AidLux智慧交通AI安全实战学习
本次参加AidLux训练营,Rocky作为主讲老师,学习到了利用目标检测算法流程和AI攻防策略进行结合,从而达到安全。
1.检测汽车模型的训练
本次目标检测的模型是Yolov5,首先对标注图片 进行转换,转换为yolov5的格式,然后利用train.py进行训练,调整输入图片的位置,car.yaml,由于本次只是训练一个类型,所以模型结构的yaml中也要修改为nc:1
数据转换代码如下:
import csv
import os
import shutil
image_dir = "/car_train_data/image_txt/"
train_val_dir = "/car_train_data/train_val_txt/"
if not os.path.exists(image_dir):
os.makedirs(image_dir)
if not os.path.exists(train_val_dir):
os.makedirs(train_val_dir)
csv_reader = csv.reader(open("/car_train_data/train.csv"))
count = -1
for line in csv_reader:
count += 1
if count == 0:
continue
with open(image_dir + line[0].split('.')[0] + ".txt", 'a+') as f:
width = float(line[3]) - float(line[1])
height = float(line[4]) - float(line[2])
x_center = float(line[1]) + width / 2
y_center = float(line[2]) + height / 2
f.write('1' + ' ' + str(x_center / 676) + ' ' + str(y_center / 380) + ' '
+ str(width / 676) + ' ' + str(height / 380) + "\n")
shutil.copy("/car_train_data/train_images/" + line[0], image_dir + line[0])
if count % 10 != 0:
with open(train_val_dir + "train.txt", "a+") as f:
f.write(image_dir + line[0] + "\n")
else:
with open(train_val_dir + "val.txt", "a+") as f:
f.write(image_dir + line[0] + "\n")
2. AI安全
2.1 常用AI对抗防御算法划分
目前主流对抗防御的总体分支与逻辑:
其中对抗训练是指在训练过程中加入对抗样本,通过不断的学习对抗样本的特征,从而提升模型的鲁 棒性。
监测识别对抗样本顾名思义,在项目关键节点处,设置一些能够识别对抗样本的特种模型,从而提前 预警对抗攻击风险。
模型鲁棒结构设计是指在模型中设计特定的滤波结构能够一定程度上增强模型鲁棒性,抵御对抗噪
声。
对抗扰动结构破坏主要在数据流处理的时候使用,通过一些滤波算法,噪声结构破坏算法,噪声覆盖算法等策略,减弱对抗噪声的影响,使其不能对模型造成攻击。
梯度掩膜则是在白盒对抗防御中非常高效的一种算法,因为其能掩盖真实梯度,从而能够使得白盒攻 击算法失效。本章中在后面小节使用到的对抗防御方法主要是基于梯度掩膜的GCM模块。
2.2 攻击算法&效果:
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.models import mobilenet_v2
from advertorch.utils import predict_from_logits
from advertorch.utils import NormalizeByChannelMeanStd
from advertorch.attacks import LinfPGDAttack
from advertorch_examples.utils import ImageNetClassNameLookup
from advertorch_examples.utils import bhwc2bchw
from advertorch_examples.utils import bchw2bhwc
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
### 读取图片
def get_image():
img_path = os.path.join(r"D:\Study\dabai-study-2\lesson-4\Lesson4_code\adv_code\images", "school_bus.png")
img_url = "https://farm1.static.flickr.com/230/524562325_fb0a11d1e1.jpg"
def _load_image():
from skimage.io import imread
return imread(img_path) / 255.
if os.path.exists(img_path):
return _load_image()
else:
import urllib
urllib.request.urlretrieve(img_url, img_path)
return _load_image()
def tensor2npimg(tensor):
return bchw2bhwc(tensor[0].cpu().numpy())
### 展示攻击结果
def show_images(model, img, advimg, enhance=127):
np_advimg = tensor2npimg(advimg)
np_perturb = tensor2npimg(advimg - img)
pred = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model(img)))
advpred = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model(advimg)))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(np_img)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("original image\n prediction: {}".format(pred))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(np_perturb * enhance + 0.5)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("the perturbation,\n enhanced {} times".format(enhance))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(np_advimg)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("perturbed image\n prediction: {}".format(advpred))
plt.show()
normalize = NormalizeByChannelMeanStd(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
### 常规模型加载
model = mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
model = nn.Sequential(normalize, model)
model = model.to(device)
### 数据预处理
np_img = get_image()
img = torch.tensor(bhwc2bchw(np_img))[None, :, :, :].float().to(device)
imagenet_label2classname = ImageNetClassNameLookup()
### 测试模型输出结果
pred = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model(img)))
print("test output:", pred)
### 输出原label
pred_label = predict_from_logits(model(img))
### 对抗攻击:PGD攻击算法
adversary = LinfPGDAttack(
model, eps=8 / 255, eps_iter=2 / 255, nb_iter=80,
rand_init=True)
### 完成攻击,输出对抗样本
advimg = adversary.perturb(img, pred_label)
### 展示源图片,对抗扰动,对抗样本以及模型的输出结果
show_images(model, img, advimg)
攻击效果:从右侧图片看出,原始图片是school_bus,错误识别成:acoustic_guitar
2.3 防御算法&效果:
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.models import mobilenet_v2
from advertorch.utils import predict_from_logits
from advertorch.utils import NormalizeByChannelMeanStd
from robust_layer import GradientConcealment, ResizedPaddingLayer
from advertorch.attacks import LinfPGDAttack
from advertorch_examples.utils import ImageNetClassNameLookup
from advertorch_examples.utils import bhwc2bchw
from advertorch_examples.utils import bchw2bhwc
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
### 读取图片
def get_image():
img_path = os.path.join(r"D:\Study\dabai-study-2\lesson-4\Lesson4_code\adv_code\images", "school_bus.png")
img_url = "https://farm1.static.flickr.com/230/524562325_fb0a11d1e1.jpg"
def _load_image():
from skimage.io import imread
return imread(img_path) / 255.
if os.path.exists(img_path):
return _load_image()
else:
import urllib
urllib.request.urlretrieve(img_url, img_path)
return _load_image()
def tensor2npimg(tensor):
return bchw2bhwc(tensor[0].cpu().numpy())
### 展示攻击结果
def show_images(model, img, advimg, enhance=127):
np_advimg = tensor2npimg(advimg)
np_perturb = tensor2npimg(advimg - img)
pred = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model(img)))
advpred = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model(advimg)))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(np_img)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("original image\n prediction: {}".format(pred))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(np_perturb * enhance + 0.5)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("the perturbation,\n enhanced {} times".format(enhance))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(np_advimg)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("perturbed image\n prediction: {}".format(advpred))
plt.show()
normalize = NormalizeByChannelMeanStd(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
### GCM模块
robust_mode = GradientConcealment()
### 常规模型+GCM模块
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, l=290):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.l = l
self.gcm = GradientConcealment()
# model = resnet18(pretrained=True)
model = mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True)
# pth_path = "/Users/rocky/Desktop/训练营/model/mobilenet_v2-b0353104.pth"
# print(f'Loading pth from {pth_path}')
# state_dict = torch.load(pth_path, map_location='cpu')
# is_strict = False
# if 'model' in state_dict.keys():
# model.load_state_dict(state_dict['model'], strict=is_strict)
# else:
# model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=is_strict)
normalize = NormalizeByChannelMeanStd(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
self.model = nn.Sequential(normalize, model)
def load_params(self):
pass
def forward(self, x):
x = self.gcm(x)
# x = ResizedPaddingLayer(self.l)(x)
out = self.model(x)
return out
### 常规模型+GCM模块 加载
model_defense = Model().eval().to(device)
### 数据预处理
np_img = get_image()
img = torch.tensor(bhwc2bchw(np_img))[None, :, :, :].float().to(device)
imagenet_label2classname = ImageNetClassNameLookup()
### 测试模型输出结果
pred_defense = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model_defense(img)))
print("test output:", pred_defense)
pre_label = predict_from_logits(model_defense(img))
### 对抗攻击:PGD攻击算法
adversary = LinfPGDAttack(
model_defense, eps=8 / 255, eps_iter=2 / 255, nb_iter=80,
rand_init=True, targeted=False)
### 完成攻击,输出对抗样本
advimg = adversary.perturb(img, pre_label)
### 展示源图片,对抗扰动,对抗样本以及模型的输出结果
show_images(model_defense, img, advimg)
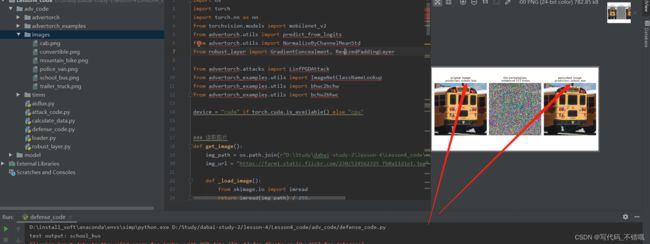
从下图可以看出,原图是school_bus,防御算法也是识别为 school_bus
3. 系统警告
当对抗攻击监测模型,监测到对抗样本或者对抗攻击后。
一般在实际场景的AI项目中,会出现一个告警弹窗,并且会告知安全人员及时进行安全排查。
当然我们此次训练营并没有业务系统,为了更加贴近实际,本次训练营采用一种简单的方式,当然也
比较实用,即通过微信“喵提醒”的方式来实现。在后面的大作业中,我们也会使用到。
3.1 喵喵提醒代码
import requests
import time
# 填写对应的喵码
id = 'xxx' # 这里填自己的ID
# 填写喵提醒中,发送的消息,这里放上前面提到的图片外链
text = "出现对抗攻击风险!!"
ts = str(time.time()) # 时间戳
type = 'json' # 返回内容格式
request_url = "http://miaotixing.com/trigger?"
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.67 Safari/537.36 Edg/87.0.664.47'}
result = requests.post(request_url + "id=" + id + "&text=" + text + "&ts=" + ts + "&type=" + type,
headers=headers)
不过代码中的id,需要填写自己的id id = 'xxx' # 这里填自己的ID
4. 运行效果,
这里我们设置的阈值为0.5,所以提醒了。
4. 收获
本次训练营的学习,让我知道了目标检测+AI安全的算法功能+消息提示的完整流程,也对生活中的一些场景的应用有收获,这里也了解到了AidLux这个软件是非常强大的,可以手机边缘设备进行计算,快速验证整体流程,收获满满。感谢主讲老师Rocky,江大白,AidLux软件。