【Hide-and-Seek】《Hide-and-Seek: A Data Augmentation Technique for Weakly-Supervised Localization xxx》
ICCV-2017
文章目录
- 1 Background and Motivation
- 2 Related Work
- 3 Advantages / Contributions
- 4 Method
- 5 Experiments
-
- 5.1 Datasets and Metrics
- 5.2 Weakly-supervised object localization
- 5.3 Weakly-supervised semantic image segmentation
- 5.4 Weakly-supervised temporal action localization
- 5.5 Image classification
- 5.6 Semantic image segmentation
- 5.7 Face based emotion recognition and age/gender estimation
- 5.8 Person re-identification
- 6 Conclusion(own) / Future work
1 Background and Motivation
弱监督定位任务中,过度关注 most discriminative 特征会导致 localization 不准(tend to focus only on the most discriminative parts, and thus fail to cover the entire spatial extent of an object)

作者提出 Hide-and-Seek 数据增广方法来缓解上述问题
-
hide patches in a training image
-
seek other relevant content when the most discriminative content is hidden
- reduce overfitting
- robust to occlusion
- force to focus on multiple relevant parts of the object beyond just the most discriminative one
2 Related Work
- Data Augmentation
- Masking pixels or activations
- Weakly-supervised object localization
3 Advantages / Contributions
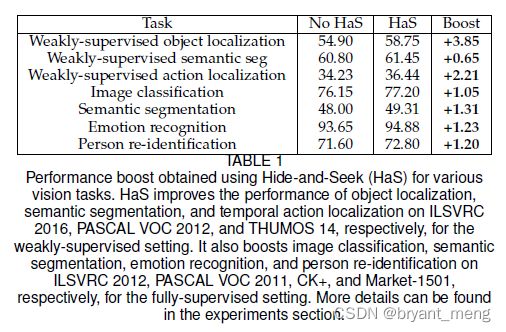
提出 Hide-and-Seek 数据增广方法,该方法在不同网络 / 不同任务上均有不错的表现
4 Method
1)Hide-and-Seek for images
randomly hiding image patches,随机挡住 grid( p h i d e p_{hide} phide probability)
masked during training,测试不挡

上图的展示了 16 patches,也即 4x4 grid
训练挡测试不挡会导致训练和测试的分布不一致(the first convolutional layer activations during training versus testing will have different distributions)
the distribution of w T x w^Tx wTx should be roughly the same during training and testing
哈哈,训练完测试时 w w w 一样,但是 x x x 不一样,分布不一致,怎么破!作者采用 mean pixels of train dataset 来 mask hidden patches,公式分析如下

权重 W = { w 1 , w 2 , . . . , w k × k } W = \{w_1, w_2,...,w_{k\times k}\} W={w1,w2,...,wk×k}, k k k 是 conv kernel size
输入 X = { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x k × k } X = \{x_1, x_2,...,x_{k\times k}\} X={x1,x2,...,xk×k} 是 patches
如图 3 所示
当卷积作用在 inside visible patch 的时候,输出为 ∑ i = 1 k × k w i T x i \sum_{i=1}^{k \times k}w_i^Tx_i ∑i=1k×kwiTxi
当卷积作用在 inside hidden patch 的时候,输出为 ∑ i = 1 k × k w i T v \sum_{i=1}^{k \times k}w_i^Tv ∑i=1k×kwiTv
当卷积作用在 partially in hidden patch 的时候,输出为 ∑ m ∈ v i s i b l e w m T x m + ∑ n ∈ h i d d e n w n T v \sum_{m \in {visible}}w_m^Tx_m + \sum_{n \in {hidden}}w_n^Tv ∑m∈visiblewmTxm+∑n∈hiddenwnTv
v v v as the vector representing the RGB value of every hidden pixel,作者设置为了 the mean RGB vector of the images over the entire dataset
v = μ = 1 N p i x e l s ∑ j x j v = \mu = \frac{1}{N_{pixels}}\sum_jx_j v=μ=Npixels1j∑xj
N p i x e l s N_{pixels} Npixels is the total number of pixels in the dataset
Why would this work? This is because in expectation, the output of a patch will be equal to that of an average-valued patch
E [ ∑ i = 1 k × k w i T x i ] = ∑ i = 1 k × k w i T μ \mathbb{E}[\sum_{i=1}^{k \times k}w_i^Tx_i] = \sum_{i=1}^{k \times k}w_i^T\mu E[i=1∑k×kwiTxi]=i=1∑k×kwiTμ
当 v v v 设置成 μ \mu μ 时
∑ m ∈ v i s i b l e w m T x m + ∑ n ∈ h i d d e n w n T v = ∑ m ∈ v i s i b l e w m T x m + ∑ n ∈ h i d d e n w n T μ ≈ ∑ m ∈ v i s i b l e w m T μ + ∑ n ∈ h i d d e n w n T μ = ∑ i = 1 k × k w i T μ \sum_{m \in {visible}}w_m^Tx_m + \sum_{n \in {hidden}}w_n^Tv = \sum_{m \in {visible}}w_m^Tx_m + \sum_{n \in {hidden}}w_n^T\mu \approx \sum_{m \in {visible}}w_m^T\mu + \sum_{n \in {hidden}}w_n^T\mu = \sum_{i=1}^{k \times k}w_i^T\mu m∈visible∑wmTxm+n∈hidden∑wnTv=m∈visible∑wmTxm+n∈hidden∑wnTμ≈m∈visible∑wmTμ+n∈hidden∑wnTμ=i=1∑k×kwiTμ
Hide and seek 是否会引入噪音?
One may wonder whether Hide-and-Seek introduces any artifacts in the learned convolutional filters due to the sharp transition between a hidden patch and a visible patch

不会太有影响,因为 conv 的 size 比 patch 小得多
Also, the artificially created transitions will not be informative for the task at hand
2)Object localization network architecture
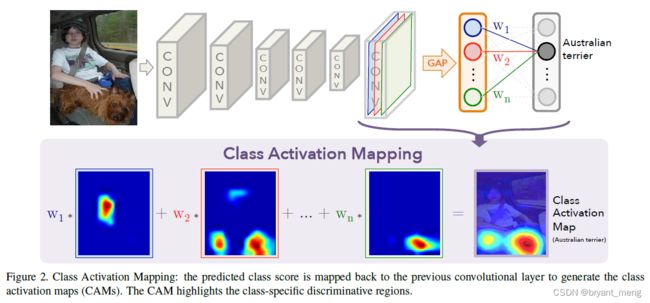
可以用任何结构,作者方便热力图分析采用的时 CAM 方法的基本结构
3)Hide-and-Seek for videos
hiding patches in images
hide frames in videos(random frame sequences are hidden),learn the relevant frames corresponding to an action
5 Experiments
5.1 Datasets and Metrics
ILSVRC 2016 for Weakly-supervised object localization
- Top-1 Loc:要与 GT 的 IoU > 50%
- GT-known Loc:fraction of images for which the predicted bounding box for the ground-truth class has more than 50% IoU with the ground-truth box
PASCAL VOC 2012 for Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation
- mIoU
THUMOS 2014 validation data for Weakly-supervised temporal action localization
- mAP,IoU > θ \theta θ with ground-truth
CIFAR-10 / CIFAR-100/ large-scale ILSVRC for Image Classification
- Top-1 acc
PASCAL 2011 for full-supervised semantic segmentation
- mIoU
Cohn-Kanade database (CK+) for Emotion recognition
- acc
APPA-REAL / IMDB-WIKI for age estimation
- MAE
UTKFace / IMDB-WIKI for gender estimation
- acc
DukeMTMC-reID and Market-1501 for ReID
- rank-1 accuracy and mAP
ps:Market-1501 was collected during summer whereas DukeMTMCreID was created during winter
5.2 Weakly-supervised object localization
1)Quantitative object localization results

GAP 是 global average pooling 的意思
HaS-16 表示 patch 的大小为 16x16
mixed 表示 chosen randomly from 16, 32, 44 and 56 as well as no hiding
2)Comparison to alternate localization methods
和其他的 weakly-supervised object location 比比看

dropout-traintest 表示 train 和 test 的时候都 drop
3)Qualitative object localization results
来看看 HaS 的效果
绿框是预测的结果,红框是 GT,这个图真的是太给力了,直抒胸臆!
同样的,作者也展示了失败案例,填坑的 C 位都标记出来了,哈哈哈,等你下一篇来 battle

第一行 lab coat 的 GT 好像有的偏差,第一行和第二行的这种预测方式,我觉得也没有毛病
第三行 HaS 会把篱笆挡住了,学成了房子,至少联动的能力给你整出来了,哈哈哈
最后一行,倒影
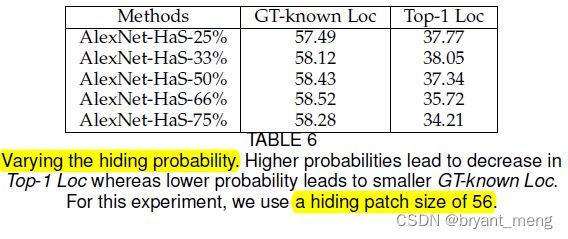
4)Further Analysis of Hide-and-Seek
<1> Do we need global average pooling?
但配合 HaS 逆袭了,likely due to max pooling being more robust to noise
<2> Hide-and-Seek in convolutional layers

patch 大小分别为 5x5 和 11x11,效果也不错的
5.3 Weakly-supervised semantic image segmentation
on the PASCAL 2012 val dataset improves from 60.80 to 61.45 (mean IU).
mean IU 也就是 mIoU,比较草率,没有表格,就一句话
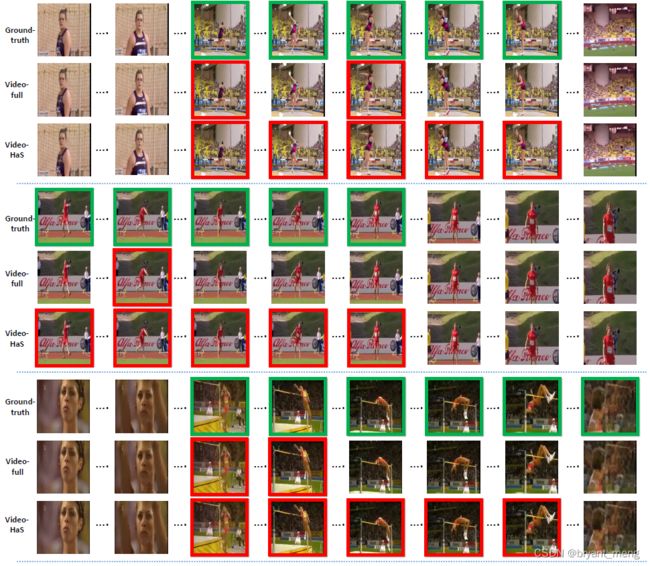
5.4 Weakly-supervised temporal action localization

hiding frames forces the network to focus on more relevant frames, which ultimately leads to better action localization.
看看预测的效果
第二个 javelin throw
第三个 high jump
最后一个 diving action,展示了 HaS 失败的例子,跳水人被 mask 掉了,学到了 pool
5.5 Image classification

tend to capture information about all relevant parts
complementary to existing data augmentation techniques
这就是 HaS 的魅力吗?
下面看看例子

标黄的图片,主要特征(头部)被挡住了,也能正确的预测出来
5.6 Semantic image segmentation
5.7 Face based emotion recognition and age/gender estimation
这里作者强调相对其他数据增广的方法(random flipping and random cropping), Hide-and-Seek brings an additional advantage to these tasks——没有 break the spatial alignment of pixels across the augmented samples,相当于没有改变人脸关键点的坐标位置
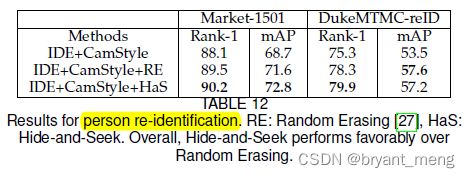
5.8 Person re-identification
这里观察到,在 DukeMTMC-reID 数据集上 Has 的效果没有 ES 好,作者的解释是
Market-1501 was collected during summer whereas DukeMTMC-reID was created during winter
DukeMTMC-reID 数据集本身遮挡的比较多,削弱了数据增广的能力
6 Conclusion(own) / Future work
1)code:https://github.com/kkanshul/Hide-and-Seek
2)the patch sizes and hiding probabilities are hyperparameters,未来可以 learn during training
3)动作检测方法比较 Temporal Action Localization Comparison
动作检测, Temporal Action Localization (= Action Detection + Classification) , 指的是针对较长一段视频(包含感兴趣的动作和不感兴趣的动作),找出其中感兴趣动作对应的视频片段(起始帧/结束帧),再对找出来的这一个动作进行分类。也就是说,这个任务包含了两个子任务,1是找到感兴趣的视频片段,2 是对其分类。
can predict the label of an action as well as its start and end time for a test video.
4)与 random erasing 对比:
a more generalized form of Random Erasing,hidden patches can also form a single continuous rectangle patch(albeit with very low probability).
provide more variations in the types of occlusions
5)《Object region mining with adversarial erasing: A simple classification to semantic segmentation approach》(CVPR-2017)
弱监督做分割
Hide-and-Seek:In contrast, we only train a single model once—and is thus less expensive—and do not rely on saliency detection to refine the localizations.
6)attribute localization
《Fashionpedia: Ontology, Segmentation, and an Attribute Localization Dataset》(ECCV-2020)
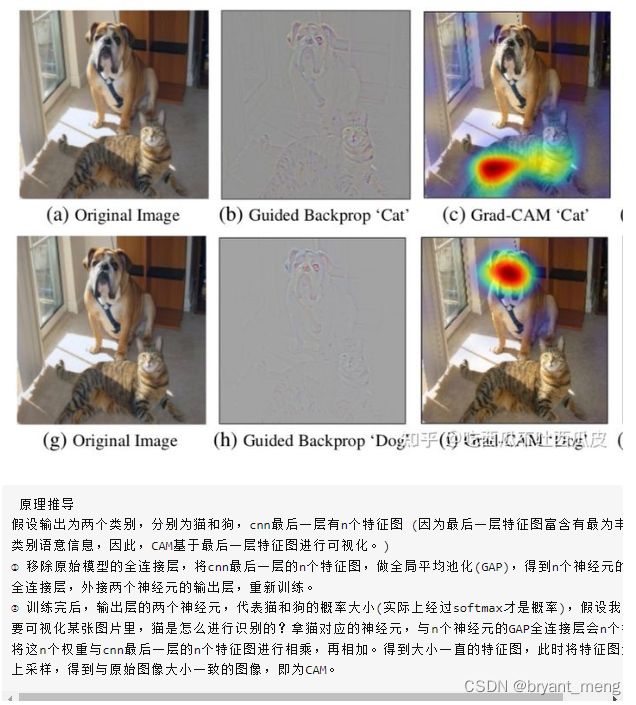
7)CAM
《Learning deep features for discriminative localization》(CVPR-2016)
8)《Discovering Class-Specific Pixels for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation》(arXiv-2017)
DCSP combines saliency and CAM to obtain a pseudo ground-truth label map to train the network for semantic segmentation
Saliency Maps的原理与简单实现(使用Pytorch实现)
9)摘抄些其他的论文解读
ICCV 2017: Hide-and-Seek 一种数据扩增Trick