机器学习sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split函数使用
splitting = train_test_split(*arrays,**options)
如:
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=0, shuffle=False)
| 参数 | 参数说明 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| splitting | X_train | list, length=2 * len(arrays) List, length=2 * len(数组) 包含输入的训练测试分割的列表。 |
划分后的训练数据集X轴 |
| X_test | 划分后的测试数据集X轴 | ||
| y_train | 划分后的训练数据集Y轴 | ||
| y_test | 划分后的测试数据集Y轴 | ||
| *arrays | 例子中的X | sequence of indexables with same length / shape[0] Allowed inputs are lists, numpy arrays, scipy-sparse matrices or pandas dataframes. |
待划分的样本X轴 |
| 例子中的y | 待划分的样本Y轴 | ||
| test_size | float or int, default=None | If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include in the test split. If int, represents the absolute number of test samples. If None, the value is set to the complement of the train size. If ``train_size`` is also None, it will be set to 0.25. |
若在0~1之间,为测试集样本数目与原始样本数目之比;若为整数,则是测试集样本的绝对数量;不设置则默认为0.25 |
| train_size | float or int, default=None | If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include in the train split. If int, represents the absolute number of train samples. If None, the value is automatically set to the complement of the test size. |
若在0~1之间,为训练集样本数目与原始样本数目之比;若为整数,则是训练集样本的绝对数量;不设置则自动设置为0.75 |
| random_state | int, RandomState instance or None, default=None | Controls the shuffling applied to the data before applying the split. 控制在应用分割之前应用于数据的变换。 |
随机数种子,不同的随机数种子划分的结果不同。 |
| stratify | array-like, default=None | If not None, data is split in a stratified fashion, using this as 如果不是None,则以分层的方式分割数据,使用它作为 类标签。 更多信息请参阅:ref: '用户指南 |
stratify是为了保持split前类的分布,例如训练集和测试集数量的比例是 A:B= 4:1,等同于split前的比例(80:20)。通常在这种类分布不平衡的情况下会用到stratify。 |
| shuffle | bool, default=True | Whether or not to shuffle the data before splitting. If shuffle=False then stratify must be None. 是否在分割之前洗牌数据。 如果为 False 那么stratify必须是None。 |
|
Examples
--------
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
>>> X, y = np.arange(10).reshape((5, 2)), range(5)
>>> X
array([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]])
>>> list(y)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
>>> X_train
array([[4, 5],
[0, 1],
[6, 7]])
>>> y_train
[2, 0, 3]
>>> X_test
array([[2, 3],
[8, 9]])
>>> y_test
[1, 4]
>>> train_test_split(y, shuffle=False)
[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4]]
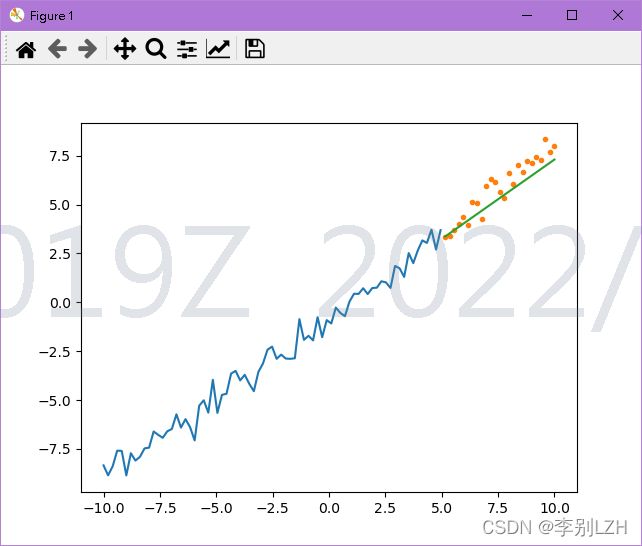
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
a = np.random.seed(0)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
y = 0.85 * x - 0.72
e = np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=0.5, size=x.shape)
y += e
# plt.plot(x, y)
# plt.show()
x = x.reshape(-1, 1)
lr = LinearRegression()
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=0, shuffle=False)
# print(x_train)
# print(x_test)
# print(y_train)
# print(y_test)
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
# print('权重', lr.coef_)
# print('截距', lr.intercept_)
y_hat = lr.predict(x_test)
# print("实际值:", y_test.ravel()[:10])
# print("预测值:", y_hat[:10])
plt.plot(x_train, y_train)
plt.plot(x_test, y_test, '.')
plt.plot(x_test, y_hat)
plt.show()