数字图像处理-----卷(一)
数字图像处理(java版)
-
- 基本Swing UI组件与图像显示
- 插值算法
-
- 1、最邻近插值算法
- 2、双线性插值算法
- 3、三次卷积插值
- 点特征提取算子
-
- 1、Moravec算子
- 线特征提取算子
-
- 1、Robot算子
- 2、Sobel算子和Prewitt算子
- 3、Laplace算子
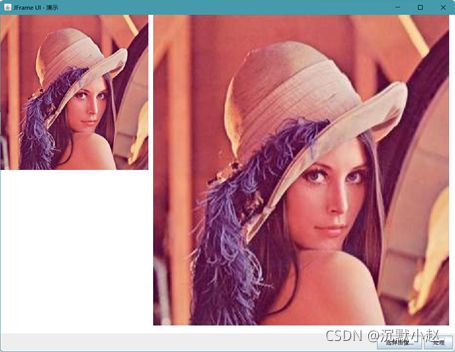
基本Swing UI组件与图像显示
要实现的功能:
1.通过文件对话框选择图像文件,刷新JFrame中的内容面板实现图像显示。
2.通过单击【处理】按钮实现对图像的必要处理,然后刷新显示图像。
大致UI组件布局如图所示。

其中支持BufferedImage对象显示的自定义JPanel类的实现如下:
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class ImagePanel extends JPanel {
/*
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private BufferedImage sourceImage;
private BufferedImage destImage;
public ImagePanel() {
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
Graphics g2d = (Graphics2D) g;
g2d.clearRect(0, 0, this.getWidth(), this.getHeight());
if (sourceImage != null) {
g2d.drawImage(sourceImage, 0, 0, sourceImage.getWidth(), sourceImage.getHeight(), null);
if (destImage != null) {
g2d.drawImage(destImage, sourceImage.getWidth() + 10, 0, destImage.getWidth(), destImage.getHeight(),
null);
}
}
}
public void process() {
// NearestZoomFilter filter = new NearestZoomFilter();
// BicubicZoomFilter filter = new BicubicZoomFilter();
// BilinearZoomFilter filter = new BilinearZoomFilter();
// filter.setDestHeight(sourceImage.getHeight() * 2);
// filter.setDestWidth(sourceImage.getWidth() * 2);
// RobotFilter filter = new RobotFilter();
// filter.setUseA(false);// 使用B模板,默认为A模板
// destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
// LaplaceFilter filter = new LaplaceFilter();
// MoravecFilter filter=new MoravecFilter();
// filter.setThreshold(5000);
// filter.setType(SobolPrewittEdgeDetector.SOBEL_TYPE);
// filter.setDirection(SobolPrewittEdgeDetector.X_DIRECTION);
ForstnerFilter filter=new ForstnerFilter();
filter.setThreshold(0.75);
filter.setWeight(133812991);
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
}
public BufferedImage getSourceImage() {
return sourceImage;
}
public void setSourceImage(BufferedImage sourImage) {
this.sourceImage = sourImage;
}
public BufferedImage getDestImage() {
return destImage;
}
public void setDestImage(BufferedImage destImage) {
this.destImage = destImage;
}
}
SwingUI界面实现与JBotton按钮监听处理的类的代码如下:
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFileChooser;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.filechooser.FileNameExtensionFilter;
public class MainUI extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
/*
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public static final String IMAGE_CMD = "选择图像...";
public static final String PROCESS_CMD = "处理";
private JButton imgBtn;
private JButton processBtn;
private ImagePanel imagePanel;
// image
private BufferedImage srcImage;
public MainUI() {
setTitle("JFrame UI - 演示");
imgBtn = new JButton(IMAGE_CMD);
processBtn = new JButton(PROCESS_CMD);
// Buttons
JPanel btnPanel = new JPanel();
btnPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
btnPanel.add(imgBtn);
btnPanel.add(processBtn);
// filters
imagePanel = new ImagePanel();
getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());
getContentPane().add(imagePanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
getContentPane().add(btnPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
// setup listener
setupActionListener();
}
private void setupActionListener() {
imgBtn.addActionListener(this);
processBtn.addActionListener(this);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (SwingUtilities.isEventDispatchThread()) {
System.out.println("Event Dispath Thread!!");
}
if (srcImage == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "请先选择图像源文件");
try {
JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser();
setFileTypeFilter(chooser);
chooser.showOpenDialog(null);
File f = chooser.getSelectedFile();
if (f != null) {
srcImage = ImageIO.read(f);
imagePanel.setSourceImage(srcImage);
imagePanel.repaint();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
if (IMAGE_CMD.equals(e.getActionCommand())) {
try {
JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser();
setFileTypeFilter(chooser);
chooser.showOpenDialog(null);
File f = chooser.getSelectedFile();
if (f != null) {
srcImage = ImageIO.read(f);
imagePanel.setSourceImage(srcImage);
imagePanel.repaint();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
imagePanel.repaint();
} else if (PROCESS_CMD.equals(e.getActionCommand())) {
imagePanel.process();
imagePanel.repaint();
}
}
public void setFileTypeFilter(JFileChooser chooser) {
FileNameExtensionFilter filter = new FileNameExtensionFilter("JPG & PNG Images", "jpg", "png");
chooser.setFileFilter(filter);
}
public void openView() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setPreferredSize(new Dimension(800, 600));
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MainUI ui = new MainUI();
ui.openView();
}
}
为了代码的简洁,实现一个抽象类AbstractBufferedImageOp,然后会把对像素数据的读写都放在抽象类中完成,这样就实现了代码的重用,也为处理像素提供更加方便的公共方法。
AbstractBufferedImageOp类的实现代码如下:
import java.awt.Rectangle;
import java.awt.RenderingHints;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImageOp;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;
/**
* A convenience class which implements those methods of BufferedImageOp which
* are rarely changed.
*/
public abstract class AbstractBufferedImageOp implements BufferedImageOp {
public final static double c1o60 = 1.0 / 60.0;
public final static double c1o255 = 1.0 / 255.0;
public BufferedImage createCompatibleDestImage(BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {
if (dstCM == null)
dstCM = src.getColorModel();
return new BufferedImage(dstCM, dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(src.getWidth(), src.getHeight()),
dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);
}
public Rectangle2D getBounds2D(BufferedImage src) {
return new Rectangle(0, 0, src.getWidth(), src.getHeight());
}
public Point2D getPoint2D(Point2D srcPt, Point2D dstPt) {
if (dstPt == null)
dstPt = new Point2D.Double();
dstPt.setLocation(srcPt.getX(), srcPt.getY());
return dstPt;
}
public RenderingHints getRenderingHints() {
return null;
}
public int clamp(int value) {
return value > 255 ? 255 : (value < 0 ? 0 : value);
}
public double[] rgb2Hsl(int[] rgb) {
double min, max, dif, sum;
double f1, f2;
double h, s, l;
// convert to HSL space
min = rgb[0];
if (rgb[1] < min)
min = rgb[1];
if (rgb[2] < min)
min = rgb[2];
max = rgb[0];
f1 = 0.0;
f2 = rgb[1] - rgb[2];
if (rgb[1] > max) {
max = rgb[1];
f1 = 120.0;
f2 = rgb[2] - rgb[0];
}
if (rgb[2] > max) {
max = rgb[2];
f1 = 240.0;
f2 = rgb[0] - rgb[1];
}
dif = max - min;
sum = max + min;
l = 0.5 * sum;
if (dif == 0) {
h = 0.0;
s = 0.0;
} else if (l < 127.5) {
s = 255.0 * dif / sum;
} else {
s = 255.0 * dif / (510.0 - sum);
}
h = (f1 + 60.0 * f2 / dif);
if (h < 0.0) {
h += 360.0;
}
if (h >= 360.0) {
h -= 360.0;
}
return new double[] { h, s, l };
}
public int[] hsl2RGB(double[] hsl) {
// conversion back to RGB space here!!
int tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
double v1, v2, v3, h1;
double s = hsl[1], l = hsl[2];
double h = hsl[0];
if (s == 0) {
tr = (int) l;
tg = (int) l;
tb = (int) l;
} else {
if (l < 127.5) {
v2 = c1o255 * l * (255 + s);
} else {
v2 = l + s - c1o255 * s * l;
}
v1 = 2 * l - v2;
v3 = v2 - v1;
h1 = h + 120.0;
if (h1 >= 360.0)
h1 -= 360.0;
if (h1 < 60.0) {
tr = (int) (v1 + v3 * h1 * c1o60);
} else if (h1 < 180.0) {
tr = (int) v2;
} else if (h1 < 240.0) {
tr = (int) (v1 + v3 * (4 - h1 * c1o60));
} else {
tr = (int) v1;
}
h1 = h;
if (h1 < 60.0) {
tg = (int) (v1 + v3 * h1 * c1o60);
} else if (h1 < 180.0) {
tg = (int) v2;
} else if (h1 < 240.0) {
tg = (int) (v1 + v3 * (4 - h1 * c1o60));
} else {
tg = (int) v1;
}
h1 = h - 120.0;
if (h1 < 0.0) {
h1 += 360.0;
}
if (h1 < 60.0) {
tb = (int) (v1 + v3 * h1 * c1o60);
} else if (h1 < 180.0) {
tb = (int) v2;
} else if (h1 < 240.0) {
tb = (int) (v1 + v3 * (4 - h1 * c1o60));
} else {
tb = (int) v1;
}
}
return new int[] { tr, tg, tb };
}
/**
* A convenience method for getting ARGB pixels from an image. This tries to
* avoid the performance penalty of BufferedImage.getRGB unmanaging the image.
*/
public int[] getRGB(BufferedImage image, int x, int y, int width, int height, int[] pixels) {
int type = image.getType();
if (type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB || type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB)
return (int[]) image.getRaster().getDataElements(x, y, width, height, pixels);
return image.getRGB(x, y, width, height, pixels, 0, width);
}
/**
* A convenience method for setting ARGB pixels in an image. This tries to avoid
* the performance penalty of BufferedImage.setRGB unmanaging the image.
*/
public void setRGB(BufferedImage image, int x, int y, int width, int height, int[] pixels) {
int type = image.getType();
if (type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB || type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB)
image.getRaster().setDataElements(x, y, width, height, pixels);
else
image.setRGB(x, y, width, height, pixels, 0, width);
}
public static float[] makeKernel(float radius) {
int r = (int) Math.ceil(radius);
int rows = r * 2 + 1;
float[] matrix = new float[rows];
float sigma = radius / 3;
float sigma22 = 2 * sigma * sigma;
float sigmaPi2 = 2 * ImageMath.PI * sigma;
float sqrtSigmaPi2 = (float) Math.sqrt(sigmaPi2);
float radius2 = radius * radius;
float total = 0;
int index = 0;
for (int row = -r; row <= r; row++) {
float distance = row * row;
if (distance > radius2)
matrix[index] = 0;
else
matrix[index] = (float) Math.exp(-(distance) / sigma22) / sqrtSigmaPi2;
total += matrix[index];
index++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
matrix[i] /= total;
return matrix;
}
}
插值算法
1、最邻近插值算法
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;
public class NearestZoomFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
private int destH; // zoom height
private int destW; // zoom width
public NearestZoomFilter() {
System.out.println("最邻近插值");
}
public void setDestHeight(int destH) {
this.destH = destH;
}
public void setDestWidth(int destW) {
this.destW = destW;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[destH * destW];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
float rowRatio = ((float) height) / ((float) destH);
float colRatio = ((float) width) / ((float) destW);
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < destH; row++) {
int srcRow = Math.round(((float) row) * rowRatio);
if (srcRow >= height) {
srcRow = height - 1;
}
for (int col = 0; col < destW; col++) {
int srcCol = Math.round(((float) col) * colRatio);
if (srcCol >= width) {
srcCol = width - 1;
}
int index2 = row * destW + col;
index = srcRow * width + srcCol;
outPixels[index2] = inPixels[index];
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, destW, destH, outPixels);
return dest;
}
public BufferedImage createCompatibleDestImage(BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {
if (dstCM == null)
dstCM = src.getColorModel();
return new BufferedImage(dstCM, dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(destW, destH),
dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);
}
}
其中重载createCompatibleDestImage( )方法目的是创建一个放大以后的BufferedImage对象。
在ImagePanel的process方法添加以下几行代码,运行MainUI.java选择需要放大的图片,单击【处理】按钮查看效果。
NearestZoomFilter filter = new NearestZoomFilter();
filter.setDestHeight(sourceImage.getHeight() * 2);
filter.setDestWidth(sourceImage.getWidth() * 2);
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
临近点插值是一种快速点插值的方法,不足之处是基于该方法产生图像明显有锯齿和模糊,不是一种很好的插值算法。
2、双线性插值算法
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;
public class BilinearZoomFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
private int destH;// zoom height
private int destW;// zoom width
public BilinearZoomFilter() {
System.out.println("双线性插值");
}
public void setDestHeight(int destH) {
this.destH = destH;
}
public void setDestWidth(int destW) {
this.destW = destW;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = creatCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[destH * destW];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
float rowRatio = ((float) height) / ((float) destH);
float colRatio = ((float) width) / ((float) destW);
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < destH; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
double srcRow = ((float) row) * rowRatio;
// 获取整数部分坐标 row Index
double j = Math.floor(srcRow);
// 获取行的小数部分坐标
double t = srcRow - j;
for (int col = 0; col < destW; col++) {
double srcCol = ((float) col) * colRatio;
// 获取整数部分坐标 column Index
double k = Math.floor(srcCol);
// 获取列的小数部分坐标
double u = srcCol - k;
int[] p1 = getPixel(j, k, width, height, inPixels);
int[] p2 = getPixel(j, k + 1, width, height, inPixels);
int[] p3 = getPixel(j + 1, k, width, height, inPixels);
int[] p4 = getPixel(j + 1, k + 1, width, height, inPixels);
double a = (1.0d - t) * (1.0d - u);
double b = (1.0d - t) * u;
double c = (t) * (1.0d - u);
double d = t * u;
ta = 255;
tr = (int) (p1[0] * a + p2[0] * b + p3[0] * c + p4[0] * d);
tg = (int) (p1[1] * a + p2[1] * b + p3[1] * c + p4[1] * d);
tb = (int) (p1[2] * a + p2[2] * b + p3[2] * c + p4[2] * d);
index = row * destW + col;
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, destW, destH, outPixels);
return dest;
}
private int[] getPixel(double j, double k, int width, int height, int[] inPixels) {
int row = (int) j;
int col = (int) k;
if (row >= height) {
row = height - 1;
}
if (row < 0) {
row = 0;
}
if (col >= width) {
col = width - 1;
}
if (col < 0) {
col = 0;
}
int index = row * width + col;
int[] rgb = new int[3];
rgb[0] = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
rgb[1] = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
rgb[2] = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
return rgb;
}
public BufferedImage creatCompatibleDestImage(BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {
if (dstCM == null)
dstCM = src.getColorModel();
return new BufferedImage(dstCM, dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(destW, destH),
dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);
}
}
在ImagePanel的process方法添加以下几行代码,运行MainUI.java选择需要放大的图片,单击【处理】按钮查看效果。
BilinearZoomFilter filter = new BilinearZoomFilter();
filter.setDestHeight(sourceImage.getHeight() * 2);
filter.setDestWidth(sourceImage.getWidth() * 2);
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
3、三次卷积插值
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;
public class BicubicZoomFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
private int destH;// zoom height
private int destW;// zoom width
public BicubicZoomFilter() {
System.out.println("三次卷积插值");
}
public void setDestHeight(int destH) {
this.destH = destH;
}
public void setDestWidth(int destW) {
this.destW = destW;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = creatCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[destH * destW];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
float rowRatio = ((float) height) / ((float) destH);
float colRatio = ((float) width) / ((float) destW);
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < destH; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
double srcRow = ((float) row) * rowRatio;
// 获取整数部分坐标 row Index
double j = Math.floor(srcRow);
// 获取行的小数部分坐标
double t = srcRow - j;
for (int col = 0; col < destW; col++) {
double srcCol = ((float) col) * colRatio;
// 获取整数部分坐标 column Index
double k = Math.floor(srcCol);
// 获取列的小数部分坐标
double u = srcCol - k;
double[][] bc1 = new double[4][3];
for (int n = 0; n < 4; n++) {
int[][] c1 = new int[4][3];
for (int m = 0; m < 4; m++) {
c1[m] = getPixel(j + n - 1, k + m - 1, width, height, inPixels);
}
for (int d = 0; d < 3; d++) {// for RGB
bc1[n][d] = get1DCubicValue(new double[] { c1[0][d], c1[1][d], c1[2][d], c1[3][d] }, u);
}
}
double[] dRGB = new double[3];
for (int dd = 0; dd < 3; dd++) {
dRGB[dd] = get1DCubicValue(new double[] { bc1[0][dd], bc1[1][dd], bc1[2][dd], bc1[3][dd] }, t);
}
ta = 255;
tr = (int) (dRGB[0]);
tg = (int) (dRGB[1]);
tb = (int) (dRGB[2]);
index = row * destW + col;
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, destW, destH, outPixels);
return dest;
}
// extract (1/2*delta) will get below formula
public double get1DCubicValue(double[] p, double delta) {
return p[1] + 0.5 * delta * (p[2] - p[0]
+ delta * (2.0 * p[0] - 5.0 * p[1] + 4.0 * p[2] - p[3] + delta * (3.0 * (p[1] - p[2]) + p[3] - p[0])));
}
private int[] getPixel(double j, double k, int width, int height, int[] inPixels) {
int row = (int) j;
int col = (int) k;
if (row >= height) {
row = height - 1;
}
if (row < 0) {
row = 0;
}
if (col >= width) {
col = width - 1;
}
if (col < 0) {
col = 0;
}
int index = row * width + col;
int[] rgb = new int[3];
rgb[0] = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
rgb[1] = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
rgb[2] = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
return rgb;
}
public BufferedImage creatCompatibleDestImage(BufferedImage src, ColorModel dstCM) {
if (dstCM == null)
dstCM = src.getColorModel();
return new BufferedImage(dstCM, dstCM.createCompatibleWritableRaster(destW, destH),
dstCM.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);
}
}
同样,测试运行该类只需要如下几行代码即可:
BicubicZoomFilter filter = new BicubicZoomFilter();
filter.setDestHeight(sourceImage.getHeight() * 2);
filter.setDestWidth(sourceImage.getWidth() * 2);
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
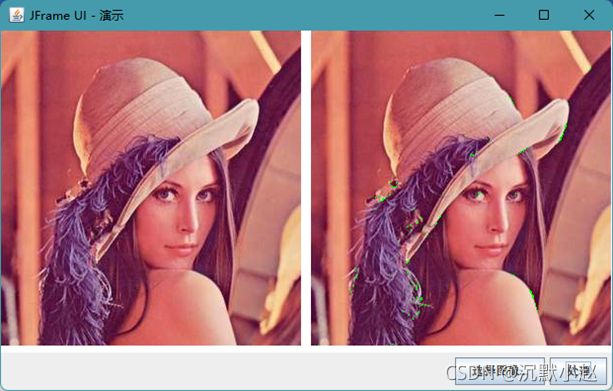
点特征提取算子
1、Moravec算子
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class MoravecFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
private int threshold;
public int getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
public void setThreshold(int threshold) {
this.threshold = threshold;
}
public MoravecFilter() {
System.out.println("Moravec算子");
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
int w = 5;
int k = w / 2;
if (dest == null)
dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
// 初始化,获取输入图像的像素数组
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width * height];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
// 每一行、每一列的循环每个像素
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
int wV1, wV2, wV3, wV4;
wV1 = wV2 = wV3 = wV4 = 0;
// 计算水平(0度)方向窗内兴趣值
for (int i = -k; i < k; i++) {// i=-2,-1,0,1
int a = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + i, row);
int b = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + i + 1, row);
wV1 += (a - b) * (a - b);
}
// 计算垂直(90度)方向窗内兴趣值
for (int i = -k; i < k; i++) {// i=-2,-1,0,1
int a = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row + i);
int b = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row + i + 1);
wV2 += (a - b) * (a - b);
}
// 计算45度方向窗内兴趣值
for (int i = -k; i < k; i++) {// i=-2,-1,0,1
int a = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + i, row + i);
int b = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + i + 1, row + i + 1);
wV3 += (a - b) * (a - b);
}
// 计算135度方向窗内兴趣值
for (int i = -k; i < k; i++) {// i=-2,-1,0,1
int a = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + i, row - i);
int b = getGrayPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + i + 1, row - i - 1);
wV4 += (a - b) * (a - b);
}
int V = Math.min(Math.min(wV1, wV2), Math.min(wV3, wV4));
// 若兴趣值大于阈值,则将点的坐标存入数组中
if (V > threshold) {
tr = 0;
tg = 255;
tb = 0;
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (tr << 16) | (tg << 8) | tb;// 标记绿色
} else {
outPixels[index] = inPixels[index];
}
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels);
return dest;
}
private int getGrayPixel(int[] inPixels, int width, int height, int col, int row) {
// 循环每个输入像素获取RGB值,将计算的到的结果作为每个像素的输出像素,即完成了图像的灰度转换
if (col < 0 || col >= width)
col = 0;
if (row < 0 || row >= height)
row = 0;
int index = row * width + col;
int tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
int tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
int tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
int gray = (int) (0.299 * tr + 0.587 * tg + 0.114 * tb);
return gray;
}
}
测试运行该类只需要如下几行代码即可:
MoravecFilter filter=new MoravecFilter();
filter.setThreshold(5000);
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
线特征提取算子
1、Robot算子
Robot算子就是检测图像边缘的卷积核(算子),而且Robot算子是从水平45°或135°两个方向进行图像边缘的寻找,对于活跃于边缘有着非常好的效果。
Robot算子及其他2×2算子对图像噪声非常敏感,但图像有噪声干扰时,边缘检测效果就会大打折扣。


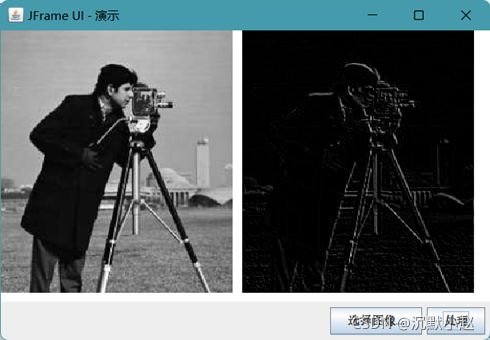
代码如下:
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class RobotFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
private boolean useA = true;
public RobotFilter() {
System.out.println("Robot 算子");
}
public boolean isUseA() {
return useA;
}
public void setUseA(boolean useA) {
this.useA = useA;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
// 初始化,获取输入图像像素数组
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width * height];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
// 每一行、每一列循环每个像素
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
// 计算Robot算子,使用A模板
if (isUseA()) {
int[] rgb1 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row);
int[] rgb2 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row + 1);
tr = rgb1[0] - rgb2[0];
tg = rgb1[1] - rgb2[1];
tb = rgb1[2] - rgb2[2];
} else {// 使用Robot算子B模板
int[] rgb1 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row);
int[] rgb2 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row + 1);
tr = rgb1[0] - rgb2[0];
tg = rgb1[1] - rgb2[1];
tb = rgb1[2] - rgb2[2];
}
// clamp来计算处理计算后的结果
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels);
return dest;
}
private int[] getPixel(int[] inPixels, int width, int height, int col, int row) {
if (col < 0 || col >= width)
col = 0;
if (row < 0 || row >= height)
row = 0;
int index = row * width + col;
int tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
int tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
int tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
return new int[] { tr, tg, tb };
}
}
测试运行该类,在ImagePanel的process方法添加以下几行代码,运行MainUI.java选择需要放大的图片,单击【处理】按钮查看效果。
RobotFilter filter = new RobotFilter();
// filter.setUseA(false);// 使用B模板,默认为A模板
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
2、Sobel算子和Prewitt算子
Sobel算子和Prewitt算子都是3×3的算子,假设有如下的像素块M:

则他的X与Y方向的偏导数计算分别如下:

当系数c=1 时的到的算子为Prewitt算子:

当系数c=2 时的到的算子为Sobel算子:

基于Prewitt算子在X方向与Y方向卷积之后得到的图像效果如下:
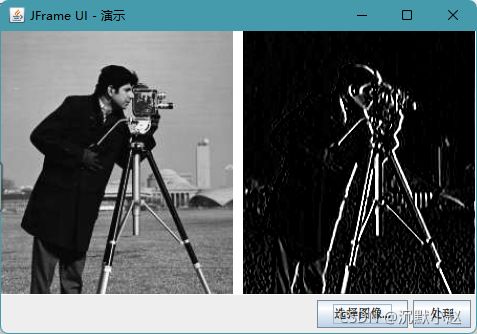

基于Sobel算子在X方向与Y方向卷积之后得到的图像效果如下:


代码如下:
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class SobolPrewittEdgeDetector extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
public final static int SOBEL_TYPE = 1;
public final static int PREWITT_TYPE = 2;
public final static int X_DIRECTION = 4;
public final static int Y_DIRECTION = 8;
private int type;
private int direction;
public SobolPrewittEdgeDetector() {
type = PREWITT_TYPE;
direction = X_DIRECTION;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public int getDirection() {
return direction;
}
public void setType(int type) {
this.type = type;
}
public void setDirection(int direction) {
this.direction = direction;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
// 初始化,获取输入图像的像素数组
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width * height];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
// 每一行、每一列的循环每个像素
int index = 0;
// 确定是否为Sobol算子
int coefficient = (getType() == SOBEL_TYPE) ? 2 : 1;
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
// X方向边缘检测
if (getDirection() == X_DIRECTION) {
int[] a2 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row - 1);
int[] a3 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row);
int[] a4 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row + 1);
int[] a0 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col - 1, row - 1);
int[] a7 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col - 1, row);
int[] a6 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col - 1, row + 1);
tr = (a2[0] + coefficient * a3[0] + a4[0]) - (a0[0] + coefficient * a7[0] + a6[0]);
tg = (a2[1] + coefficient * a3[1] + a4[1]) - (a0[1] + coefficient * a7[1] + a6[1]);
tb = (a2[2] + coefficient * a3[2] + a4[2]) - (a0[2] + coefficient * a7[2] + a6[2]);
} else {// Y方向边缘检测
int[] a6 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col - 1, row + 1);
int[] a5 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row + 1);
int[] a4 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row + 1);
int[] a0 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col - 1, row - 1);
int[] a1 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row - 1);
int[] a2 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row - 1);
tr = (a6[0] + coefficient * a5[0] + a4[0]) - (a0[0] + coefficient * a1[0] + a2[0]);
tg = (a6[1] + coefficient * a5[1] + a4[1]) - (a0[1] + coefficient * a1[1] + a2[1]);
tb = (a6[2] + coefficient * a5[2] + a4[2]) - (a0[2] + coefficient * a1[2] + a2[2]);
}
// clamp来处理计算后的结果
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels);
return dest;
}
private int[] getPixel(int[] inPixels, int width, int height, int col, int row) {
if (col < 0 || col >= width)
col = 0;
if (row < 0 || row >= height)
row = 0;
int index = row * width + col;
int tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
int tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
int tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
return new int[] { tr, tg, tb };
}
}
其中参数type选择Sobel算子类型或Prewitt算子类型,参数direction决定是进行X方向边缘检测还是Y方向边缘检测。运行于测试SobolPrewittEdgeDetector类时,只需要如下几行代码:
SobolPrewittEdgeDetector filter = new SobolPrewittEdgeDetector();
filter.setType(SobolPrewittEdgeDetector.SOBEL_TYPE);
filter.setDirection(SobolPrewittEdgeDetector.X_DIRECTION);
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);
3、Laplace算子
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class LaplaceFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
public LaplaceFilter() {
System.out.println("拉普拉斯算子");
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if (dest == null)
dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
// 初始化,获取输入图像的像素数组
int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width * height];
getRGB(src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
// 每一行、每一列的循环每个像素
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
int[] a = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row);
int[] a1 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row - 1);
int[] a3 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col + 1, row);
int[] a5 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col, row + 1);
int[] a7 = getPixel(inPixels, width, height, col - 1, row);
tr = (a1[0] + a3[0] + a5[0] + a7[0]) - (a[0] * 4);
tg = (a1[1] + a3[1] + a5[1] + a7[1]) - (a[1] * 4);
tb = (a1[2] + a3[2] + a5[2] + a7[2]) - (a[2] * 4);
// clamp来处理计算后的结果
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
}
}
setRGB(dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels);
return dest;
}
private int[] getPixel(int[] inPixels, int width, int height, int col, int row) {
if (col < 0 || col >= width)
col = 0;
if (row < 0 || row >= height)
row = 0;
int index = row * width + col;
int tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
int tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
int tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
return new int[] { tr, tg, tb };
}
}
运行于测试LaplaceFilter类时,只需要如下几行代码:
LaplaceFilter filter = new LaplaceFilter();
destImage = filter.filter(sourceImage, null);