='Spectral')上图中每个点都代表一个产品。图上几处聚集的数据点代表相似产品。
开始推荐产品
恭喜!数据集中每一个产品的word2vec嵌入都已完成。现在,需要为特定产品或产品向量推荐相似产品。
首先创建产品ID以及产品描述库,以便于将产品描述和ID相互匹配。
products = train_df[["StockCode", "Description"]]
# remove duplicatesproducts.drop_duplicates(inplace=True, subset='StockCode', keep="last")
# create product-ID and product-description dictionaryproducts_dict = products.groupby('StockCode')['Description'].apply(list).to_dict()# test the dictionaryproducts_dict['84029E']输出:[‘RED WOOLLY HOTTIE WHITE HEART.’]
以下对该函数进行了定义。将产品向量作为输入,相似性最大的6个产品为输出:
def similar_products(v, n = 6): # extract most similar products for the input vector ms = model.similar_by_vector(v, topn= n+1)[1:] # extract name and similarity score of the similar products new_ms = [] for j in ms: pair = (products_dict[j[0]][0], j[1]) new_ms.append(pair) return new_ms尝试运行函数,传输产品‘90019A’的向量(‘SILVER M.O.P ORBIT BRACELET’):
similar_products(model['90019A'])输出:
[(‘SILVER M.O.P ORBIT DROP EARRINGS’, 0.766798734664917),
(‘PINK HEART OF GLASS BRACELET’, 0.7607438564300537),
(‘AMBER DROP EARRINGS W LONG BEADS’, 0.7573930025100708),
(‘GOLD/M.O.P PENDANT ORBIT NECKLACE’, 0.7413625121116638),
(‘ANT COPPER RED BOUDICCA BRACELET’, 0.7289256453514099),
(‘WHITE VINT ART DECO CRYSTAL NECKLAC’, 0.7265784740447998)]
很好!结果关联度很高,且与输入产品匹配度高。然而,输出只是基于单一产品向量。如果要基于多次购物历史推荐产品呢?
一个简单的解决办法是:提取顾客所购买全部产品向量平均值并根据其找到相似产品。将使用如下包含众多产品ID的函数,其输出了一个100维向量,这是输入产品向量之一:
def aggregate_vectors(products): product_vec = [] for i in products: try: product_vec.append(model[i]) except KeyError: continue return np.mean(product_vec, axis=0)注意之前已创建购买顺序的单独列表以便验证。现在将其利用起来。
len(purchases_val[0])输出:314
第一个已购产品的列表长度为314。将用于验证的产品顺序表输入函数aggregate_vectors。
aggregate_vectors(purchases_val[0]).shape输出:(100,)
函数输出100个维度。这意味着函数运转正常。现在用此结果得出最相似的产品:
similar_products(aggregate_vectors(purchases_val[0]))输出:
[(‘PARTY BUNTING’, 0.661663293838501),
(‘ALARM CLOCK BAKELIKE RED ‘, 0.640213131904602),
(‘ALARM CLOCK BAKELIKE IVORY’, 0.6287959814071655),
(‘ROSES REGENCY TEACUP AND SAUCER ‘, 0.6286610960960388),
(‘SPOTTY BUNTING’, 0.6270893216133118),
(‘GREEN REGENCY TEACUP AND SAUCER’, 0.6261675357818604)]
结果显示,系统可根据顾客全部消费历史推荐6个产品。而且,若想根据最后几次购买记录得到推荐,也可以使用相同的函数。
以下仅以近十次购买记录作为输入:
similar_products(aggregate_vectors(purchases_val[0][-10:]))输出:
[(‘PARISIENNE KEY CABINET ‘, 0.6296610832214355),
(‘FRENCH ENAMEL CANDLEHOLDER’, 0.6204789876937866),
(‘VINTAGE ZINC WATERING CAN’, 0.5855435729026794),
(‘CREAM HANGING HEART T-LIGHT HOLDER’, 0.5839680433273315),
(‘ENAMEL FLOWER JUG CREAM’, 0.5806118845939636)]
可代入不同编码和验证组中的顺序生成不同推荐。