pytorch学习笔记一:张量的操作与线性回归
目录
-
- 一、张量的简介
-
- 1、张量的基本概念
- 2、张量的属性
- 二、张量的创建
-
- 1、直接创建
- 2、依数值创建
- 3、依概率创建
- 三、张量的操作
-
- 1、张量的拼接
- 2、张量的切分
- 3、张量的索引
- 4、张量变换
- 5、算术运算
- 6、高级操作
- 四、线性回归模型
一、张量的简介
1、张量的基本概念
张量是一个【多维数组】,它是一个标量、向量、矩阵的高维拓展。

2、张量的属性
在 PyTorch 0.4.0 之前,torch.autograd 包中存在 Variable 这种数据类型,主要是用于封装 Tensor,进行自动求导。Variable 主要包含下面几种属性。
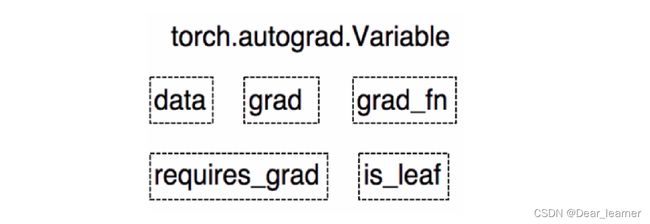
● data: 被包装的 Tensor。
● grad: data 的梯度。
● grad_fn: 创建 Tensor 所使用的 Function,是自动求导的关键,因为根据所记录的函数才能计算出导数。
● requires_grad: 指示是否需要梯度,并不是所有的张量都需要计算梯度。
● is_leaf: 指示是否叶子节点(张量)。
在 PyTorch 0.4.0 之后,Variable 并入了 Tensor。在之后版本的 Tensor 中,除了具有上面 Variable 的 5 个属性,还有另外 3 个属性。
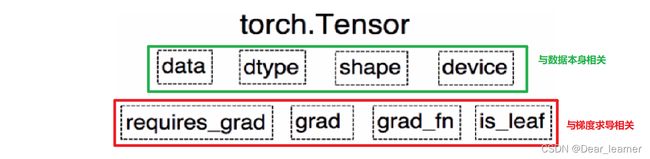
- dtype:张量的数据类型
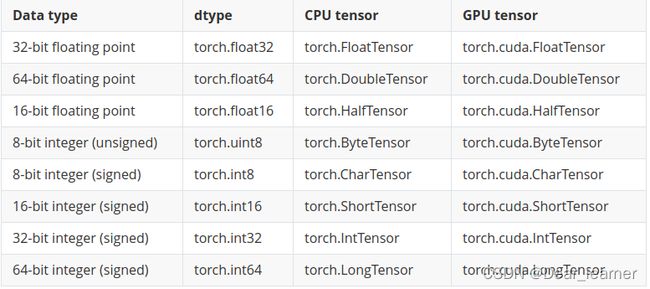
每种类型都有CPU和GPU两个版本,张量运算必须发生在相同类型的数据之间。 - shape:张量的形状,如(1, 3, 64, 64)
- device:张量所在的设备,CPU/GPU,决定张量的计算在哪里进行,张量放在GPU上才能使用加速。
二、张量的创建
1、直接创建
torch.tensor():从data创建Tensor
torch.tensor(data,
dtype=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False,
pin_memory=False) -> Tensor
- data:数据,可以是list,也可以是numpy
- dtype:数据类型,默认和data一致
- device:tensor所在的设备
- requires_grad:是否需要梯度,默认False,在搭建神经网络时需要将求导的参数设为True
- pin_memory:是否存于锁页内存,默认False
示例:
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
print('ndarray的数据类型:',arr.dtype)
tensor_arr = torch.tensor(arr)
print(tensor_arr)
#result
ndarray的数据类型: float64
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
.from_numpy() 将ndarray转换成tensor,两者共享内存,当修改一个数据时另一个也会被修改
array_b = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
tensor_b = torch.from_numpy(array_b)
print(array_b)
print(tensor_b)
#result
[1 2 3 4]
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=torch.int32)
array_b[0] = 5
print(array_b)
print(tensor_b)
#result
[5 2 3 4]
tensor([5, 2, 3, 4], dtype=torch.int32)
tensor_b[0] = 10
print(array_b)
print(tensor_b)
#result
[10 2 3 4]
tensor([10, 2, 3, 4], dtype=torch.int32)
2、依数值创建
torch.zeros()依size创建全0的张量,torch.ones()依据size创建值全为1的张量
torch.zeros(*size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
- size:张量的形状,如(3,3)
- layout :这个是内存中的布局形式,有strided和sparse_coo等
- out:表示输出张量,就是再把这个张量赋值给别的一个张量,但是这两个张量时一样的,指的同一个内存地址
- device:所在的设备,gpu/cpu
- requires_grad:是否需要梯度
示例:
out_t = torch.tensor([2])
t = torch.zeros((3, 3), out=out_t)
print(out_t)
print(t)
print(id(t), id(out_t), id(out_t)==id(t))
# result
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
140531404201664 140531404201664 True
torch.eye()创建对角线为1的张量
torch.eye(n, m=None,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
torch.zeros_like()创建与input同shape的值全为0张量,torch.ones_like()创建与input同shape的值全为1的张量
#创建与input同shape的全1张量
torch.ones_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False,
memory_format=torch.preserve_format) -> Tensor
out_t = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
print('out_t:', out_t)
t = torch.ones((3,1), out=out_t)
print('\n')
print('t:',t)
print('out_t:', out_t)
print('id(t:):', id(t), 'id(out_t):', id(out_t), id(t)==id(out_t))
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
out_ = torch.ones_like(inputs)
print('\n')
print('out_:', out_)
###result
out_t: tensor([1, 2, 3])
t: tensor([[1],
[1],
[1]])
out_t: tensor([[1],
[1],
[1]])
id(t:): 2564793927864 id(out_t): 2564793927864 True
out_: tensor([[1, 1],
[1, 1]])
torch.full()自定义数值张量
torch.full(size,
fill_value,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
# fill_value:自定义的数值
torch.full_like(input,
fill_value,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False,
memory_format=torch.preserve_format) -> Tensor
full_t = torch.full((2,3), 3)
print('full_t:', full_t)
full_like_t = torch.full_like(full_t, 5)
print('full_like_t:', full_like_t)
##result
full_t: tensor([[3, 3, 3],
[3, 3, 3]])
full_like_t: tensor([[5, 5, 5],
[5, 5, 5]])
torch.arange()创建等差的一维张量,数值区间[start, end)
torch.arange(start=0,
end,
step=1, #数列公差,默认为1
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
torch.linspace()创建均分的一维张量,包含在区间start和end均匀间隔的step个值,数值区间[start, end]
torch.linspace(start,
end, steps, # steps指数列的长度
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
torch.arange(1, 10, 2)
#result
tensor([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
torch.linspace(1, 10, 5)
#result
tensor([ 1.0000, 3.2500, 5.5000, 7.7500, 10.0000])
#这里step的计算是(end-start)/(step-1)
torch.logspace()创建对数均分的一维张量,数值区间为[start, end],长度为steps,底为base默认为10
logspace(start, end, steps,
base=10.0,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
torch.logspace(2, 10, 6)
#result
tensor([1.0000e+02, 3.9811e+03, 1.5849e+05, 6.3096e+06, 2.5119e+08, 1.0000e+10])
3、依概率创建
torch.normal()生成正态分布,torch.randn()生成标准正态分布,torch.randn_like()生成标准正态分布,shape同input相同,torch.rand()、torch.rand_like()生成区间[0,1)上的均匀分布,torch.randint()、torch.randint_like()生成区间[low, high)区间上的均匀分布
#mean和std都是标量,需要设置size
torch.normal(0, 4, (4,5))
#result
tensor([[-0.3452, -0.9280, -1.2737, 2.4642, -2.8298],
[ 2.2866, -2.7351, 2.5361, -3.3591, 0.3584],
[-2.0955, 8.1288, -4.2677, 4.1769, -7.6397],
[ 0.4677, -1.8013, -5.2755, -4.9442, -1.4894]])
#mean为张量,std标量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = 1
torch.normal(mean, std)
#result
tensor([0.6424, 1.6814, 2.6214, 3.7179])
#mean为标量,std为张量
mean = 2
std = torch.ones((2, 3))
torch.normal(mean, std)
#result
tensor([[2.3587, 3.1138, 2.5852],
[3.0468, 1.3177, 3.0816]])
#mean为张量,std为张量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
torch.normal(mean, std)
#result
tensor([ 3.9392, 2.5605, 5.2616, -2.8300])
#生成标准正态分布
torch.rand((3,4))
#result
tensor([[0.4366, 0.1921, 0.0110, 0.4311],
[0.9431, 0.5463, 0.1594, 0.0875],
[0.1984, 0.9109, 0.9961, 0.0784]])
ones = torch.ones((4, 4))
torch.rand_like(ones)
#result
tensor([[0.9565, 0.2871, 0.9714, 0.4637],
[0.9190, 0.6885, 0.1923, 0.9143],
[0.2151, 0.0512, 0.9051, 0.4186],
[0.5376, 0.9068, 0.0917, 0.1121]])
torch.randperm()生成0-n-1的随机排列,常用于生成索引;torch.bernoulli()以input为概率生成伯努利分布
torch.randperm(5)
#result
tensor([0, 4, 2, 3, 1])
#生成范围为[0,1]的均匀随机矩阵
a = torch.empty(3, 3).uniform_(0, 1)
torch.bernoulli(a)
#result
tensor([[1., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
b = torch.ones((3,3))
torch.bernoulli(b)
#result
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
c = torch.zeros((3,3))
torch.bernoulli(c)
#result
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
三、张量的操作
1、张量的拼接
● torch.cat()将tensor序列按维度进行拼接,不会扩张张量的维度
● torch.stack()将tensor序列在新建的维度上进行拼接,会扩张张量的维度
t = torch.ones((2,3))
print('t:',t)
t_0 = torch.cat([t, t], dim=0)
print('\n')
print('t_0:',t_0)
t_1 = torch.cat([t, t], dim=1)
print('\n')
print('t_1:',t_1)
t_2 = torch.stack([t, t, t], dim=0)
print('\n')
print('t_2:', t_2)
print('t_2 shape:', t_2.shape)
t_3 = torch.stack([t, t, t], dim=1)
print('\n')
print('t_3:', t_3)
print('t_3 shape:', t_3.shape)
#####result#####
t: tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
t_0: tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
t_1: tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
t_2: tensor([[[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]],
[[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]],
[[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]]])
t_2 shape: torch.Size([3, 2, 3])
t_3: tensor([[[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]],
[[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]]])
t_3 shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 3])
2、张量的切分
.chunk():将张量按维度进行平均切分,返回值是张量列表
torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0) -> List of Tensors
#input:需要切分的张量
#chunks:切分的份数
#dim:维度
#若不能平均切分,最后一个张量小于其他张量
a = torch.ones((2, 7))
a_chunk = torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=3)
for idx, t in enumerate(a_chunk):
print('第{}个张量:{},shape is {}'.format(idx, t, t.shape))
####result
第0个张量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]]),shape is torch.Size([2, 3])
第1个张量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]]),shape is torch.Size([2, 3])
第2个张量:tensor([[1.],
[1.]]),shape is torch.Size([2, 1])
.split() 按维度dim将张量进行切分
torch.split(tensor,
split_size_or_sections,
dim=0)
# tensor:要切分的张量
# split_size_or_sections:为int时表示每一份的切分长度,为list时,按list元素进行切分
# dim:要切分的维度
t = torch.ones((2, 5))
# list里面的元素之和要和tensor的长度要一样,否则会报错。如果是[2, 1, 1]就报错
list_of_tensors = torch.split(t, [2, 1, 2], dim=1)
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1, t, t.shape))
###result
第1个张量:tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 2])
第2个张量:tensor([[1.],
[1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 1])
第3个张量:tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 2])
3、张量的索引
● 切片索引:与numpy的操作类似
● .index_select()在维度dim上按index索引数据
● .masked_select()按mask中的True进行索引数据,返回一维的张量
t = torch.arange(6).reshape(3,2)
idx = torch.tensor([1, 2])
t_idx = torch.index_select(t, dim=0, index=idx)
# index的指定类型为torch.long
print('t:', t)
print('t_idx:', t_idx)
###result
t: tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5]])
t_idx: tensor([[2, 3],
[4, 5]])
t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3))
#.ge()选择大于等于5的值
mask = t.ge(5)
t_select = torch.masked_select(t, mask)
print("t:\n{}\nmask:\n{}\nt_select:\n{} ".format(t, mask, t_select))
###result
t:
tensor([[8, 1, 6],
[0, 7, 3],
[7, 1, 7]])
mask:
tensor([[ True, False, True],
[False, True, False],
[ True, False, True]])
t_select:
tensor([8, 6, 7, 7, 7])
4、张量变换
- .reshape()变换张量的形状,当张量在内存中是连续时,新张量和input共享数据内存
- .view()只能改变连续的(contiguous)张量,返回的张量和原张量共享基础数据
- .resize_()改变数据的形状时,只截取一部分数据
x = torch.randn(3, 4)
print(x.shape)
x=x.permute(1,0)
print(x.shape)
print(x.is_contiguous())
##result
torch.Size([3, 4])
torch.Size([4, 3])
False
#非连续状态下使用.reshape()和.view()
x = x.view(3,4)
x = x.reshape(3,4)
print(x.shape)
###result
torch.Size([3, 4])
#使用.contiguous()将tensor变成连续的
x=x.contiguous()
print(x.is_contiguous())
x=x.view(1,12)
print(x.shape)
x=x.reshape(2,6)
print(x.shape)
###result
True
torch.Size([1, 12])
torch.Size([2, 6])
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
x.resize_(2, 2)
print(x)
###result
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
- .transpose()交换张量的两个维度。常用于图像的变换,比如把chw变换为hwc
- .T对二维张量的转置
- permute:可以对多个维度进行变换
- .squeeze()压缩长度为1的维度,dim若为None,移除所有长度为1的轴,若指定维度,当且仅当该轴的长度为1时,可以被移除
- .unsqueeze():依据dim扩张维度
t = torch.rand((2, 3, 4))
t_transpose = torch.transpose(t, dim0=1, dim1=2)
print(t_transpose.shape)
###result
torch.Size([2, 4, 3])
t = torch.arange(6).reshape(2,3)
print(t.T.shape)
###result
torch.Size([3, 2])
t = torch.rand((1,3, 4, 4))
print(t.squeeze(0).shape)
print(t.unsqueeze(2).shape)
###result
torch.Size([3, 4, 4])
torch.Size([1, 3, 1, 4, 4])
- expand:broadcasting
- repeat:memory copies
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 14, 14)
b = torch.rand(1, 32, 1, 1)
b.expand(4, 32, 14, 14).shape # torch.Size([4, 32, 14, 14])
b.expand(-1, 32, -1, -1).shape # torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
#维度不变则可以用-1,其他负数没有意义
b.expand(-1, 32, -1, -4).shape # torch.Size([1, 32, 1, -4])
#reshape是将维度复制多少次
b.repeat(4, 32, 1, 1).shape # torch.Size([4, 1024, 1, 1])
b.repeat(4, 1, 32, 32).shape # torch.Size([4, 32, 32, 32])
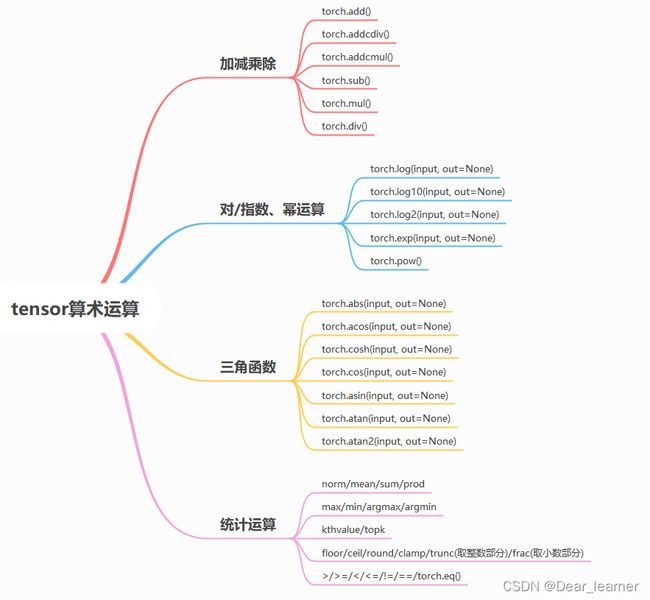
5、算术运算
6、高级操作
- torch.where():按照一定的规则合并两个tensor
- torch.where(condition, a, b)其中参数condition为条件限制,若满足condition,则为a,否则为b
a = torch.tensor([[0.0349, 0.0670, -0.0612, 0.0280, -0.0222, 0.0422],
[-1.6719, 0.1242, -0.6488, 0.3313, -1.3965, -0.0682],
[-1.3419, 0.4485, -0.6589, 0.1420, -0.3260, -0.4795]])
b = torch.tensor([[-0.0658, -0.1490, -0.1684, 0.7188, 0.3129, -0.1116],
[-0.2098, -0.2980, 0.1126, 0.9666, -0.0178, 0.1222],
[ 0.1179, -0.4622, -0.2112, 1.1151, 0.1846, 0.4283]])
cc = torch.where(a>0,a,b) #合并a,b两个tensor,如果a中元素大于0,则c中与a对应的位置取a的值,否则取b的值
print(cc)
### result
tensor([[ 0.0349, 0.0670, -0.1684, 0.0280, 0.3129, 0.0422],
[-0.2098, 0.1242, 0.1126, 0.3313, -0.0178, 0.1222],
[ 0.1179, 0.4485, -0.2112, 0.1420, 0.1846, 0.4283]])
- torch.gather():收集输入维度上指定位置的参数
参数:
input(tensor):输入tensor
dim(int):带操作的维度
index(LongTensor):如何对input进行操作
output(tensor):输出和index的维度是一致的
input = [
[2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 0],
[1, 4, 3, 0, 0, 0],
[4, 2, 2, 5, 7, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]
input = torch.tensor(input)
#注意index的类型
length = torch.LongTensor([[4],[3],[5],[1]])
#index之所以减1,是因为序列维度是从0开始计算的
out = torch.gather(input, 1, length-1)
### result
tensor([[5],
[3],
[7],
[1]])
# torch.gather()利用index来索引input指定位置上的值
四、线性回归模型
线性回归是分析一个变量与另外一(多)个变量之间关系的方法。因变量是 y,自变量是 x,关系线性:
y = w×x + b
任务是求解w、b
求解步骤:
1、确定模型:y = wx + b
2、选择损失函数:
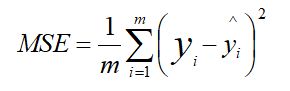
3、求解梯度并更新:
w = w - lr * w.grad
b = b - lr * b.grad
4、实现:
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(10)
lr = 0.05 # 学习率
# 创建训练数据
x = torch.rand(20, 1) * 10 # x data (tensor), shape=(20, 1)
# torch.randn(20, 1) 用于添加噪声
y = 2*x + (5 + torch.randn(20, 1)) # y data (tensor), shape=(20, 1)
# 构建线性回归参数
w = torch.randn((1), requires_grad=True) # 设置梯度求解为 true
b = torch.zeros((1), requires_grad=True) # 设置梯度求解为 true
# 迭代训练 1000 次
for iteration in range(1000):
# 前向传播,计算预测值
wx = torch.mul(w, x)
y_pred = torch.add(wx, b)
# 计算 MSE loss
loss = (0.5 * (y - y_pred) ** 2).mean()
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
b.data.sub_(lr * b.grad)
w.data.sub_(lr * w.grad)
# 每次更新参数之后,都要清零张量的梯度
w.grad.zero_()
b.grad.zero_()
# 绘图,每隔 20 次重新绘制直线
if iteration % 20 == 0:
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), y_pred.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(2, 20, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.xlim(1.5, 10)
plt.ylim(8, 28)
plt.title("Iteration: {}\nw: {} b: {}".format(iteration, w.data.numpy(), b.data.numpy()))
plt.pause(0.5)
plt.show()
# 如果 MSE 小于 1,则停止训练
if loss.data.numpy() < 1:
break