SKlearn之手写数字识别(Recognizing hand-written digits)
题目链接:Recognizing hand-written digits
函数解释
zip函数:python zip函数
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
matplotlib.pyplot.imshow(X, cmap=None, norm=None, aspect=None, interpolation=None, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, origin=None, extent=None, shape=
cmap=plt.cm.gray_r指的是画灰度图,其中还有四种方法:Python中matplotlib.pyplot.imshow画灰度图的多种方法
interpolation代表的是插值运算,'nearest'只是选取了其中的一种插值方式。
reshape(m,n) n,m 其中正实数表示具体的行(列),-1 表示未指定值,(samples, feature)
fit(self, X, y, sample_weight=None) 根据给定的训练数据对模型进行拟合
enumerate():Python enumerate() 函数
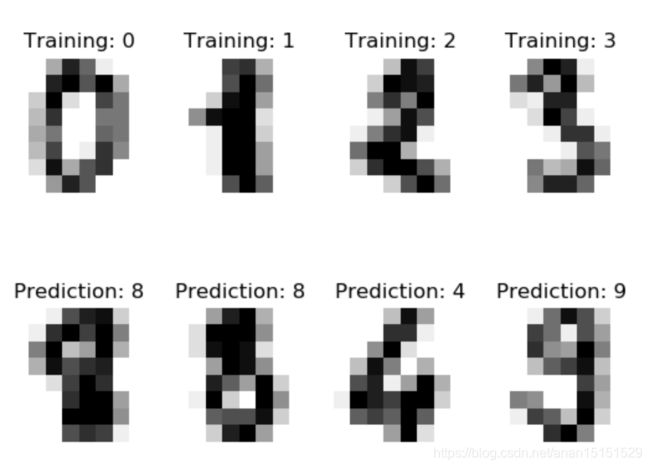
结果:
输出:
Classification report for classifier SVC(gamma=0.001):
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.99 0.99 88
1 0.99 0.97 0.98 91
2 0.99 0.99 0.99 86
3 0.98 0.87 0.92 91
4 0.99 0.96 0.97 92
5 0.95 0.97 0.96 91
6 0.99 0.99 0.99 91
7 0.96 0.99 0.97 89
8 0.94 1.00 0.97 88
9 0.93 0.98 0.95 92
accuracy 0.97 899
macro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
Confusion matrix:
[[87 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 88 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1]
[ 0 0 85 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 79 0 3 0 4 5 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 88 0 0 0 0 4]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 88 1 0 0 2]
[ 0 1 0 0 0 0 90 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 88 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 88 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 90]]
程序:
# encoding: utf-8
print(__doc__)
# 引用数据库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets, svm, metrics
# 加载数据
digits = datasets.load_digits()
images_and_labels = list(zip(digits.images, digits.target))
# 显示训练数据
for index, (image, label) in enumerate(images_and_labels[:5]):
plt.subplot(2, 4, index + 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.title('Training: %i' % label)
# 数据预处理
n_samples = len(digits.images)
data = digits.images.reshape((n_samples, -1))
# 学习训练,用前半部分
classifier = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001)
classifier.fit(data[:n_samples // 2], digits.target[:n_samples // 2])
# 预测数值,用后本部分数据
expected = digits.target[n_samples // 2:]
predicted = classifier.predict(data[n_samples // 2:])
# 分类器测试及混淆矩阵
print("Classification report for classifier %s:\n%s\n"
% (classifier, metrics.classification_report(expected, predicted)))
print("Confusion matrix:\n%s" % metrics.confusion_matrix(expected, predicted))
# 显示预测数值
images_and_predictions = list(zip(digits.images[n_samples // 2:], predicted))
for index, (image, prediction) in enumerate(images_and_predictions[:4]):
plt.subplot(2, 4, index + 5)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.title('Prediction: %i' % prediction)
plt.show()