基于Netty的高性能API网关设计
0. 本文目的
对于网关设计,业界已有很多成熟的解决方案,开箱即用或者稍作自定义都能满足需求。本文主要是通过网关需求了解底层netty的使用,所以重心在netty的实践使用上。
1. 什么是网关
网关(Gateway)又称网间连接器、协议转换器。网关在网络层以上实现网络互连,通俗来讲就是讲两个不同网络环境连接起来的连接器。
2. 为什么要做网关
从网关的定义上可以看出,其最主要的功能就是解耦。随着解耦扩展开来,网关还具有以下特性:
- 请求路由:对于调用端来讲,只需关注网关的接口即可,无需关注网关背后的服务集群信息。
- 负载均衡:如果服务端集群有多台服务器,需要考虑到服务器的资源分配,充分压榨服务器性能;
- 协议转换:业务客户端可能有多种通信协议,对于服务端来讲做多种协议适配复杂度和健壮性都会有影响,所以可以通过网关消化掉协议的差别,保持网关后服务端的统一性和简单性。
- 安全校验:SSL 加密及证书管理、Session 验证、授权、数据校验,以及对请求源进行恶意攻击的防范,都可以在网关层拦截掉。
- 流量控制:可以通过网关区分灰度流量和生成流量,对服务做不同版本控制;还可以限制流量和熔断降级。
- API编排&聚合:可以在网关层对服务调用做编排和聚合,减少客户端和服务端之前的网络交互,提升网络性能。
- 弹力设计:客户端请求异步、重试、幂等、监视等都可以交给网关控制,让应用服务只关心自己的业务逻辑而不是控制逻辑。
当然,统一的网关应用在满足上述特性后,各业务系统接入后就不用自行重复造轮子,一方面能省去重复网关搭建的服务器资源和人力运维成本,另一方面统一专业人士维护,提升服务研发运维效能。
3. 业界内的网关介绍
从功能上网关分为流量网关和业务网关。流量网关,顾名思义就是控制流量进入集群的网关,流量网关通常只专注于全局的Api管理策略,比如全局流量监控、日志记录、全局限流、黑白名单控制、接入请求到业务系统的负载均衡等,有点类似防火墙。Kong 就是典型的流量网关。
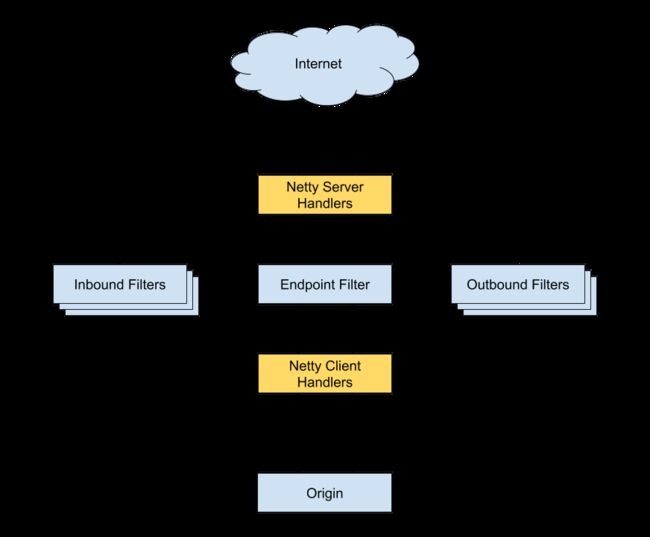
kong是一款基于OpenRetry(Nginx + Lua) 编写的高可用、易扩展的API Gateway,官网地址:Kong Gateway - v3.0.x | Kong Docs,架构图如下:
与流量网关相对应的就是业务网关,业务网关更接近业务服务器,一个业务网关的功能包括:
(图片来自亿级流量架构网关设计思路,常用网关对比,写得太好了。。_wadfdhsajd的博客-CSDN博客_网关架构设计)
比较常见的业务网关有zuul/zuul2/springcloud-gateway。
| 名称 | OpenResty | Kong | zuul | zuul2 | springcloud gateway |
| 所属公司 | OpenResty | Kong | Netfix | Netfix | Apache |
| 架构 | nginx+lua | 基于openRestry | 基于servlet2.5, 使用阻塞架构 | 基于Netty非阻塞 | 基于Netty非阻塞 |
| 特征 | 简单易用,但是需要进行的lua开发很多 | 简单易用,api转发通过管理员接口配置,随着规则复杂仍需要开发维护大量lua脚本 | 已过时 | 支持长连接,可以通过配置文件配置集群限流和单服务器filter限流, | 支持长连接,可通过IP、用户、集群限流,支持Oauth2和普通鉴权 |
| 社区成熟度 | 社区成熟 | 社区成熟 | 过时不再用 | 参考资料相对较少,可维护性弱 | spring系列可扩展强,易配置 可维护性好 |
4. 如何设计一个高性能网关
结合网关的功能作用,所以对网关的设计可以简化分为以下几个方面:
- 高性能,全链路异步请求。异步化方式有两种:Tomcat/Jetty+NIO+servlet3。这种方式通过成熟的servlet容器处理http请求,在servlet3中开启异步化;另一种是netty+NIO。这种方式需要自行处理http的协议,但是能支撑更大的并发量;
- 业务隔离。不同业务对网关请求的需求不一致,SLA也不尽相同,所以需要做业务上的隔离。有信号隔离、线程池隔离和集群隔离等方式,这里不做赘述;
- 限流。分为集群限流和单机限流;
- 熔断降级。
- 链式过滤。可参考springcloud和zuul2等处理模式。
- 泛化调用。泛化调用指的是一些通信协议的转换,比方将HTTP转换成Thrift,rpc和http的转换等。
- 后端治理平台,主要是对已有网关业务的健康监控配置处理。
5. 手撸一个简单的网关
借鉴zuul2的设计模式,
// 首先定义过滤器
public interface RequestFilter {
void filter(FullHttpRequest request, ChannelHandlerContext ctx);
}
public interface ResponseFilter {
void filter(FullHttpResponse response);
}
// 简单的过滤器实现
public class MyRequestFilter implements RequestFilter {
@Override
public void filter(FullHttpRequest request, ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
request.headers().set("branch", "test");
System.out.printf("=========" + request.headers().get("branch"));
}
}
public class MyResponseFilter implements ResponseFilter {
@Override
public void filter(FullHttpResponse response) {
response.headers().set("branch","test123");
}
}按照netty server端的开发模式,我们处理逻辑应该放在ChannelPipeline中,所以先定义出我们自由的channel处理pipeline。
public class UrlChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer {
// 简单的路由规则表转发
private Map urlMap;
public UrlChannelInitializer(Map urlMap) {
this.urlMap = urlMap;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(1024*1024));
// 添加自定义拦截器
pipeline.addLast(new MyChannelHandlerAdapter());
pipeline.addLast(new UrlChannelHandler(urlMap));
}
}
// request拦截器生效
public class MyChannelHandlerAdapter extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private MyRequestFilter requestFilter = new MyRequestFilter();
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
FullHttpRequest fullHttpRequest = (FullHttpRequest) msg;
requestFilter.filter(fullHttpRequest, ctx);
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
}
// response拦截器生效
public class UrlChannelHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
Map urlMap;
MyResponseFilter myResponseFilter ;
public UrlChannelHandler(Map urlMap) {
this.urlMap = urlMap;
this.myResponseFilter = new MyResponseFilter();
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
// 自定义处理器读取。 这里做对应的简单路由转发
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
FullHttpRequest fullHttpRequest = (FullHttpRequest) msg;
ByteBuf byteBuf = fullHttpRequest.content();
processHandleRequest(ctx, readByteBuf(byteBuf), fullHttpRequest);
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
// 这里做协议转换
private void processHandleRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String content, FullHttpRequest fullHttpRequest) {
String url = urlMap.get(fullHttpRequest.getUri());
FullHttpResponse response = null;
try {
String value = HttpClientUtil.doPost(url, JSONObject.parseObject(content));
response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(value.getBytes("UTF-8")));
response.headers().set("Content-Type", "application/json");
response.headers().set("Content-Length", response.content().readableBytes());
myResponseFilter.filter(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("处理异常" + e.getMessage());
response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.NO_CONTENT);
}finally {
if(fullHttpRequest != null){
if(!HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(fullHttpRequest)){
ctx.write(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}else {
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION, HttpHeaderNames.KEEP_ALIVE);
ctx.write(response);
}
}
}
}
private static String readByteBuf(ByteBuf byteBuf){
int size = byteBuf.readableBytes();
byte[] data = new byte[size];
byteBuf.readBytes(data);
return new String(data);
}
}
最后的server端启动监听端口
public class MyNettyServer {
private int port;
private Map urlMap;
public MyNettyServer(int port, Map urlMap) {
this.port = port;
this.urlMap = urlMap;
}
// 初始化构造
public void init(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16);
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 21*1024)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 32*1024)
.childOption(EpollChannelOption.SO_REUSEPORT, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG))
.handler(new UrlChannelInitializer(urlMap));
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(port).channel();
System.out.println("开启netty http服务器,监听地址和端口为 http://127.0.0.1:" + port + '/');
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}