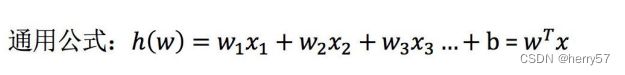线性回归算法
目录
1.概念
2.例子
3.线性回归经常使⽤的两种优化算法
3.0背景(损失函数)
3.1正规⽅程
3.2梯度下降
3.3两个方法对比
4.岭回归
5.模型的保存和加载
1.概念
线性回归(Linear regression)是利⽤回归⽅程(函数)对⼀个或多个⾃变量(特征值)和因变量(⽬标值)之间关系进⾏建模的 ⼀种分析⽅式。
理解为: 1.期末成绩:0.7×考试成绩+0.3×平时成绩
2.房⼦价格 = 0.02×中⼼区域的距离 + 0.04×城市⼀氧化氮浓度 + (-0.12×⾃住房平均房价) + 0.254×城镇犯罪率
2.例子
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
x = [[80, 86],
[82, 80],
[85, 78],
[90, 90],
[86, 82],
[82, 90],
[78, 80],
[92, 94]]
#第一列平均成绩,第二列期末成绩
y = [84.2, 80.6, 80.1, 90, 83.2, 87.6, 79.4, 93.4]
# 实例化API
estimator = LinearRegression()
# 使⽤fit⽅法进⾏训练
estimator.fit(x,y)
prediction=estimator.predict([[100, 80]])
print(prediction)
print(estimator.coef_)3.线性回归经常使⽤的两种优化算法
3.0背景(损失函数)
y 为第i个训练样本的真实值 h(x )为第i个训练样本特征值组合预测函数
⼜称最⼩⼆乘法,求损失函数最小值
3.1正规⽅程
理解:X为特征值矩阵,y为⽬标值矩阵。直接求到最好的结果
缺点:当特征过多过复杂时,求解速度太慢并且得不到结果
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 1.获取数据
data = load_boston()
# 2.数据集划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data.data, data.target, random_state=22) #数据划分默认0.25
# 3.特征⼯程-标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.fit_transform(x_test)
# 4.机器学习-线性回归(正规⽅程)
estimator = LinearRegression()
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5.模型评估
# 5.1 获取系数等值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测值为:\n", y_predict)
print("模型中的系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("模型中的偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 5.2 评价
# 均⽅误差
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("误差为:\n", error)3.2梯度下降
1.α在梯度下降算法中被称作为学习率或者步⻓,意味着我们可以通过α来控制每⼀步⾛的距离,走太快,错过最低点,走太慢,效率慢
2.梯度的⽅向实际就是函数在此点上升最快的 ⽅向!⽽我们需要朝着下降最快的⽅向⾛,⾃然就是负的梯度的⽅向
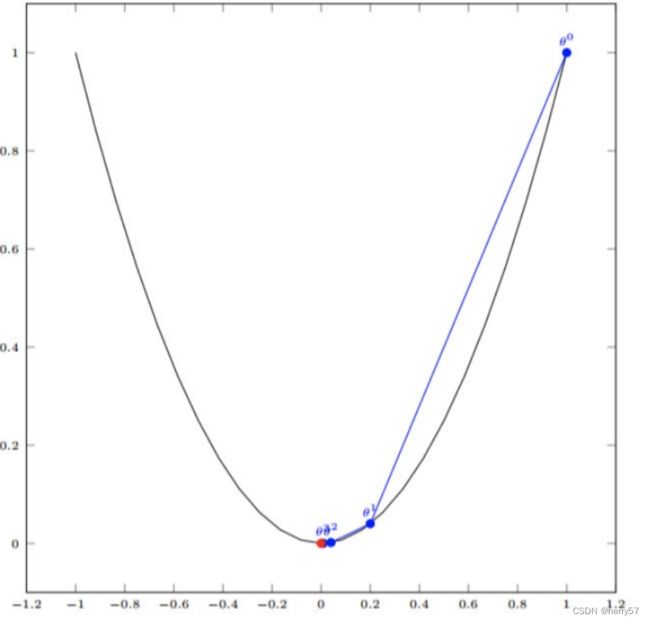
公式步骤演示:我们假设有⼀个单变量的函数 :J(θ) = θ 函数的微分:J (θ) = 2θ 初始化,起点为: θ = 1 学习率:α = 0.4
如图,经过四次的运算,也就是⾛了四步,基本就抵达了函数的最低点,也就是⼭底
3.3两个方法对比
梯度下降法和正规⽅程选择依据
⼩规模数据: 正规⽅程:LinearRegression(不能解决拟合问题)
岭回归
⼤规模数据: 梯度下降法:SGDRegressor
4.岭回归
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge,RidgeCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 1.获取数据
data = load_boston()
# 2.数据集划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data.data, data.target, random_state=22) #数据划分默认0.25
# 3.特征⼯程-标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.fit_transform(x_test)
# 4.机器学习-线性回归(岭回归)
estimator = Ridge(alpha=1) #alpha为正则化
# estimator = RidgeCV(alphas=(0.1, 1, 10))
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5.模型评估
# 5.1 获取系数等值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测值为:\n", y_predict)
print("模型中的系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("模型中的偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 5.2 评价
# 均⽅误差
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("误差为:\n", error)5.模型的保存和加载
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge,RidgeCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
import joblib
# 1.获取数据
data = load_boston()
# 2.数据集划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data.data, data.target, random_state=22) #数据划分默认0.25
# 3.特征⼯程-标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.fit_transform(x_test)
# 4.机器学习-线性回归(岭回归)
# #4.1模型训练
# estimator = Ridge(alpha=1) #alpha为正则化
# # estimator = RidgeCV(alphas=(0.1, 1, 10))
# estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# #4.2模型保存
# joblib.dump(estimator,"./machineLearnCode/LinearRegressionTest/test.pkl")
#4.3模型加载
estimator=joblib.load("./machineLearnCode/LinearRegressionTest/test.pkl")
# 5.模型评估
# 5.1 获取系数等值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测值为:\n", y_predict)
print("模型中的系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("模型中的偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 5.2 评价
# 均⽅误差
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("误差为:\n", error)