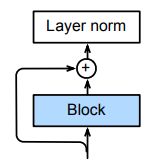
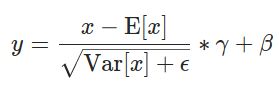批量归一化和层归一化
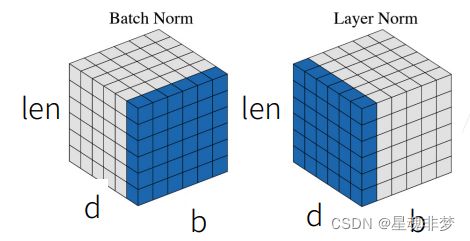
- 批量归一化是对每个特征/通道里的元素进行归一化。(不适合序列长度会变的NLP应用)
- 层归一化是对每个样本里面的元素进行归一化。
ln = nn.LayerNorm(2)
bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(2)
X = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 3]], dtype=torch.float32)
# 在训练模式下计算X的均值和方差
print('layer norm:', ln(X), '\nbatch norm:', bn(X))输出:
layer norm: tensor([[-1.0000, 1.0000],
[-1.0000, 1.0000]], grad_fn=)
batch norm: tensor([[-1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, 1.0000]], grad_fn=)
显然,[1, 2] 为样本1,[2, 3] 为样本2。layer norm对每个样本(2-D 数据里面的行)进行归一化。batch norm则是对每个特征(2-D 数据里面的列)进行归一化。
这里,对NLP任务,b为 batch,d为tokens的维度, len 为序列的长度。所以,由于序列是变长的,所以不适用于Batch Norm。右图的LN 是对当前样本(序列)进行的归一化。
NLP中的LayerNorm
# NLP Example
batch, sentence_length, embedding_dim = 20, 5, 10
embedding = torch.randn(batch, sentence_length, embedding_dim)
layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(embedding_dim)
# Activate module
layer_norm(embedding)这里是:nn.LayerNorm(embedding_dim)。所以是对序列中的每个单词进行的归一化。
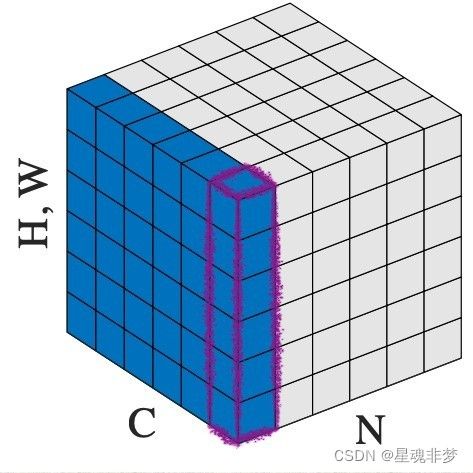
CV 中的LayerNorm
# Image Example
N, C, H, W = 20, 5, 10, 10
input = torch.randn(N, C, H, W)
# Normalize over the last three dimensions (i.e. the channel and spatial dimensions)
# as shown in the image below
layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm([C, H, W])
output = layer_norm(input)这里,红色部分代表一张特征图,C代表有C张特征图。LN是对单个样本的归一化。
LayerNorm公式
不同的Norm的区别, 来自https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.08494.pdf。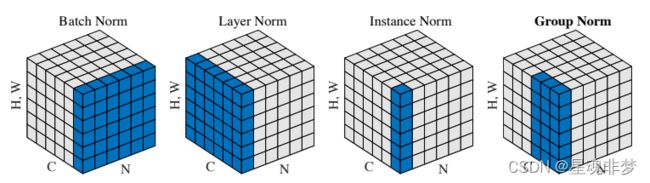
参考:
1. 深入理解NLP中LayerNorm的原理以及LN的代码详解_白马金羁侠少年的博客-CSDN博客_layernorm层
2. 68 Transformer【动手学深度学习v2】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
3. 7.5. 批量规范化 — 动手学深度学习 2.0.0-beta0 documentation
4. LayerNorm — PyTorch 1.10.1 documentation