分类预测 | MATLAB实现PSO-SVM粒子群算法优化支持向量机多特征分类预测
分类预测 | MATLAB实现PSO-SVM粒子群算法优化支持向量机多特征分类预测
目录
-
- 分类预测 | MATLAB实现PSO-SVM粒子群算法优化支持向量机多特征分类预测
-
- 分类效果
- 基本介绍
- 程序设计
- 参考资料
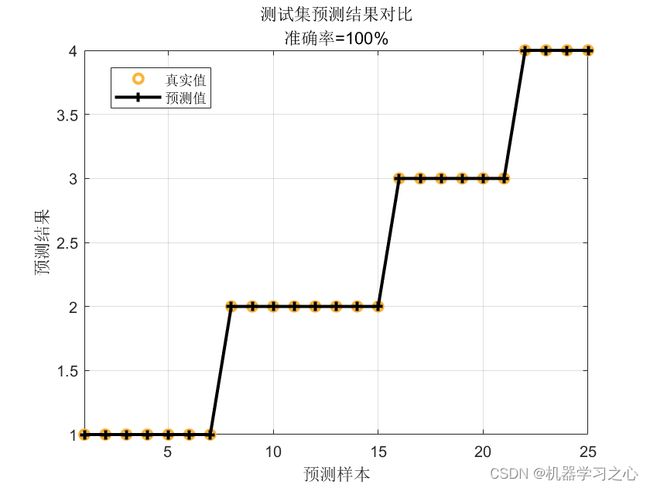
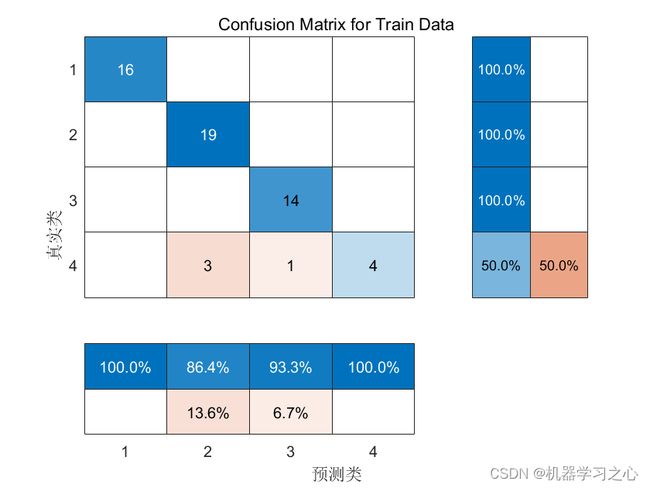
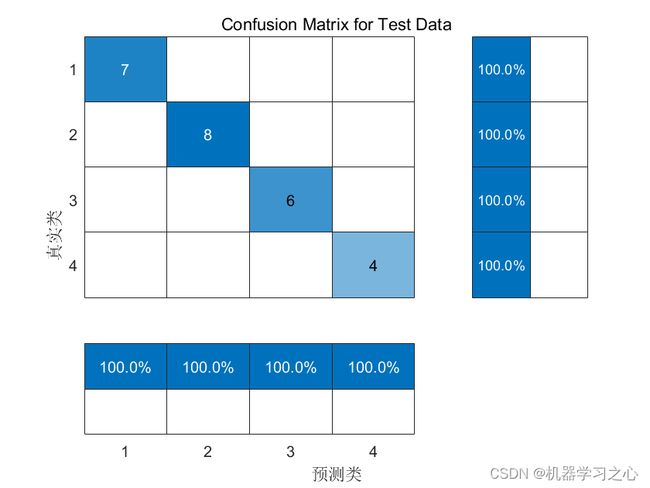
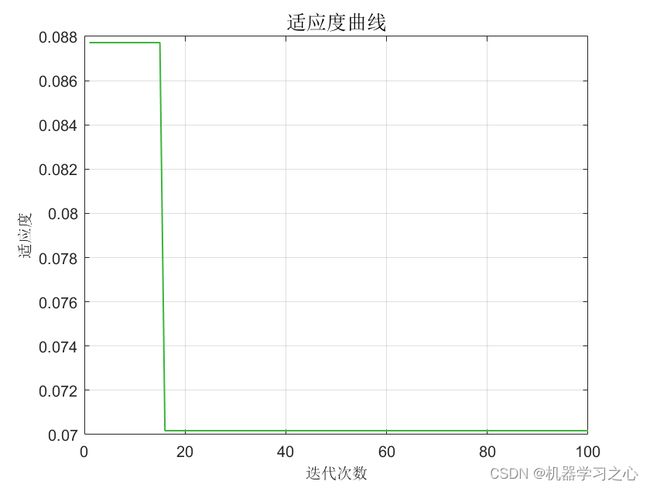
分类效果
基本介绍
MATLAB实现PSO-SVM粒子群算法优化支持向量机多特征分类预测,PSO选择最佳的SVM参数c和g。SVM模型有两个非常重要的参数C与gamma。其中 C是惩罚系数,即对误差的宽容度。c越高,说明越不能容忍出现误差,容易过拟合。C越小,容易欠拟合。C过大或过小,泛化能力变差 。gamma是选择RBF函数作为kernel后,该函数自带的一个参数。隐含地决定了数据映射到新的特征空间后的分布,gamma越大,支持向量越少,gamma值越小,支持向量越多。支持向量的个数影响训练与预测的速度。
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据下载方式1(资源处直接下载):MATLAB实现PSO-SVM粒子群算法优化支持向量机多特征分类预测
- 完整程序和数据下载方式2(订阅《智能学习》专栏,同时获取《智能学习》专栏收录程序6份,数据订阅后私信我获取):MATLAB实现PSO-SVM粒子群算法优化支持向量机多特征分类预测
%% 设置最大速度
Vcmax = pso_option.k * pso_option.popcmax;
Vcmin = -Vcmax ;
Vgmax = pso_option.k * pso_option.popgmax;
Vgmin = -Vgmax ;
%% 误差阈值
eps = 10^(-10);
%% 种群初始化
for i = 1 : pso_option.sizepop
% 随机产生种群和速度
pop(i, 1) = (pso_option.popcmax - pso_option.popcmin) * rand + pso_option.popcmin;
pop(i, 2) = (pso_option.popgmax - pso_option.popgmin) * rand + pso_option.popgmin;
V(i, 1) = Vcmax * rands(1, 1);
V(i, 2) = Vgmax * rands(1, 1);
% 计算初始适应度
cmd = [' -v ', num2str(pso_option.v), ' -c ',num2str(pop(i, 1)), ' -g ', num2str(pop(i, 2))];
fitness(i) = (100 - svmtrain(t_train, p_train, cmd)) / 100;
end
%% 初始化极值和极值点
[global_fitness, bestindex] = min(fitness); % 全局极值
local_fitness = fitness; % 个体极值初始化
global_x = pop(bestindex, :); % 全局极值点
local_x = pop; % 个体极值点初始化
%% 平均适应度
avgfitness_gen = zeros(1, pso_option.maxgen);
%% 迭代寻优
for i = 1 : pso_option.maxgen
for j = 1 : pso_option.sizepop
% 速度更新
V(j, :) = pso_option.wV * V(j, :) + pso_option.c1 * rand * (local_x(j, :) ...
- pop(j, :)) + pso_option.c2 * rand * (global_x - pop(j, :));
if V(j, 1) > Vcmax
V(j, 1) = Vcmax;
end
if V(j, 1) < Vcmin
V(j, 1) = Vcmin;
end
if V(j, 2) > Vgmax
V(j, 2) = Vgmax;
end
if V(j, 2) < Vgmin
V(j, 2) = Vgmin;
end
% 种群更新
pop(j, :) = pop(j, :) + pso_option.wP * V(j, :);
if pop(j, 1) > pso_option.popcmax
pop(j, 1) = pso_option.popcmax;
end
if pop(j, 1) < pso_option.popcmin
pop(j, 1) = pso_option.popcmin;
end
if pop(j, 2) > pso_option.popgmax
pop(j, 2) = pso_option.popgmax;
end
if pop(j, 2) < pso_option.popgmin
pop(j, 2) = pso_option.popgmin;
end
% 自适应粒子变异
if rand > 0.5
k = ceil(2 * rand);
if k == 1
pop(j, k) = (20 - 1) * rand + 1;
end
if k == 2
pop(j, k) = (pso_option.popgmax - pso_option.popgmin) * rand + pso_option.popgmin;
end
end
% 适应度值
cmd = [' -v ', num2str(pso_option.v), ' -c ', num2str(pop(j, 1)), ' -g ', num2str(pop(j, 2))];
fitness(j) = (100 - svmtrain(t_train, p_train, cmd)) / 100;
% 个体最优更新
if fitness(j) < local_fitness(j)
local_x(j, :) = pop(j, :);
local_fitness(j) = fitness(j);
end
if abs(fitness(j)-local_fitness(j)) <= eps && pop(j, 1) < local_x(j, 1)
local_x(j, :) = pop(j, :);
local_fitness(j) = fitness(j);
end
% 群体最优更新
if fitness(j) < global_fitness
global_x = pop(j, :);
global_fitness = fitness(j);
end
if abs(fitness(j) - global_fitness) <= eps && pop(j, 1) < global_x(1)
global_x = pop(j, :);
global_fitness = fitness(j);
end
end
% 平均适应度和最佳适应度
fit_gen(i) = global_fitness;
avgfitness_gen(i) = sum(fitness) / pso_option.sizepop;
end
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128440985?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128368295?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502