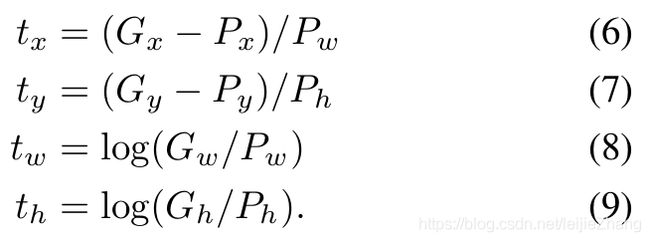maskrcnn-benchmark 代码详解之 box_coder.py
前言
box_coder.py主要用于候选边框(proposal)的编码和解码,即求解RCNN论文中回归目标中的![]() 以及预测边框。其主要针对的是RCNN和faster RCNN中的Bounding-box regression部分的操作。
以及预测边框。其主要针对的是RCNN和faster RCNN中的Bounding-box regression部分的操作。
1b-box 回归(RCNN)
假设现有获得的候选框(proposal)为![]()
![]() , 而基准框(ground-truth)为
, 而基准框(ground-truth)为![]() , 我们需要找一种映射方式使得我们选取出来的候选框
, 我们需要找一种映射方式使得我们选取出来的候选框![]() 能够变换成或者映射到
能够变换成或者映射到![]() . 针对每一个边框涉及到的x, y, w, h即边框中心坐标的x,y,以及边框的宽和高,我们分别设定有
. 针对每一个边框涉及到的x, y, w, h即边框中心坐标的x,y,以及边框的宽和高,我们分别设定有![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 这四种映射方式,分别可以帮助将
这四种映射方式,分别可以帮助将![]() 的x, y, w, h变换成
的x, y, w, h变换成![]() 或者接近
或者接近![]() 的x, y, w, h。
的x, y, w, h。
我们设定有![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 中,
中,![]() 和
和![]() 只是尺度方面的变换,即对坐标进行变大或变小以次来移动边框的中心坐标。而针对
只是尺度方面的变换,即对坐标进行变大或变小以次来移动边框的中心坐标。而针对![]() 和
和![]() 采用对数空间的变幻,以此来控制边框高和宽的变换。因此候选框proposal)可以通过
采用对数空间的变幻,以此来控制边框高和宽的变换。因此候选框proposal)可以通过![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 这四个映射函数变换到接近或者等于基准框(ground-truth),我们称之为基于候选框proposal)的预测框(predicted ground-truth box)
这四个映射函数变换到接近或者等于基准框(ground-truth),我们称之为基于候选框proposal)的预测框(predicted ground-truth box)![]() .
.
那么![]() 的公式就可以获得:
的公式就可以获得:
到目前位置,我们假定的四个映射函数![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 都还没有具体的值,都是假设有这么一些函数可以完成这样的功能。接下来,我们就要定义一些固定的衡量尺度
都还没有具体的值,都是假设有这么一些函数可以完成这样的功能。接下来,我们就要定义一些固定的衡量尺度![]() (包括
(包括![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,),
,),![]() 直接衡量候选框(proposal)
直接衡量候选框(proposal)![]() 和基准框(ground-truth)
和基准框(ground-truth)![]() 在x, y, w, h上的差距。我们将
在x, y, w, h上的差距。我们将![]() 规定为:
规定为:
规定完这些差距之后,候选框(proposal)![]() 可以通过逆
可以通过逆![]() 变换就可以得到基准框(ground-truth)
变换就可以得到基准框(ground-truth)![]() ,这是我们想要得到的变换函数。于是,我们就让
,这是我们想要得到的变换函数。于是,我们就让![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 无限的逼近
无限的逼近![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,,去拟合正确的映射函数。在卷积神经网络中,数据的映射关系是通过卷积层或者全连接层实现的,也就是说
,,去拟合正确的映射函数。在卷积神经网络中,数据的映射关系是通过卷积层或者全连接层实现的,也就是说![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 可以由卷积神经网络模拟出来,用一个全连接层或者一个卷基层就可以,这个操作等价于数据的线性变换。
可以由卷积神经网络模拟出来,用一个全连接层或者一个卷基层就可以,这个操作等价于数据的线性变换。
设候选区域提取出来的特征图为![]() , 那么
, 那么![]() ,即我们文章一开始提到的
,即我们文章一开始提到的![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 可以由特征图的卷积操作实现,我们只需要调整卷积过程的权重
可以由特征图的卷积操作实现,我们只需要调整卷积过程的权重![]() (也就是卷积核),让
(也就是卷积核),让![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 无限的逼近
无限的逼近![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,,去拟合正确的映射函数,这就不用再提了,卷积神经网络的梯度反传会实现这一过程,因此边框回归也就完成了。
,,去拟合正确的映射函数,这就不用再提了,卷积神经网络的梯度反传会实现这一过程,因此边框回归也就完成了。
之所以称之为边框回归(Bounding-box regression),是因为论文采用的是最小二乘的形式,将这个特征变换做成了回归的形式,即:
2代码解析
class BoxCoder(object):
"""
This class encodes and decodes a set of bounding boxes into
the representation used for training the regressors.
BoxCoder主要用于编码和解码基准边框(bounding boxes),并将其应用到回归训练中
本BoxCoder主要用于解决RCNN论文里提到的Bounding-box regression
"""
def __init__(self, weights, bbox_xform_clip=math.log(1000. / 16)):
"""
Arguments:
weights (4-element tuple)
weights:表示的是x, y, w, h在运算中所占的权重
bbox_xform_clip (float)
"""
self.weights = weights
# 边框的长和宽的最高值
self.bbox_xform_clip = bbox_xform_clip
def encode(self, reference_boxes, proposals):
"""
Encode a set of proposals with respect to some
reference boxes
Arguments:
reference_boxes (Tensor): reference boxes
proposals (Tensor): boxes to be encoded
"""
"""
这个Encode的作用是实现RCNN中提到的边框回归,其中的回归目标(regression target)t*
的计算,主要是计算候选框与与之相关的基准框的偏差
参数:
proposals:候选边框,由一定规则选出来的可能含有目标的目标边框
reference_boxes:与候选边框重叠度最高的基准边框gt
"""
# 计算两个数之间的真实距离,需要相减之后加1
TO_REMOVE = 1 # TODO remove
# 计算候选框的宽度
ex_widths = proposals[:, 2] - proposals[:, 0] + TO_REMOVE
# 计算候选框的高度
ex_heights = proposals[:, 3] - proposals[:, 1] + TO_REMOVE
# 计算候选框中心的x坐标
ex_ctr_x = proposals[:, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
# 计算候选框中心的y坐标
ex_ctr_y = proposals[:, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights
# 计算基准边框(ground truth)的宽度
gt_widths = reference_boxes[:, 2] - reference_boxes[:, 0] + TO_REMOVE
# 计算基准边框(ground truth)的高度
gt_heights = reference_boxes[:, 3] - reference_boxes[:, 1] + TO_REMOVE
# 计算基准边框(ground truth)中心的x坐标
gt_ctr_x = reference_boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths
# 计算基准边框(ground truth)中心的y坐标
gt_ctr_y = reference_boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights
# 得到计算回归目标时各个部分的权重
wx, wy, ww, wh = self.weights
# 计算带有权重的回归目标的各个部分
targets_dx = wx * (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = wy * (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = ww * torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = wh * torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights)
# 将回归目标的各个部分合并为一个元组,并依次保存到一个栈里
targets = torch.stack((targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh), dim=1)
return targets
def decode(self, rel_codes, boxes):
"""
From a set of original boxes and encoded relative box offsets,
get the decoded boxes.
Arguments:
rel_codes (Tensor): encoded boxes
boxes (Tensor): reference boxes.
"""
"""
根据得到的候选框以及与之对应的中心x,y宽和高的各部分的回归值和得到预测边框
参数:
rel_codes:根据候选框与基准边框(ground truth)的差距计算出来的候选边框中心x,y宽和高的各部分的变差回归值
boxes:候选边框
"""
# 将候选边框的数据类型设置成回归目标值一样的类型
boxes = boxes.to(rel_codes.dtype)
# 计算两个数之间的真实距离,需要相减之后加1
TO_REMOVE = 1 # TODO remove
# 计算候选框的宽度
widths = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] + TO_REMOVE
# 计算候选框的高度
heights = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] + TO_REMOVE
# 计算候选框中心的x坐标
ctr_x = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * widths
# 计算候选框中心的y坐标
ctr_y = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * heights
# 得到计算回归目标时各个部分的权重
wx, wy, ww, wh = self.weights
# 计算去除权重的回归目标的各个部分
dx = rel_codes[:, 0::4] / wx
dy = rel_codes[:, 1::4] / wy
dw = rel_codes[:, 2::4] / ww
dh = rel_codes[:, 3::4] / wh
# Prevent sending too large values into torch.exp()
# 防止候选框的长和宽过大影响到torch.exp(),控制其大小
dw = torch.clamp(dw, max=self.bbox_xform_clip)
dh = torch.clamp(dh, max=self.bbox_xform_clip)
# 计算预测框中心的x坐标
pred_ctr_x = dx * widths[:, None] + ctr_x[:, None]
# 计算预测框中心的y坐标
pred_ctr_y = dy * heights[:, None] + ctr_y[:, None]
# 计算预测框的宽度
pred_w = torch.exp(dw) * widths[:, None]
# 计算预测框的高度
pred_h = torch.exp(dh) * heights[:, None]
# 将预测狂转换为标准边框格式
pred_boxes = torch.zeros_like(rel_codes)
# x1
pred_boxes[:, 0::4] = pred_ctr_x - 0.5 * pred_w
# y1
pred_boxes[:, 1::4] = pred_ctr_y - 0.5 * pred_h
# x2 (note: "- 1" is correct; don't be fooled by the asymmetry)
pred_boxes[:, 2::4] = pred_ctr_x + 0.5 * pred_w - 1
# y2 (note: "- 1" is correct; don't be fooled by the asymmetry)
pred_boxes[:, 3::4] = pred_ctr_y + 0.5 * pred_h - 1
return pred_boxes