A*算法,简单实现八数码问题
A*算法求解N数码问题的设计与实现
Table of Contents
任务要求:
1. 关于A*算法:
2. 算法复杂度:
3. Solution:
4. CODE
任务要求:
- 以八数码问题为例实现A*算法的求解程序(编程语言不限),要求设计两种以上的不同估价函数;
- 在求解八数码问题的A*算法程序中,设置相同的初始状态和目标状态,针对不同的估价函数,求得问题的解,并比较它们对搜索算法性能的影响,包括扩展节点数、生成节点数等;
- 对于八8数码问题,设置与上述2相同的初始状态和目标状态,用宽度优先搜索算法(即令估计代价h(n)=0的A*算法)求得问题的解,以及搜索过程中的扩展节点数、生成节点数;
- 上交源程序(要求有代码注释)。
1. 关于A*算法:
A*算法的核心代价函数的设计,loss = g + h,g为当前状态深度,h是关键,h代表当前状态到达目标状态的估计值,h必须满足某些条件,而最重要的条件是h < r,r为当前状态到目标状态的估计值。
以实例理解上述条件。例如在八数码问题中,h可以被设计为“各个数到目标状态需要走的步数的和”,这显然是小于真实需要步数和的,h也可以被设计为“各个数和目标状态不同的个数和”,这个条件显然比第一个条件更加宽松,必然小于真实需要步数。以上即为本次设计的两个代价函数。
另一个例子是连续地图中的寻路算法,h一般设计为欧式距离,即直线距离,这显然比真实需要走的路要短(可能有障碍,弯路等等)。
通过以上两个例子,我们可以直观地理解,为什么估计值h必须小于真实值,但要尽可能的大,接近真实值的下界。例如寻路算法中,你估算的距离越接近真实距离,那么你启发式找到可能的路径就会越准确。理论上,可以严格证明满足这些条件,必然可以找到最优解。
从另一个角度来审视A*算法,它可以视为以代价为步长的广度优先算法,这一点要从代码实现上才能感受到。每次都优先处理代价最小的状态,如果观察搜索树,将会看到它在整个搜索数的节点之间无序跳动(选全局估计代价最小)。
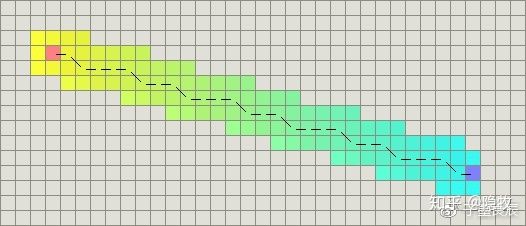
再次,例如在寻路算法中,A*算法在实际运行中,类似于我们人类在找两点之间的最快路径,尽管我们无法确定中间要从何处绕开障碍,但是我们却知道要忘目标靠。下面是A*算法运行实例,它在每个状态,都会对目标计算一次欧式距离,以此约束选择,就仿佛被欧式距离牵引到目标状态一样。
2. 算法复杂度:
- 广度优先搜索,算法复杂度为O(4^n),或者从另外的角度,八字码的所有状态为n个数字的全排列,估计O(n!)。
- A*算法的好坏和代价函数h的设计密切相关,h必须尽可能小于并贴近真实代价,这样朝目标贴近的方向越笔直(参考上图),算法的一个上界和广度搜索是一样的,但实际上可以很快,我感觉在一些问题中可以接近线性复杂度。
- A*算法的空间消耗非常大,和实际复杂度类似,它需要保存每个状态,同样和h的设计相关。
- 过小的h的估计,会导致“这条路比较最短,我要深入下去,但其实这条路是错的”这种现象,即会在错误的路上深入太深,h太小,那么g就要越大才会发现走错,越深的搜索,节点增长得越快,越接近指数级别。
3. Solution:
init_state
[[3 1 7]
[6 8 0]
[4 2 5]]
target
[[7 2 1]
[4 8 6]
[3 0 5]]
----------A star with cost_function 1-----------
27 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 5383
耗时:0.9075729846954346
----------A star with cost_function 2-----------
27 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 181440
耗时:29.369495630264282
----------breadth search-----------
27 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 9698
耗时:19.344292402267456
=========================================================
init_state
[[2 6 7]
[5 0 3]
[4 1 8]]
target
[[5 2 3]
[4 1 0]
[8 7 6]]
----------A star with cost_function 1-----------
16 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 115
耗时:0.016954660415649414
----------A star with cost_function 2-----------
16 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 132050
耗时:18.046760320663452
----------breadth search-----------
16 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 3629
耗时:0.7639575004577637
===================================================================
init_state
[[2 8 7]
[4 5 1]
[0 6 3]]
target
[[5 7 4]
[6 1 8]
[3 2 0]]
----------A star with cost_function 1-----------
无解
耗时:0.0
----------A star with cost_function 2-----------
无解
耗时:0.0
----------breadth search-----------
无解
耗时:0.0009975433349609375
==================================================================
init_state
[[3 2 1]
[6 7 5]
[4 8 0]]
target
[[1 8 0]
[5 2 6]
[3 7 4]]
----------A star with cost_function 1-----------
25 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 1805
耗时:0.26030421257019043
----------A star with cost_function 2-----------
27 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 181440
耗时:31.541586875915527
----------breadth search-----------
25 步之后能到达目标
生成节点数 15633
耗时:16.068492650985718
4. CODE
import numpy as np
from queue import PriorityQueue, Queue
import time
np.random.seed(0)
# 计算g(n)
def g(cur):
return cur.depth
# 计算h(n)
def h(cur):
h = 0
for x1 in range(3):
for y1 in range(3):
if cur.data[x1][y1] == 0:
continue
x2,y2 = n2posi[cur.data[x1][y1]]
# print(x1,y1,np.abs(x1 - x2) + np.abs(y1 - y2))
h += np.abs(x1 - x2) + np.abs(y1 - y2)
return h
def h2(cur):
return np.sum(cur.data == target_state.data)
# 计算cost(n)
def cost(cur):
return g(cur) + h(cur)
def cost2(cur):
return g(cur) + h2(cur)
# 测试是否有界
def is_solutable(init_, target):
sum_a = 0
sum_b = 0
a = init_.data.reshape(-1)
b = target.data.reshape(-1)
for i in range(len(a)):
sum_a += np.sum((a[i:] < a[i])&(a[i:]!=0))
for i in range(len(b)):
sum_b += np.sum((b[i:] < b[i])&(b[i:]!=0))
# print(sum_a, sum_b)
return (sum_a%2) == (sum_b%2)
# a star
def a_star(init_state, target_state, cost):
if is_solutable(init_state,target_state) == False:
print("无解")
return None
opens_ = PriorityQueue() # 存放已观察未访问节点
closes_ = PriorityQueue() # 存放已经访问节点
states = {}
directions = [(-1,0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)]
opens_.put(init_state)
cur = init_state
while(True):
# 获得当前代价最小的进行访问
cur = opens_.get()
closes_.put(cur)
if cur == target_state:
break
for dx,dy in directions:
x,y = cur.position()
x_n,y_n = x+dx, y+dy
# 越界跳出
if x_n < 0 or x_n >= 3 or y_n < 0 or y_n >= 3:
continue
# 移动空白,创建新节点
data = cur.data.copy()
depth = cur.depth + 1
data[x,y],data[x_n,y_n] = data[x_n,y_n],data[x,y]
new_state = State(data, depth, x_n, y_n)
new_state.root = cur
new_state.cost_ = cost(new_state)
# 该状态是否已经访问过,如果是则更新状态
if new_state in states:
if new_state.cost_ < states[new_state].cost_:
# 更新
states[new_state].root = cur
states[new_state].cost_ = new_state.cost_
# 更新两个最小堆
opens_.put(opens_.get())
closes_.put(closes_.get())
else:
states[new_state] = new_state
opens_.put(new_state)
r = cur
num = 0
# 输出路径
while True:
if cur is None:
break
num += 1
# print("----^----")
# print(cur)
cur = cur.root
print('{} 步之后能到达目标'.format(num))
print('生成节点数 {}'.format(len(states)))
return r
# 广度搜索
def bf_search(init_state, target_state):
if is_solutable(init_state, target_state) == False:
print("无解")
return
q = Queue() # 队列
states = {} # 访问状态记录
directions = [(-1,0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)]
states[init_state] = init_state
q.put(init_state)
while q.empty() != True:
cur = q.get()
if cur == target_state:
break
for dx,dy in directions:
x,y = cur.position()
x_n,y_n = x+dx, y+dy
# 越界跳出
if x_n < 0 or x_n >= 3 or y_n < 0 or y_n >= 3:
continue
# 移动空白,创建新节点
data = cur.data.copy()
depth = cur.depth + 1
data[x,y],data[x_n,y_n] = data[x_n,y_n],data[x,y]
new_state = State(data, depth, x_n, y_n)
new_state.root = cur
# 是否访问过,如果是且更近更新状态
if new_state in states:
if new_state.depth < states[new_state].depth:
states[new_state].depth = new_state.depth
states[new_state].root = cur
else:
states[new_state] = new_state
q.put(new_state)
r = cur
num = 0
# 输出路径
while True:
if cur is None:
break
num += 1
# print("----^----")
# print(cur)
cur = cur.root
print('{} 步之后能到达目标'.format(num))
print('生成节点数 {}'.format(q.qsize()))
class State:
def __init__(self, data, depth, blank_x, blank_y, cost_ = 1000):
self.data = data
# fac 用于状态hash值的计算
self.fac = np.array([10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000])
self.depth = depth
self.x = blank_x
self.y = blank_y
self.cost_ = cost_
self.root = None
# 返回空白位置
def position(self):
return self.x, self.y
# 重载方法,便于在字典,最小堆等数据结构的使用自定义类
def __hash__(self):
return int(np.dot(self.data.reshape(-1), self.fac))
def __eq__(self, other):
return np.sum(self.data == other.data)==9
def __str__(self):
return str(self.data)
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.cost_ < other.cost_
# 目标状态
target = np.random.choice(range(9), (3,3), replace=False).reshape(3, 3)
x,y = np.where(target == 0)
target_state = State(target, 0, x[0], y[0], cost_ = 0)
# 保存目标矩阵各个数字的position
n2posi = {}
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
n2posi[target[i][j]] = (i,j)
'''
a_star 代价函数一
'''
cost_func = cost
# 初始状态
init_ = np.random.choice(range(9), (3,3), replace=False).reshape(3, 3)
x,y = np.where(init_ == 0)
init_state = State(init_, 0, x[0], y[0])
init_state.cost_ = cost_func(init_state)
print("init_state")
print(init_state)
print("target")
print(target)
print('----------A star with cost_function 1-----------')
start_time = time.time()
a_star(init_state,target_state, cost_func)
end_time = time.time()
print("耗时:{}".format(end_time - start_time))
'''
a_star 代价函数二
'''
print('----------A star with cost_function 2-----------')
cost_func = cost2
# 初始状态
init_state = State(init_, 0, x[0], y[0])
init_state.cost_ = cost_func(init_state)
# print("init_state")
# print(init_state)
# print("target")
# print(target)
start_time = time.time()
a_star(init_state,target_state, cost_func)
end_time = time.time()
print("耗时:{}".format(end_time - start_time))
'''
广搜
'''
print('----------breadth search-----------')
# 初始状态
x,y = np.where(init_ == 0)
init_state = State(init_, 0, x[0], y[0])
init_state.cost_ = cost_func(init_state)
# print("init_state")
# print(init_state)
# print("target")
# print(target)
start_time = time.time()
bf_search(init_state, target_state)
end_time = time.time()
print("耗时:{}".format(end_time - start_time))