自然语言处理实验代码
实验二代码摘自知乎,其他实验代码修改自课本。
实验一,基于规则的分词算法
from pyhanlp import *
def load_dictionary():
IOUtil = JClass('com.hankcs.hanlp.corpus.io.IOUtil')
path = HanLP.Config.CoreDictionaryPath.replace('.txt', 'mini.txt')
dic = IOUtil.loadDictionary([path])
return set(dic.keySet())
def fully_segment(text, dic):
word_list = []
for i in range(len(text)):
for j in range(len(text)):
word = text[i:j]
if word in dic:
word_list.append(word)
return word_list
def forward_segment(text, dic):
word_list = []
i = 0
while i < len(text):
longest_word = text[i]
for j in range(i+1, len(text) + 1):
word = text[i:j]
if word in dic:
if len(word) > len(longest_word):
longest_word = word
word_list.append(longest_word)
i += len(longest_word)
return word_list
def backward_segment(text, dic):
word_list = []
i = len(text) - 1
while i >= 0:
longest_word = text[i]
for j in range(0, i):
word = text[j: i+1]
if word in dic:
if len(word) > len(longest_word):
longest_word = word
break
word_list.insert(0, longest_word)
i -= len(longest_word)
return word_list
def count_single_char(word_list:list):
return sum(1 for word in word_list if len(word) == 1)
def bidirectional_segment(text, dic):
f = forward_segment(text, dic)
b = backward_segment(text, dic)
if len(f) < len(b):
return f
elif len(f) > len(b):
return b
else:
if count_single_char(f) < count_single_char(b):
return f
else:
return b
dic = load_dictionary()
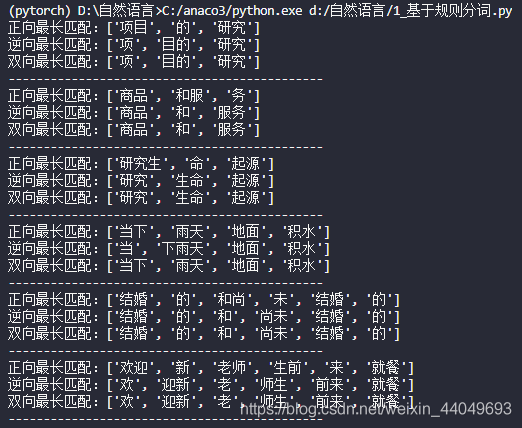
text = ['项目的研究', '商品和服务', '研究生命起源', '当下雨天地面积水', '结婚的和尚未结婚的', '欢迎新老师生前来就餐']
for i in text:
print('正向最长匹配:' + str(forward_segment(i, dic)))
print('逆向最长匹配:' + str(backward_segment(i, dic)))
print('双向最长匹配:' + str(bidirectional_segment(i, dic)))
print('---------------------------------------------')
实验二,隐马尔可夫求πAB
import numpy as np
def train(fileName):
# HMM模型由三要素决定 lambda=(A,B,pi)
# A为状态转移矩阵
# B为观测概率矩阵
# pi为初始状态概率向量
# 在该函数中,我们需要通过给定的训练数据(包含S个长度相同的观测序列【每一句话】和对应的状态序列【每一句话中每个词的词性】
# 在中文分词中,包含一下集中状态(词性)
# B:词语的开头(单词的头一个字)
# M:中间词(即在一个词语的开头和结尾之中)
# E:单词的结尾(即单词的最后一个字)
# S:单个字
# 定义一个状态映射字典。方便我们定位状态在列表中对应位置
status2num={'B':0,'M':1,'E':2,'S':3}
# 定义状态转移矩阵。总共4个状态,所以4x4
A=np.zeros((4,4))
#定义观测概率矩阵
#在ord中,中文编码大小为65536,总共4个状态
#所以B矩阵4x65536
#就代表每一种状态(词性)得到观测状态(字)
B=np.zeros((4,65536))
# 初始状态,每一个句子的开头只有4中状态(词性)
PI=np.zeros(4)
with open(fileName,encoding='utf-8') as file:
for line in file.readlines():
wordStatus=[]#用于保存该行所有单词的状态
words=line.strip().split() #除去前后空格,然后依照中间空格切分为单词
for i,word in enumerate(words):
# 根据长度判断状态
if len(word)==1:
status='S'# 保存每一个单词状态
code=ord(word)
B[status2num[status[0]]][code]+=1
else:
# 当长度为2,M*0。这样可以一起更新
status='B'+(len(word)-2)*'M'+'E'
for s in range(len(word)):
code=ord(word[s])
B[status2num[status[s]]][code]+=1
# i==0意味着这是句首。我们需要更新PI中每种状态出现次数
if i==0:
PI[status2num[status[0]]]+=1
# 使用extend,将status中每一个元素家在列表之中。而不是append直接将整个status放在后面
wordStatus.extend(status)
for i in range(1,len(wordStatus)):
# wordStatus获得状态,使用status2num来映射到正确位置
A[status2num[wordStatus[i-1]]][status2num[wordStatus[i]]]+=1
# 计算PI向量
total=sum(PI)
for i in range(len(PI)):
if PI[i]==0:
PI[i]=-3.14e+100
else:
# 别忘了去取对数
PI[i]=np.log(PI[i]/total)
# 计算A矩阵
for i in range(len(A)):
total=sum(A[i])
for j in range(len(A[i])):
if A[i][j]==0:
A[i][j]=-3.14e+100
else:
A[i][j]=np.log(A[i][j]/total)
# 更新B矩阵
for i in range(len(B)):
total=sum(B[i])
for j in range(len(B[i])):
if B[i][j]==0:
B[i][j]=-3.14e+100
else:
B[i][j]=np.log(B[i][j]/total)
# 返回三个参数
return (PI,A,B)
PI, A, B = train('D:/自然语言/HMMTrainSet.txt')
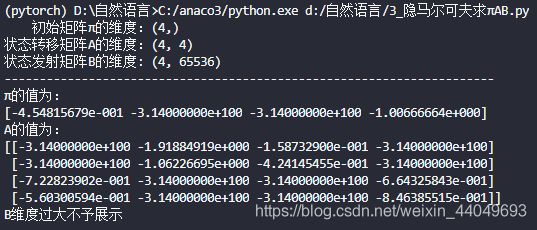
print(' 初始矩阵π的维度:' + str(PI.shape))
print('状态转移矩阵A的维度:' + str(A.shape))
print('状态发射矩阵B的维度: ' + str(B.shape))
print('----------------------------------')
print('π的值为:')
print(PI)
print('A的值为:')
print(str(A))
print('B维度过大不予展示')
实验三,隐马尔可夫维特比算法分词
from pyhanlp import *
import os
import zipfile
from pyhanlp.static import download, remove_file, HANLP_DATA_PATH
CWSEvaluator = SafeJClass('com.hankcs.hanlp.seg.common.CWSEvaluator')
def test_data_path():
"""
获取测试数据路径,位于$root/data/test,根目录由配置文件指定。
:return:
"""
data_path = os.path.join(HANLP_DATA_PATH, 'test')
if not os.path.isdir(data_path):
os.mkdir(data_path)
return data_path
def ensure_data(data_name, data_url):
root_path = test_data_path()
dest_path = os.path.join(root_path, data_name)
if os.path.exists(dest_path):
return dest_path
if data_url.endswith('.zip'):
dest_path += '.zip'
download(data_url, dest_path)
if data_url.endswith('.zip'):
with zipfile.ZipFile(dest_path, "r") as archive:
archive.extractall(root_path)
remove_file(dest_path)
dest_path = dest_path[:-len('.zip')]
return dest_path
sighan05 = ensure_data('icwb2-data', 'http://sighan.cs.uchicago.edu/bakeoff2005/data/icwb2-data.zip')
msr_dict = os.path.join(sighan05, 'gold', 'msr_training_words.utf8')
msr_train = os.path.join(sighan05, 'training', 'msr_training.utf8')
msr_model = os.path.join(test_data_path(), 'msr_cws')
msr_test = os.path.join(sighan05, 'testing', 'msr_test.utf8')
msr_output = os.path.join(sighan05, 'testing', 'msr_bigram_output.txt')
msr_gold = os.path.join(sighan05, 'gold', 'msr_test_gold.utf8')
FirstOrderHiddenMarkovModel = JClass('com.hankcs.hanlp.model.hmm.FirstOrderHiddenMarkovModel')
HMMSegmenter = JClass('com.hankcs.hanlp.model.hmm.HMMSegmenter')
def train(corpus, model):
segmenter = HMMSegmenter(model)
segmenter.train(corpus)
print(segmenter.segment('商品和货币'))
return segmenter.toSegment()
def evaluate(segment):
result = CWSEvaluator.evaluate(segment, msr_test, msr_output, msr_gold, msr_dict)
print(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
segment = train(msr_train, FirstOrderHiddenMarkovModel())
evaluate(segment)
实验四,K-means文本聚类
from pyhanlp import *
ClusterAnalyzer = JClass('com.hankcs.hanlp.mining.cluster.ClusterAnalyzer')
analyzer = ClusterAnalyzer()
analyzer.addDocument("赵一", "流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 蓝调, 蓝调, 蓝调, 蓝调, 蓝调, 蓝调, 摇滚, 摇滚, 摇滚, 摇滚")
analyzer.addDocument("钱二", "爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲")
analyzer.addDocument("张三", "古典, 古典, 古典, 古典, 民谣, 民谣, 民谣, 民谣")
analyzer.addDocument("李四", "爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 爵士, 金属, 金属, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲, 舞曲")
analyzer.addDocument("王五", "流行, 流行, 流行, 流行, 摇滚, 摇滚, 摇滚, 嘻哈, 嘻哈, 嘻哈")
analyzer.addDocument("马六", "古典, 古典, 古典, 古典, 古典, 古典, 古典, 古典, 摇滚")
print(analyzer.kmeans(3))