Self-supervised Learning 中的 Contrastive Learning
目前大多数深度学习的方法都依赖于人类所标注的信息,但是这会造成一些问题:
- 数据内部的结构信息比标注提供的信息要丰富,而监督方法忽视其重要性;
- 通过标签信息所训练得到的模型通常用于解决特定的任务,而不能作为知识一样可以被重新利用。
因此,自监督学习通过数据本身的信息来完成表征的学习。而且在Downstream( Pacal VOC检测)任务上,已经能比肩或超过监督方法。
通常,自监督学习通过构建一些不专注于像素细节的表征(representation learning)而对高层特征进行编码而区分不同对象。
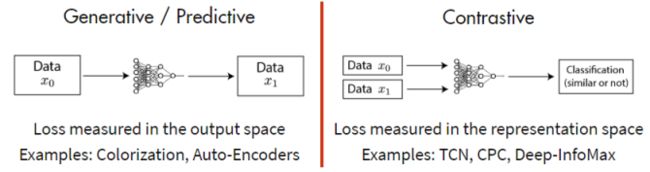
目前,自监督方法大致可以分为两类:
Generative model更加专注于像素的特征,而会造成一下两点问题:
- 像素级的loss使得model缺乏抽象的语义信息;
- 难以有效地建立空间关联及对象的复杂结构。
Some Recent Works:
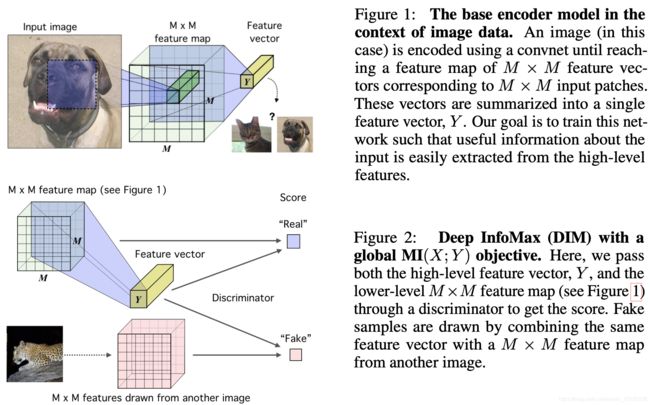
Deep InfoMax (ICLR2019)
(https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03748)
Main Idea: 通过maximize input和deep encoder的mutual information。
正样本对为input image的全局特征(feature vector)与局部特征(feature map),而负样本对来自全局特征与另外一张图片的match。
Contrasctive MultiView Coding
(http://arxiv.org/abs/1906.05849)
除了想上面这样构建正负样本对,还可以通过多模态的信息去构造。

现在我们能够拿到很多正样本,问题是怎么获得大量的负样本,对于 contrastive loss 而言,如何 sample 到很多负样本是关键,mini-batch 里面的负样本太少了,而每次对图片重新提取特征又非常的慢。虽然可以通过 memory bank 将负样本都存下来,但是效果并不好,所以如何节省内存和空间获得大量的负样本仍然没有很好地解决。
MoCo

端到端方法,是通过反向传播对计算查询和键的表征进行端到端更新。
Memory bank方法中,键的表征是从存储库中提取的。
而MoCo方法则通过基于动量更新的编码器对键进行动态编码,并维持键的队列。
可以具体读一读以下的论文:
[1] Oord, Aaron van den, Yazhe Li, and Oriol Vinyals. “Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748, 2018.
[2] Hjelm, R. Devon, Alex Fedorov, Samuel Lavoie-Marchildon, Karan Grewal, Phil Bachman, Adam Trischler, and Yoshua Bengio. “Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization.” ICLR, 2019
[3] Sohn, Kihyuk. “Improved deep metric learning with multi-class n-pair loss objective.” NeurIPS, 2016.
[4] Hénaff, Olivier J., Ali Razavi, Carl Doersch, S. M. Eslami, and Aaron van den Oord. “Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.09272, 2019.
[5] He, Kaiming, Haoqi Fan, Yuxin Wu, Saining Xie, and Ross Girshick. “Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.05722, 2019.
[6] Bachman, Philip, R. Devon Hjelm, and William Buchwalter. “Learning representations by maximizing mutual information across views.” NeurIPS, 2019.
[7] Tian, Yonglong, Dilip Krishnan, and Phillip Isola. “Contrastive multiview coding.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.05849, 2019.
[8] Veličković, Petar, William Fedus, William L. Hamilton, Pietro Liò, Yoshua Bengio, and R. Devon Hjelm. “Deep graph infomax.” ICLR, 2019.
[8] Anand, Ankesh, Evan Racah, Sherjil Ozair, Yoshua Bengio, Marc-Alexandre Côté, and R. Devon Hjelm. “Unsupervised state representation learning in atari.” NeurIPS, 2019.
[9] Sermanet, Pierre, Corey Lynch, Jasmine Hsu, and Sergey Levine. “Time-contrastive networks: Self-supervised learning from multi-view observation.” CVPRW, 2017.
[10] Poole, Ben, Sherjil Ozair, Aaron van den Oord, Alexander A. Alemi, and George Tucker. “On variational bounds of mutual information.” ICML, 2019.