强化学习——Sarsa算法
表格型方法——Sarsa
-
- 简介
- 实战
简介
-
Sarsa全称是state-action-reward-state’-action’,目的是学习特定的state下,特定action的价值Q,最终建立和优化一个Q表格,以state为行,action为列,根据与环境交互得到的reward来更新Q表格,更新公式为:
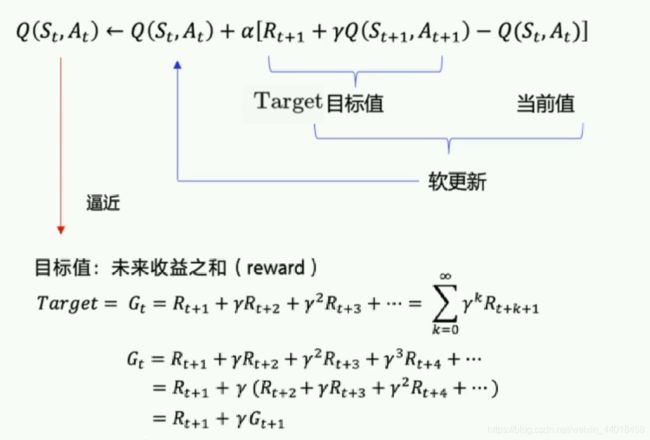
-
Sarsa在训练中为了更好的探索环境,采用ε-greedy方式来训练,有一定概率随机选择动作输出。
实战
- 使用 Sarsa 解决机器人找金币问题。
机器人找金币环境下载
Agent
- Agent是和环境environment交互的主体。
- predict()方法:输入观察值observation(或者说状态state),输出动作值
- sample()方法:再predict()方法基础上使用ε-greedy增加探索
- learn()方法:输入训练数据,完成一轮Q表格的更新
# agent.py
class SarsaAgent(object):
def __init__(self, obs_n, act_n, learning_rate=0.01, gamma=0.9, e_greed=0.1):
self.act_n = act_n # 动作维度,有几个动作可选
self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率
self.gamma = gamma # reward的衰减率
self.epsilon = e_greed # 按一定概率随机选动作
self.Q = np.zeros((obs_n, act_n))
# 根据输入观察值,采样输出的动作值,带探索
def sample(self, obs):
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < (1.0 - self.epsilon): #根据table的Q值选动作
action = self.predict(obs)
else:
action = np.random.choice(self.act_n) #有一定概率随机探索选取一个动作
return action
# 根据输入观察值,预测输出的动作值
def predict(self, obs):
Q_list = self.Q[obs, :]
maxQ = np.max(Q_list)
action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action
action = np.random.choice(action_list)
return action
# 学习方法,也就是更新Q-table的方法
def learn(self, obs, action, reward, next_obs, next_action, done):
""" on-policy
obs: 交互前的obs, s_t
action: 本次交互选择的action, a_t
reward: 本次动作获得的奖励r
next_obs: 本次交互后的obs, s_t+1
next_action: 根据当前Q表格, 针对next_obs会选择的动作, a_t+1
done: episode是否结束
"""
predict_Q = self.Q[obs, action]
if done:
target_Q = reward # 没有下一个状态了
else:
target_Q = reward + self.gamma * self.Q[next_obs, next_action] # Sarsa
self.Q[obs, action] += self.lr * (target_Q - predict_Q) # 修正q
# 保存Q表格数据到文件
def save(self):
npy_file = './q_table.npy'
np.save(npy_file, self.Q)
print(npy_file + ' saved.')
# 从文件中读取Q值到Q表格中
def restore(self, npy_file='./q_table.npy'):
self.Q = np.load(npy_file)
print(npy_file + ' loaded.')
Training && Test(训练&&测试)
- run_episode():agent在一个episode中训练的过程,使用agent.sample()与环境交互,使用agent.learn()训练Q表格。
- test_episode():agent在一个episode中测试效果,评估目前的agent能在一个episode中拿到多少总reward。
def run_episode(env, agent, render=False):
total_steps = 0 # 记录每个episode走了多少step
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset() # 重置环境, 重新开一局(即开始新的一个episode)
action = agent.sample(obs) # 根据算法选择一个动作
while True:
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(env.actions[action]) # 与环境进行一个交互
next_action = agent.sample(next_obs-1) # 根据算法选择一个动作
# 训练 Sarsa 算法
agent.learn(obs-1, action, reward, next_obs-1, next_action, done)
action = next_action
obs = next_obs # 存储上一个观察值
total_reward += reward
total_steps += 1 # 计算step数
if render:
env.render() #渲染新的一帧图形
if done:
break
return total_reward, total_steps
def test_episode(env, agent):
total_reward = 0
obs = env.reset()
while True:
action = agent.predict(obs-1) # greedy
next_obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(env.actions[action])
total_reward += reward
obs = next_obs
time.sleep(0.5)
env.render()
if done:
break
return total_reward
创建环境和Agent,启动训练
env = GridEnv()
agent = SarsaAgent(
obs_n = len(env.states), # 状态维度
act_n = len(env.actions), # 动作维度,有几个动作可选
learning_rate = 0.1, # 学习率
gamma = 0.9, # reward的衰减率
e_greed = 0.1 # 按一定概率随机选动作
)
# 训练500个episode,打印每个episode的分数
for episode in range(500):
ep_reward, ep_steps = run_episode(env, agent, True)
print('Episode %s: steps = %s , reward = %.1f' % (episode, ep_steps, ep_reward))
print("保存权重")
agent.save()
# 全部训练结束,查看算法效果
# agent.restore()
test_reward = test_episode(env, agent)
print('test reward = %.1f' % (test_reward))
env.close()