神经网络优化之学习率
基本概念
在训练神经网络时,需要设置学习率(learning rate)控制参数更新的速度。学习率决定了参数每次更新的幅度,如果幅度过大,那么可能导致参数在极优值的两侧来回移动。相反,当学习率过小时,虽然能保证收敛性,但是这会大大降低优化速度。
通过指数衰减的方法设置梯度下降算法中的学习率,既可以让模型在训练的前期快速接近较优解,又可以保证模型在训练后期不会有太大的波动。Tensorflow提供了tf.train,expoential_decay函数实现了指数衰减学习率。原理如下
decayed_learning_rate =
learning_rate*decay_rate^(global_step / decay_steps)
其中,decayed_learning_rate为每一轮优化时使用的学习率,learning_rate为事先设定的初始学习率,decay_rate为衰减系数,decay_steps为衰减速度。下面函数的输入参数
def exponential_decay(learning_rate,
global_step,
decay_steps,
decay_rate,
staircase=False,
name=None):
使用tf.train.exponential_decay函数。
global_step = tf.Variable(0)
#通过exponential_decay函数生成学习率
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.1, global_step,
100, 0.96, staircase=True)
#反向传播算法应用
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy,
global_step=global_step)
示例演示
通过指数衰减法设置学习率。
import tensorflow as tf
from numpy.random import RandomState
#定义训练数据batch的大小
batch_size = 8
#定义神经网络的参数,随机初始化
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 3], stddev=1, seed=1))
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 1], stddev=1, seed=1))
#在shape上的一个维度上使用None可以方便使用不同的batch大小
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2), name='x-input')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1), name='y-input')
#定义神经网络前向传播的过程
a = tf.matmul(x, w1)
y = tf.matmul(a, w2)
y = tf.sigmoid(y)
#定义损失函数:交叉熵
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_mean(y_ * tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(y, 1e-10, 1.0))
+(1-y_) * tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(1 - y, 1e-10, 1.0)))
global_step = tf.Variable(0)
#通过exponential_decay函数生成学习率
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.1, global_step,
100, 0.96, staircase=True)
#反向传播算法应用
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy,
global_step=global_step)
#通过随机数生成一个数据集
rdm = RandomState(1)
dataset_size = 128
X = rdm.rand(dataset_size, 2)
#认为x1+x2<1的样本都认为是正样本,用0表示负样本,1来表示正样本
Y = [[int(x1+x2 < 1)] for (x1, x2) in X]
with tf.Session() as sess:
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
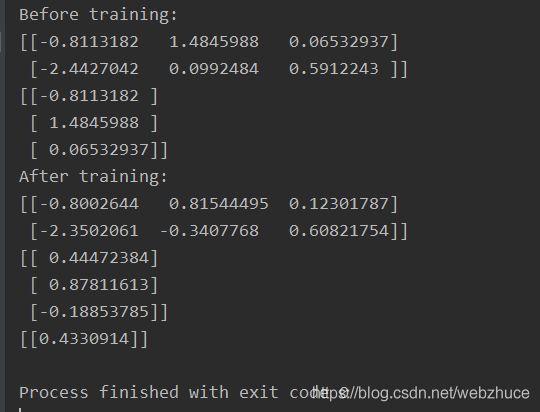
print("Before training:")
print(sess.run(w1))
print(sess.run(w2))
#设定训练的次数
STEPS = 5000
for i in range(STEPS):
#每次选取batch_size个样本进行训练
start = (i * batch_size) % dataset_size
end = min(start + batch_size, dataset_size)
#通过选取的样本训练神经网络并更新参数
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: X[start:end], y_: Y[start:end]})
print("After training:")
print(sess.run(w1))
print(sess.run(w2))
result = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: [[0.5, 0.3]]})
print(result)