Machine Learing HW3
Task:
1使用CNN完成食物分类任务,共11个classes;
2使用数据增强操作;
3使用Residual提高模型性能;
DataSet:
训练集9866 labeled图像; 验证集3430 labeled 图像;测试集:3347图像;
Baseline:
Simple : 0.50099
Medium : 0.73207 Training Augmentation + Train Longer
Strong : 0.81872 Training Augmentation + Model Design + Train Looonger (+ Cross Validation + Ensemble)
Boss : 0.88446 Training Augmentation + Model Design +Test Time Augmentation + Train Looonger (+ Cross Validation + Ensemble)
Simple base:
Sample code,并没有做数据增强,训练没几个epoch就停止了,且模型复杂数据不够,acc如上图;
1基于助教提示,首先优化添加五个数据增强操作;
train_tfm = transforms.Compose([
# Resize the image into a fixed shape (height = width = 128)
# You may add some transforms here.
transforms.RandomResizedCrop((128, 128), scale=(0.7, 1.0)), # 随机截取并resize
# 几何变换
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(0.5),
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(0.5),
transforms.RandomRotation(180),
transforms.RandomAffine(30),
# 像素变换
transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.2),
# ToTensor() should be the last one of the transforms.
transforms.ToTensor(),
])关于数据增强:为了获得更多的数据,我们只要对现有的数据集进行微小的改变。比如旋转(flips)、移位(translations)、旋转(rotations)等微小的改变。我们的网络会认为这是不同的图片。这样就可以丰富我们的数据集;
几何变换类:即对图像进行几何变换,包括翻转,旋转,移位,裁剪,变形,缩放等各类操作。
像素变化类:属于颜色变换类的数据增强了,常见的包括噪声、模糊、颜色变换、擦除、填充等等。
在数据增强过程中,有一个需要注意的问题:在使用增强技术时,我们必须确保不增加不相关的数据。在使用有限的数据来进行模型的训练,因此数据增强操作是不可缺少的一环。
2尝试网络结构:添加dropout层避免过拟合;
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512*4*4, 1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0,25),
nn.Linear(1024, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0,25),
nn.Linear(512, 11)
)3 调整超参:training epochs, patience.
# The number of training epochs and patience.
n_epochs = 50
patience = 8 # If no improvement in 'patience' epochs, early stop第一次优化后,得到的为ACC提高至如图:
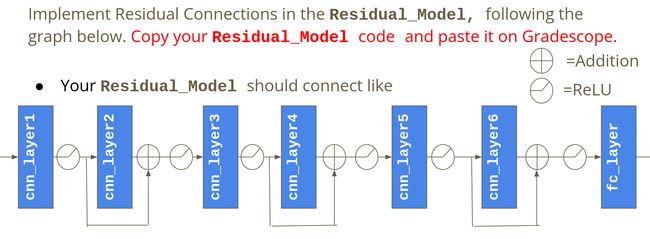
使用Residual Implementation
class Residual_Network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Residual_Network, self).__init__()
self.cnn_layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
)
self.cnn_layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
)
self.cnn_layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
)
self.cnn_layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
)
self.cnn_layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, 2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
)
self.cnn_layer6 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
)
self.fc_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256* 32* 32, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 11)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
# input (x): [batch_size, 3, 128, 128]
# output: [batch_size, 11]
# Extract features by convolutional layers.
x1 = self.cnn_layer1(x)
x1 = self.relu(x1)
x2 = self.cnn_layer2(x1)
x2 = self.relu(x2)
x3 = self.cnn_layer3(x2)
x3 = self.relu(x3)
x4 = self.cnn_layer4(x3)
x4 = self.relu(x4)
x5 = self.cnn_layer5(x4)
x5 = self.relu(x5)
x6 = self.cnn_layer6(x5)
x6 = self.relu(x6)
# The extracted feature map must be flatten before going to fully-connected layers.
xout = x6.flatten(1)
# The features are transformed by fully-connected layers to obtain the final logits.
xout = self.fc_layer(xout)
return xout
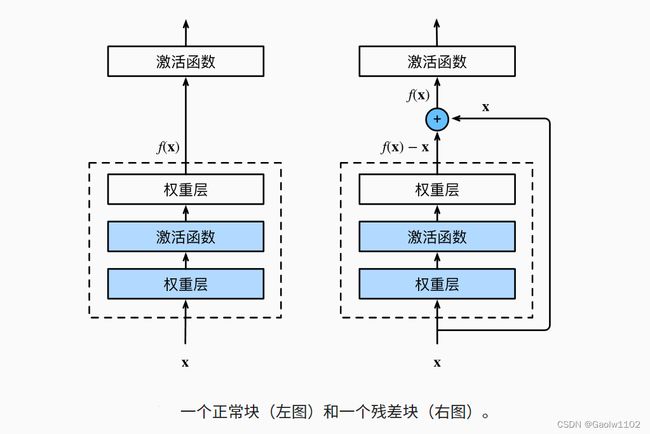
model = Residual_Network().to(device)残差网络最本质公式为:f(x)=g(x)+x
参考链接:LINK,利用残差块(residual blocks)可以训练出一个有效的深层神经网络:输入可以通过层间的残余连接更快地向前传播。
再次增大epochs为100,训练更久;
第二次优化后,得到的为ACC提高至如图: