“深度学习”学习日记。神经网络的学习。--学习算法的实现
2023.1.13 愿望世界没有新冠,复阳的感觉真的难受
这一段时间学习了 “损失函数”、“mini-batch”、“梯度”、“梯度下降法”,今天通过他们取实现神经网络学习算法的实现,做一次总结。
实现的思路(“学习”的步骤):
一,前提
神经网络的“学习”是,在存在合适的权重和偏置下,对其调整以拟合训练数据的过程。
步骤1: 我们从训练数据中随机选取一部分数据(mini-batch),目的是减小其损失函数的值。
步骤2: 为了完成步骤1,需要求出各个权重参数的梯度,寻找mini-batch的损失函数的值减少最多的方向。
步骤3: 进行权重参数沿梯度的微小更新。
步骤4: 重复步骤1,2,3
这样的四个步骤也被称为随机梯度下降法 ,意思是对随机选择的数据进行梯度下降法法寻找最小值。一般有一个SGD的函数去实现
利用MNIST数据集去进行一个两层(输入层、隐藏层、输出层)的神经网络学习的实现:
import sys, os
import numpy as np
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
def numerical_gradient(f, x):
h = 1e-4 # 0.0001
grad = np.zeros_like(x)
it = np.nditer(x, flags=['multi_index'], op_flags=['readwrite']) # np.nditer() 迭代器处理多维数组
while not it.finished:
idx = it.multi_index
tmp_val = x[idx]
x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + h
fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)
x[idx] = tmp_val - h
fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)
grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2 * h)
x[idx] = tmp_val # 还原值
it.iternext()
return grad
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x.T
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x)
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
delta = 1e-7
return -1 * np.sum(t * np.log(y + delta))
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input, hidden, output, weight__init__std=0.01):
# 权重的初始化 假设一个权重
self.params = {}
self.params['w1'] = weight__init__std * np.random.randn(input, hidden)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden)
self.params['w2'] = weight__init__std * np.random.randn(hidden, output)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output)
def predict(self, x):
w1, w2 = self.params['w1'], self.params['w2']
b1, b2 = self.params['b1'], self.params['b2']
a1 = np.dot(x, w1) + b1
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(z1, w2) + b2
y = softmax(a2)
return y
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return cross_entropy_error(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1) # 正确解标签
t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0])
return accuracy
def numerical_grandient(self, x, t):
loss_w = lambda w: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
grads['w1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['w1'])
grads['b1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['b1'])
grads['w2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['w2'])
grads['b2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['b2'])
return grads
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True)
train_loss_list = []
iters_num = 10000
train_size = x_train.shape[0] # 60000
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.1
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1)
networks = TwoLayerNet(input=784, hidden=50, output=10)
for i in range(iters_num):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
grad = networks.numerical_grandient(x_batch, t_batch)
for key in ('w1', 'b1', 'w2', 'b2'):
networks.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key]
loss = networks.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
if i % iter_per_epoch == 0:
train_acc = networks.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
test_acc = networks.accuracy(x_test, t_test)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
print("train acc, test acc |" + str(train_acc) + ",", str(test_acc))神经网络学习的最初目的是掌握泛化能力,所以要评价神经网络的泛化能力,就必须不能包含训练集中的数据。必须确认是否能正确识别训练集以外的其它数据(是否发生过拟合)。
过拟合现象:虽然训练集的数据被正确识别,但是无法识别不在训练集之外的数据的现象
代码在学习的过程中,应该要定期自动地记录识别精度。所以我们引入一个epoch单位,一个epoch表示学习中所有训练集均被用来使用过一次数据更新。在以上代码60000个训练数据,会先将数据打乱,按指定批次大小,按序生成mini-batch,每个mini-batch均有一个索引号,用大小为mini-batch的数据作为学习时,遍历一次所有的数据,就称为一个epoch。
以上代码是利用数值微分法计算参数的梯度,这方法耗时长。所以我们利用一种名为误差反向传播法 高效率计算梯度,具体原理在以后的学习。
import sys, os
import numpy as np
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
def numerical_gradient(f, x):
h = 1e-4 # 0.0001
grad = np.zeros_like(x)
it = np.nditer(x, flags=['multi_index'], op_flags=['readwrite']) # np.nditer() 迭代器处理多维数组
while not it.finished:
idx = it.multi_index
tmp_val = x[idx]
x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + h
fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)
x[idx] = tmp_val - h
fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)
grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2 * h)
x[idx] = tmp_val # 还原值
it.iternext()
return grad
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x.T
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x)
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
delta = 1e-7
return -1 * np.sum(t * np.log(y + delta))
def sigmoid_grad(x):
return (1.0 - sigmoid(x)) * sigmoid(x)
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input, hidden, output, weight__init__std=0.01):
# 权重的初始化 假设一个权重
self.params = {}
self.params['w1'] = weight__init__std * np.random.randn(input, hidden)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden)
self.params['w2'] = weight__init__std * np.random.randn(hidden, output)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output)
def predict(self, x):
w1, w2 = self.params['w1'], self.params['w2']
b1, b2 = self.params['b1'], self.params['b2']
a1 = np.dot(x, w1) + b1
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(z1, w2) + b2
y = softmax(a2)
return y
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return cross_entropy_error(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1) # 正确解标签
t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0])
return accuracy
def numerical_grandient(self, x, t):
loss_w = lambda w: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
grads['w1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['w1'])
grads['b1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['b1'])
grads['w2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['w2'])
grads['b2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['b2'])
return grads
def gradient(self, x, t):
w1, w2 = self.params['w1'], self.params['w2']
b1, b2 = self.params['b1'], self.params['b2']
grads = {}
batch_num = x.shape[0]
# forward
a1 = np.dot(x, w1) + b1
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(z1, w2) + b2
y = softmax(a2)
# backward
dy = (y - t) / batch_num
grads['w2'] = np.dot(z1.T, dy)
grads['b2'] = np.sum(dy, axis=0)
da1 = np.dot(dy, w2.T)
dz1 = sigmoid_grad(a1) * da1
grads['w1'] = np.dot(x.T, dz1)
grads['b1'] = np.sum(dz1, axis=0)
return grads
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True)
train_loss_list = []
iters_num = 10000
train_size = x_train.shape[0] # 60000
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.1
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1)
networks = TwoLayerNet(input=784, hidden=50, output=10)
for i in range(iters_num):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
# grad = networks.numerical_grandient(x_batch, t_batch)
grad = networks.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
for key in ('w1', 'b1', 'w2', 'b2'):
networks.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key]
loss = networks.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
if i % iter_per_epoch == 0:
train_acc = networks.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
test_acc = networks.accuracy(x_test, t_test)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
print("train acc, test acc |" + str(train_acc) + ",", str(test_acc))
markers = {'train': 'o', 'test': 's'}
x = np.arange(len(train_acc_list))
plt.plot(x, train_acc_list, label='train acc')
plt.plot(x, test_acc_list, label='test acc', linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel("epochs")
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
plt.ylim(0, 1.0)
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
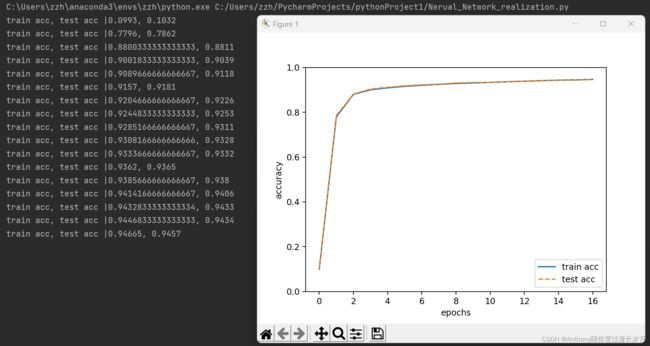
plt.show()这样没经过一个epoch就能对所有的训练数据和测试数据计算识别别精度。我们也可以通过图表从大方向上把握识别精度:
随着epoch的进行,可以看出使用训练数据或者测试数据的识别精度都提高了,而且,这两个精度基本上没有太大差异,呈现基本重叠的现象,说明神经网络的这次学习没有法伤过拟合现象
参考MINIST数据集的导入代码:
# coding: utf-8
try:
import urllib.request
except ImportError:
raise ImportError('You should use Python 3.x')
import os.path
import gzip
import pickle
import os
import numpy as np
url_base = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
key_file = {
'train_img':'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'train_label':'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
'test_img':'t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'test_label':'t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
}
dataset_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
save_file = dataset_dir + "/mnist.pkl"
train_num = 60000
test_num = 10000
img_dim = (1, 28, 28)
img_size = 784
def _download(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
if os.path.exists(file_path):
return
print("Downloading " + file_name + " ... ")
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url_base + file_name, file_path)
print("Done")
def download_mnist():
for v in key_file.values():
_download(v)
def _load_label(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
labels = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
print("Done")
return labels
def _load_img(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
data = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16)
data = data.reshape(-1, img_size)
print("Done")
return data
def _convert_numpy():
dataset = {}
dataset['train_img'] = _load_img(key_file['train_img'])
dataset['train_label'] = _load_label(key_file['train_label'])
dataset['test_img'] = _load_img(key_file['test_img'])
dataset['test_label'] = _load_label(key_file['test_label'])
return dataset
def init_mnist():
download_mnist()
dataset = _convert_numpy()
print("Creating pickle file ...")
with open(save_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(dataset, f, -1)
print("Done!")
def _change_one_hot_label(X):
T = np.zeros((X.size, 10))
for idx, row in enumerate(T):
row[X[idx]] = 1
return T
def load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False):
"""读入MNIST数据集
Parameters
----------
normalize : 将图像的像素值正规化为0.0~1.0
one_hot_label :
one_hot_label为True的情况下,标签作为one-hot数组返回
one-hot数组是指[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]这样的数组
flatten : 是否将图像展开为一维数组
Returns
-------
(训练图像, 训练标签), (测试图像, 测试标签)
"""
if not os.path.exists(save_file):
init_mnist()
with open(save_file, 'rb') as f:
dataset = pickle.load(f)
if normalize:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].astype(np.float32)
dataset[key] /= 255.0
if one_hot_label:
dataset['train_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['train_label'])
dataset['test_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['test_label'])
if not flatten:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28)
return (dataset['train_img'], dataset['train_label']), (dataset['test_img'], dataset['test_label'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
init_mnist()