【RL】算法简介与实现
获取更多内容,请访问博主的个人博客 爱吃猫的小鱼干的Blog
一 Value-Based
Q-Learning
Q-Learning是RL算法中Value-Based的算法,Q即为Q(s,a)就是在某一时刻的s状态下(s∈S),采取 动作a (a∈A)能够获得收益的期望,环境会根据agent的动作反馈相应的回报reward。所以算法的主要思想就是将State与Action构建成一张Q-table来存储Q值,然后根据Q值来选取能够获得最大的收益的动作。
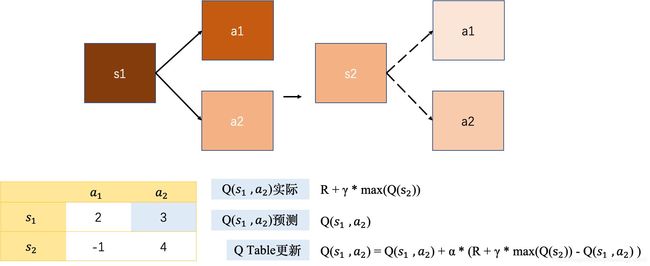
下面是Q-Learning的TensorFlow实现
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
class QLearning:
def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):
"""
QLearning
:param actions:
:param learning_rate:
:param reward_decay:
:param e_greedy:
"""
self.actions = actions
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon = e_greedy
self.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions)
def chooseAction(self, observation):
"""Choose action with state and observation"""
self.checkStateExist(observation)
if np.random.uniform()<self.epsilon:
opt_actions = self.q_table.loc[observation, :]
# opt_actions = opt_actions.reindex(np.random.permutation(opt_actions))
# action = opt_actions.argmax()
action = np.random.choice(opt_actions[opt_actions == np.max(opt_actions)].index)
else:
action = np.random.choice(self.actions)
return action
def updateParams(self, state, action, reward, state_):
self.checkStateExist(state_)
q_pre = self.q_table.loc[state, action]
if state_ != 'terminal':
q_target = reward + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[state_, :].max()
else:
q_target = reward
self.q_table.loc[state, action] += self.lr * (q_target - q_pre)
def checkStateExist(self, state):
if state not in self.q_table.index:
self.q_table = self.q_table.append(
pd.Series([0]*len(self.actions), index=self.q_table.columns, name=state)
)
DQN

当状态动作很多时,Q-Learning使用Table存储Value的方式不再实用(甚至不可行)。
如何不使用Table而得到每个状态下采取各个动作的Value呢?DQN用神经网络将State映射到Value。

DQN是在Q-Learning的主框架上做了扩展,包括:
- 记忆库(用于重复学习,随机抽取的经历也打乱的状态之间的相关性,使神经网络的更新更有效率)
- MLP计算Q值
- 暂时冻结Q_target参数(切断相关性),target网络用来计算Q现实
下面是DQN的TensorFlow实现
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
class DeepQNet:
def __init__(self,
n_actions,
n_features,
learning_rate=0.01,
reward_decay=0.9,
e_greedy=0.9,
update_target_iter=300,
memory_size=500,
batch_size=32,
e_greedy_increment=None,
output_graph=False,
):
"""
DQN
:param n_actions:
:param n_features:
:param learning_rate:
:param reward_decay:
:param e_greedy:
:param update_target_iter:
:param memory_size:
:param batch_size:
:param e_greedy_increment:
:param output_graph:
"""
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.update_target_iter = update_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# total learning step(Cooperate with update_target_iter in learn() to update the parameters of target net)
self.learn_step_counter = 0
# memory: row = memory_size, col = observation + observation_ + action + reward
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, self.n_features*2+2))
self._buildNet()
self.sess = tf.Session()
if output_graph:
tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/', self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
self.cost = []
def _buildNet(self):
""""Build evaluate network and target network"""
# build evaluate net
self.state = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='state')
self.q_target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_actions], name='Q_target')
with tf.variable_scope('evaluate_net'):
c_names, n_l1 = ['evaluate_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES], 10
w_initializer, b_initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0, 0.3), tf.constant_initializer(0.1)
with tf.variable_scope('layer1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.state, w1) + b1)
with tf.variable_scope('layer2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_evaluate = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2)
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.q_target, self.q_evaluate))
with tf.variable_scope('train'):
self.opt = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss)
# build target net
self.state_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='state_')
with tf.variable_scope('target_net'):
c_names = ['target_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
with tf.variable_scope('layer1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.state_, w1) + b1)
with tf.variable_scope('layer2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_next = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2)
def storeTransition(self, state, action, reward, state_):
"""Store the state, observation and reward experienced during the train process to enable batch training"""
if not hasattr(self, 'memory_counter'):
self.memory_counter = 0
transition = np.hstack((state, [action, reward], state_))
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def chooseAction(self, observation):
"""Choose action with state and observation"""
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
actions = self.sess.run(self.q_evaluate, feed_dict={self.state: observation})
action = np.argmax(actions)
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
def updateTargetNet(self):
"""Update the target net with the latest evaluate net parameters"""
evaluate_params = tf.get_collection('evaluate_net_params')
target_params = tf.get_collection('target_net_params')
self.sess.run([tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(target_params, evaluate_params)])
def learn(self):
# check to update target net
if self.learn_step_counter % self.update_target_iter == 0:
self.updateTargetNet()
print('Update target net!')
# Get batch training data from the memory
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size=self.batch_size)
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size=self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
q_evaluate, q_next = self.sess.run([self.q_evaluate, self.q_next],
feed_dict={
self.state: batch_memory[:, 0:self.n_features],
self.state_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:]})
q_target = q_evaluate.copy()
batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype=np.int32)
eval_act_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int)
reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1] # Related to memory format, here means [action, reward]
q_target[batch_index, eval_act_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis=1)
_, cost = self.sess.run([self.opt, self.loss],
feed_dict={
self.state: batch_memory[:, 0:self.n_features],
self.q_target: q_target
})
self.cost.append(cost)
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
self.learn_step_counter += 1
def showCost(self):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(np.arange(len(self.cost)), self.cost)
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.xlabel('training steps')
plt.show()
二 Policy-Based
直接输出动作,可以在连续区间内选择动作;而Value-Based要在连续区间中,对无数个动作计算价值选择行为是不可行的。
误差如何反向传递呢?没有误差,它的目的是选的动作在下次更有可能被选择,但怎么知道动作的好坏呢,用reward,reward小,动作在下次被选择的可能性增加的少。
Actor-Critic
Actor:Policy-Based,输入State,预测输出采取各种Action的概率。
Critic;Value-Based,输入State,预测输出当前State的Value,并与下一状态的next_stateValue求TD_error
在Actor-Critic中,Actor可以每一步都更新学习(而单纯的Policy-Based方法要在回合结束后才能更新)
但也带来了问题:由于两个网络在连续状态中更新参数,每次跟新前后的参数具有相关性,导致网络只能片面的看待问题,甚至学不到有效的参数,不能收敛。
TRPO
PPO
Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient(DDPG)
获取更多内容,请访问博主的个人博客 爱吃猫的小鱼干的Blog