python中mean的用法_Python Pandas dataframe.mean()用法及代码示例
Python是进行数据分析的一种出色语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的python软件包具有奇妙的生态系统。 Pandas是其中的一种,使导入和分析数据更加容易。
Pandas dataframe.mean()函数返回所请求轴的平均值。如果将方法应用于 Pandas 系列对象,则该方法将返回标量值,该标量值是 DataFrame 中所有观测值的平均值。如果将方法应用于pandas DataFrame 对象,则该方法将返回pandas系列对象,该对象包含指定轴上的值的平均值。
用法: DataFrame.mean(axis=None, skipna=None, level=None, numeric_only=None, **kwargs)
参数:
axis:{索引(0),列(1)}
skipna:计算结果时排除NA /空值
level:如果轴是MultiIndex(分层),则沿特定级别计数,折叠成一个系列
numeric_only:仅包括浮点型,整数型和布尔型列。如果为None,将尝试使用所有内容,然后仅使用数字数据。未针对系列实施。
返回值:意思是:Series或DataFrame(如果指定级别)
范例1:采用mean()函数查找索引轴上所有观测值的平均值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
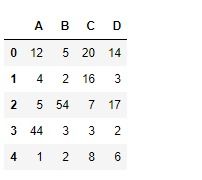
# Creating the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, 44, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 16, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 17, 2, 6]})
# Print the dataframe
df
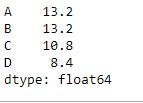
让我们使用dataframe.mean()函数查找索引轴上的均值。
# Even if we do not specify axis = 0,
# the method will return the mean over
# the index axis by default
df.mean(axis = 0)
输出:
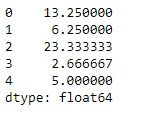
范例2:采用mean()在具有Na值。还要找到列轴的平均值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1],
"B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None],
"C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8],.
"D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
# skip the Na values while finding the mean
df.mean(axis = 1, skipna = True)
输出: