JAVA算法:子集求和问题(Subset Sum Problem)
JAVA算法:子集求和问题(Subset Sum Problem)
题目:给定一个正整数数组,和一个目标值,找出是否存在数组的一个子数组,使得子数组元素之和等于目标值。
例如:给定数组 { 3, 2, 7, 1} 和目标值 S = 6
返回结果: True , 子数组为 (3, 2, 1}
问题分析:
使用递归算法和动态规划算法两种算法来求解上述问题。
递归算法
对于数组中的每个元素有两个选择,我们在子数组中包括该元素和在子数组中不包括该元素。
在给定的例子中:数组 { 3, 2, 7, 1} 和目标值 S = 6
如果我们考虑另一个数组A,它也包括4个元素(数组A和给定的数组具有相同的长度)
如果数组A中包括原数组的元素,则数组A的元素设置为1(对应于原数组元素的下标位置);否则设置为0
这样,我们需要找到每一个可能的子集,并且检查是否子集的元素之和等于目标值。
package com.bean.algorithm.dp;
public class SubSetSumRecursion {
public static void find(int[] A, int currSum, int index, int sum, int[] solution) {
if (currSum == sum) {
System.out.println("\nSum found");
for (int i = 0; i < solution.length; i++) {
if (solution[i] == 1) {
System.out.print(" " + A[i]);
}
}
} else if (index == A.length) {
return;
} else {
solution[index] = 1;// select the element
currSum += A[index];
find(A, currSum, index + 1, sum, solution);
currSum -= A[index];
solution[index] = 0;// do not select the element
find(A, currSum, index + 1, sum, solution);
}
return;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] A = { 3, 2, 7, 1 };
int[] solution = new int[A.length];
find(A, 0, 0, 6, solution);
}
}
程序运行结果:
Sum found
3 2 1
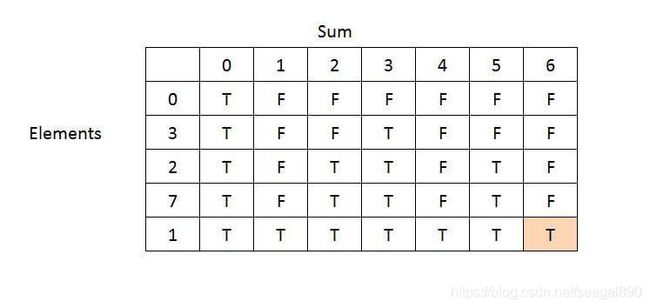
动态规划算法
Base Cases:
- If no elements in the set then we can’t make any subset except for 0.
- If sum needed is 0 then by returning the empty subset we can make the subset with sum 0.
Given – Set = arrA[], Size = n, sum = S
- Now for every element in he set we have 2 options, either we include it or exclude it.
- for any ith element-
- If include it => S = S-arrA[i], n=n-1
- If exclude it => S, n=n-1.
状态方程推导:
Recursive Equation: Base Cases: SubsetSum(arrA, n, S)= false, if sum > 0 and n == 0 SubsetSum(arrA, n, S)= true, if sum == 0 (return empty set) Rest Cases SubsetSum(arrA, n, S) = SubsetSum(arrA, n-1, S)|| SubsetSum(arrA, n-1, S-arrA[n-1])
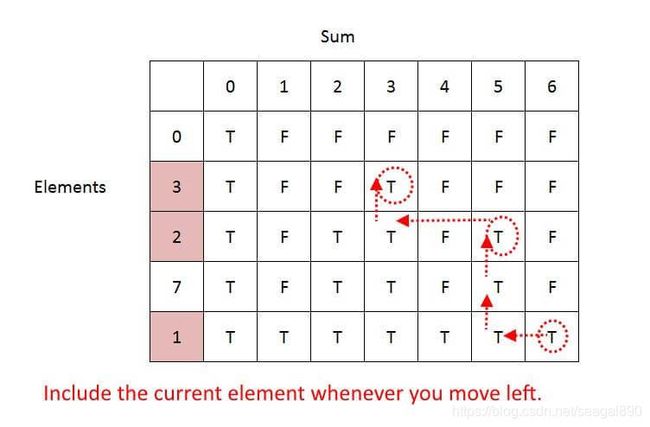
推算过程
如何跟踪元素。
从右下角开始,然后回溯,从True开始检查。
如果上面单元格中的值为 false,则表示当前单元格在包含当前元素后变为 true。
因此,包括当前元素并检查 sum=sum–current元素。
package com.bean.algorithm.dp;
public class SubsetSumProblem {
public static boolean subSetDP(int[] A, int sum) {
boolean[][] solution = new boolean[A.length + 1][sum + 1];
// if sum is not zero and subset is 0, we can't make it
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++) {
solution[0][i] = false;
}
// if sum is 0 the we can make the empty subset to make sum 0
for (int i = 0; i <= A.length; i++) {
solution[i][0] = true;
}
//
for (int i = 1; i <= A.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sum; j++) {
// first copy the data from the top
solution[i][j] = solution[i - 1][j];
// If solution[i][j]==false check if can be made
if (solution[i][j] == false && j >= A[i - 1])
solution[i][j] = solution[i][j] || solution[i - 1][j - A[i - 1]];
}
}
return solution[A.length][sum];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] A = { 3, 2, 7, 1 };
System.out.println("\nFrom DP: " + subSetDP(A, 6));
}
}
程序运行结果:
From DP: true
表示存在子数组之和等于目标值。