动手学深度学习 第二章练习(Pytorch版)
记录一下学习《动手学深度学习》的过程中完成的课后练习以及自己整理的课程相关知识点,部分内容有参考课程讨论区和网上一些大佬的解答。如有错误欢迎指教!
文章目录
- 2. 预备知识
-
- 2.1 数据操作
-
- 小结
- 课后练习
- 2.2 数据预处理
-
- 小结
- 课后练习
- 2.3 线性代数
-
- 小结
- 课后练习
- 2.4 微积分
-
- 小结
- 课后练习
- 2.5 自动微分
-
- 小结
- 课后练习
- 2.6 概率
-
- 小结
- 课后练习
2. 预备知识
2.1 数据操作
小结
- 深度学习存储和操作数据的主要接口是张量( n n n维数组)。它提供了各种功能,包括基本数学运算、广播、索引、切片、内存节省和转换其他Python对象。
课后练习
- 运行本节中的代码。将本节中的条件语句 X == Y 更改为 X < Y 或 X > Y,然后看看你可以得到什么样的张量。
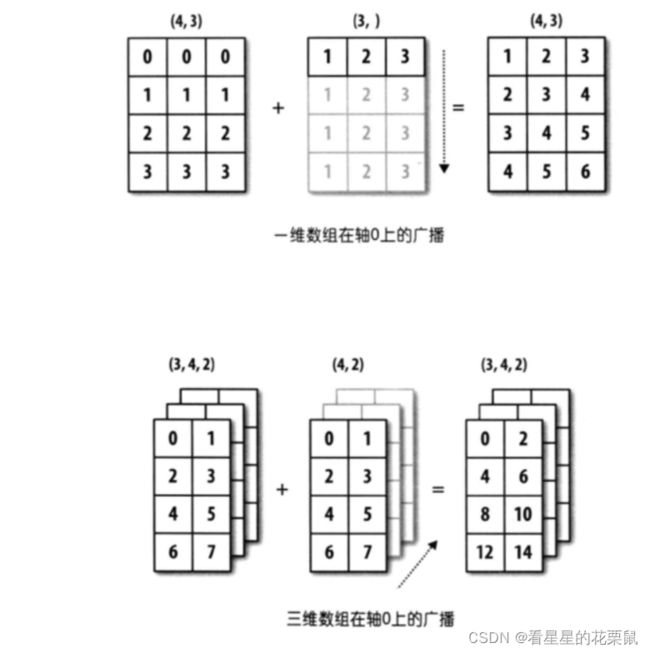
- 用其他形状(例如三维张量)替换广播机制中按元素操作的两个张量。结果是否与预期相同?
import torch
import d2l
import numpy as np
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2, 4, 8])
y = torch.tensor([2, 2, 2, 2])
print('x > y',x > y,'\nx < y',x < y,'\nx == y',x == y)
运行结果:
x > y tensor([False, False, True, True])
x < y tensor([ True, False, False, False])
x == y tensor([False, True, False, False])
广播
广播主要发生在两种情况,一种是两个数组的维数不相等,但是它们的后缘维度的轴长相符,另外一种是有一方的长度为1。
- 有一方的长度为1
a = torch.arange(12).reshape((3, 4))
b = torch.arange(4).reshape((1, 4))
a+b
运行结果:
tensor([[ 0, 2, 4, 6],
[ 4, 6, 8, 10],
[ 8, 10, 12, 14]])
- 后缘维度的轴长相符
a = torch.arange(6).reshape((3, 1, 2))
b = torch.arange(2).reshape((1, 2))
a+b
运行结果;
tensor([[[0, 2]],
[[2, 4]],
[[4, 6]]])
2.2 数据预处理
小结
pandas软件包是Python中常用的数据分析工具中,pandas可以与张量兼容。- 用
pandas处理缺失的数据时,我们可根据情况选择用插值法和删除法。
课后练习
创建包含更多行和列的原始数据集。
- 删除缺失值最多的列。
- 将预处理后的数据集转换为张量格式。
import torch
import os
import pandas as pd
os.makedirs(os.path.join('..', 'data/test_data'), exist_ok=True)
data_file = os.path.join('..', 'data/test_data', 'homework_data.csv')
with open(data_file, 'w') as f:
f.write('NumRooms,Alley,Year,Area,Price\n') # 列名
f.write('NA,Pave,3,200,127500\n') # 每行表示一个数据样本
f.write('2,Pave,5,150,106000\n')
f.write('4,Pave,2,200,178100\n')
f.write('NA,NA,1,NA,140000\n') # 直接向csv写入数据
data = pd.read_csv(data_file)
print(data)
NumRooms Alley Year Area Price
0 NaN Pave 3 200.0 127500
1 2.0 Pave 5 150.0 106000
2 4.0 Pave 2 200.0 178100
3 NaN NaN 1 NaN 140000
删除缺失值最多的列:
na_sum = data.isnull().sum()
na_sum_max = na_sum.idxmax()
data.drop(na_sum_max, axis = 1, inplace = True)
print(data)
Alley Year Area Price
0 Pave 3 200.0 127500
1 Pave 5 150.0 106000
2 Pave 2 200.0 178100
3 NaN 1 NaN 140000
缺失值处理
插值法:
data1 = data
X,y = data1.iloc[:,0:3], data1.iloc[:,3]
X1 = X.fillna(round(X.mean(),1)) # 处理数值型变量
X1 = pd.get_dummies(X1, dummy_na=True)
print(X1)
Year Area Alley_Pave Alley_nan
0 3 200.0 1 0
1 5 150.0 1 0
2 2 200.0 1 0
3 1 183.3 0 1
# 转换为张量
X_tensor, y_tensor = torch.tensor(X1.values), torch.tensor(y)
X_tensor, y_tensor
(tensor([[ 3.0000, 200.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000],
[ 5.0000, 150.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000],
[ 2.0000, 200.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000],
[ 1.0000, 183.3000, 0.0000, 1.0000]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([127500, 106000, 178100, 140000]))
删除法:
data2 = data.dropna()
X2,y2 = data2.iloc[:,0:3], data2.iloc[:,3]
X2 = pd.get_dummies(X2)
X_tensor2, y_tensor2 = torch.tensor(X2.values), torch.tensor(y2)
X_tensor2, y_tensor2
(tensor([[ 3., 200., 1.],
[ 5., 150., 1.],
[ 2., 200., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64),
tensor([127500, 106000, 178100]))
2.3 线性代数
小结
- 标量、向量、矩阵和张量是线性代数中的基本数学对象。
- 向量泛化自标量,矩阵泛化自向量。
- 标量、向量、矩阵和张量分别具有零、一、二和任意数量的轴。
- 一个张量可以通过
sum和mean沿指定的轴降低维度。 - 两个矩阵的按元素乘法被称为他们的Hadamard积。它与矩阵乘法不同。
- 在深度学习中,我们经常使用范数,如 L 1 L_1 L1范数、 L 2 L_2 L2范数和Frobenius范数。
- 我们可以对标量、向量、矩阵和张量执行各种操作。
课后练习
- 证明一个矩阵 A \mathbf{A} A的转置的转置是 A \mathbf{A} A,即 ( A ⊤ ) ⊤ = A (\mathbf{A}^\top)^\top = \mathbf{A} (A⊤)⊤=A。
- 给出两个矩阵 A \mathbf{A} A和 B \mathbf{B} B,证明“它们转置的和”等于“它们和的转置”,即 A ⊤ + B ⊤ = ( A + B ) ⊤ \mathbf{A}^\top + \mathbf{B}^\top = (\mathbf{A} + \mathbf{B})^\top A⊤+B⊤=(A+B)⊤。
- 给定任意方阵 A \mathbf{A} A, A + A ⊤ \mathbf{A} + \mathbf{A}^\top A+A⊤总是对称的吗?为什么?
- 我们在本节中定义了形状 ( 2 , 3 , 4 ) (2,3,4) (2,3,4)的张量
X。len(X)的输出结果是什么? - 对于任意形状的张量
X,len(X)是否总是对应于X特定轴的长度?这个轴是什么? - 运行
A/A.sum(axis=1),看看会发生什么。你能分析原因吗? - 考虑一个具有形状 ( 2 , 3 , 4 ) (2,3,4) (2,3,4)的张量,在轴0、1、2上的求和输出是什么形状?
- 为
linalg.norm函数提供3个或更多轴的张量,并观察其输出。对于任意形状的张量这个函数计算得到什么?
1 .
import torch
A = torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
B = A.T
print(A == B.T)
[[ True True True]
[ True True True]]
2 .
B = torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[1,2,3]])
print((A+B).T)
print(A.T + B.T)
print((A+B).T == A.T + B.T)
tensor([[ 8, 5],
[10, 7],
[12, 9]])
tensor([[ 8, 5],
[10, 7],
[12, 9]])
tensor([[True, True],
[True, True],
[True, True]])
3 .
C = torch.randn(3,3)
print(C + C.T)
print((C+C.T) == (C+C.T).T)
tensor([[ 4.4318, 3.8084, -1.6643],
[ 3.8084, -2.1554, -0.9012],
[-1.6643, -0.9012, -1.4590]])
tensor([[True, True, True],
[True, True, True],
[True, True, True]])
4 .
X = torch.ones(2,3,4, dtype = torch.float32)
len(X)
2
5 . 会显示在0轴的长度
6 .
# A/A.sum(axis = 1) #报错
A/A.sum(axis = 1, keepdims = True)
tensor([[0.1667, 0.3333, 0.5000],
[0.2667, 0.3333, 0.4000]])
A为方阵时不会报错。维度不同,无法相除,也无法广播。最好不要使用向量,而是将其reshape为n行1列的矩阵,更不容易出问题。
7 .
print(X.sum(axis = 0).shape)
print(X.sum(axis = 1).shape)
print(X.sum(axis = 2).shape)
torch.Size([3, 4])
torch.Size([2, 4])
torch.Size([2, 3])
8 .
torch.linalg.norm(X) # L2范数
tensor(4.8990)
2.4 微积分
小结
- 微分和积分是微积分的两个分支,前者可以应用于深度学习中的优化问题。
- 导数可以被解释为函数相对于其变量的瞬时变化率,它也是函数曲线的切线的斜率。
- 梯度是一个向量,其分量是多变量函数相对于其所有变量的偏导数。
- 链式法则使我们能够微分复合函数。
课后练习
- 绘制函数 y = f ( x ) = x 3 − 1 x y = f(x) = x^3 - \frac{1}{x} y=f(x)=x3−x1和其在 x = 1 x = 1 x=1处切线的图像。
- 求函数 f ( x ) = 3 x 1 2 + 5 e x 2 f(\mathbf{x}) = 3x_1^2 + 5e^{x_2} f(x)=3x12+5ex2的梯度。
- 函数 f ( x ) = ∥ x ∥ 2 f(\mathbf{x}) = \|\mathbf{x}\|_2 f(x)=∥x∥2的梯度是什么?
- 你可以写出函数 u = f ( x , y , z ) u = f(x, y, z) u=f(x,y,z),其中 x = x ( a , b ) x = x(a, b) x=x(a,b), y = y ( a , b ) y = y(a, b) y=y(a,b), z = z ( a , b ) z = z(a, b) z=z(a,b)的链式法则吗?
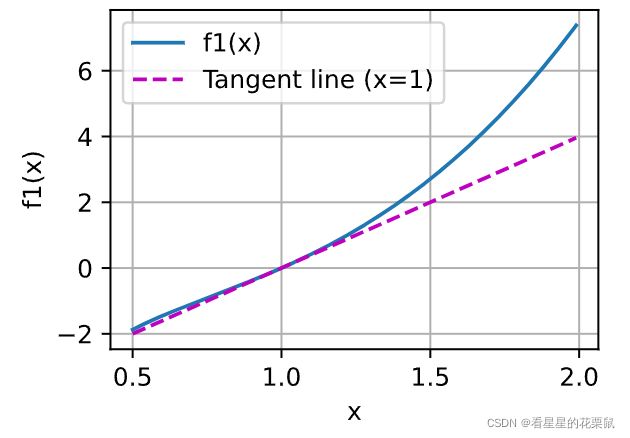
#1
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
from d2l import torch as d2l
def f1(x):
return x**3 - x**(-1)
x = np.arange(0.5, 2, 0.01)
d2l.plot(x, [f1(x), 4*x - 4], 'x', 'f1(x)', legend=['f1(x)', 'Tangent line (x=1)'])
2. f ′ ( x 1 ) = 6 x 1 , f ′ ( x 2 ) = 5 e x 2 , ▽ f ( x ) = [ 6 x 1 , 5 e x 2 ] f'(x_1) = 6 x_1, f'(x_2) = 5e^{x_2} , ▽f(x) = [6x_1, 5e^{x_2}] f′(x1)=6x1,f′(x2)=5ex2,▽f(x)=[6x1,5ex2]
3 .
∂ f ( x ) ∂ x = ∂ ∥ x ∥ 2 ∂ x = x x 2 = x ∥ x ∥ 2 \frac{\partial f(x)}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial\|x\|_{2}}{\partial x}=\frac{x}{\sqrt{x^{2}}}=\frac{x}{\|x\|_{2}} ∂x∂f(x)=∂x∂∥x∥2=x2x=∥x∥2x
4.
d u d a = d u d x d x d a + d u d y d y d a + d u d z d z d a \frac{du}{da} = \frac{du}{dx} \frac{dx}{da} + \frac{du}{dy} \frac{dy}{da} + \frac{du}{dz} \frac{dz}{da} dadu=dxdudadx+dydudady+dzdudadz
d u d b = d u d b d x d b + d u d b d y d b + d u d z d z d b \frac{du}{db} = \frac{du}{db} \frac{dx}{db} + \frac{du}{db} \frac{dy}{db} + \frac{du}{dz} \frac{dz}{db} dbdu=dbdudbdx+dbdudbdy+dzdudbdz
2.5 自动微分
小结
- 深度学习框架可以自动计算导数:我们首先将梯度附加到想要对其计算偏导数的变量上。然后我们记录目标值的计算,执行它的反向传播函数,并访问得到的梯度。
课后练习
- 为什么计算二阶导数比一阶导数的开销要更大?
- 在运行反向传播函数之后,立即再次运行它,看看会发生什么。
- 在控制流的例子中,我们计算
d关于a的导数,如果我们将变量a更改为随机向量或矩阵,会发生什么? - 重新设计一个求控制流梯度的例子,运行并分析结果。
- 使 f ( x ) = sin ( x ) f(x)=\sin(x) f(x)=sin(x),绘制 f ( x ) f(x) f(x)和 d f ( x ) d x \frac{df(x)}{dx} dxdf(x)的图像,其中后者不使用 f ′ ( x ) = cos ( x ) f'(x)=\cos(x) f′(x)=cos(x)。
1 .
一阶导数: f ′ ( x ) = lim h → 0 f ( x + h ) − f ( x ) h . f'(x) = \lim_{h \rightarrow 0} \frac{f(x+h) - f(x)}{h}. f′(x)=h→0limhf(x+h)−f(x).
二阶导数:二阶导数是一阶导数的导数,是在一阶导数的基础上再次求导
f ′ ′ ( x ) = lim h → 0 f ( x + 2 h ) − 2 f ( x ) + f ( x − h ) h 2 . f''(x) = \lim_{h \rightarrow 0} \frac{f(x+2h) -2 f(x) + f(x-h)}{h^2}. f′′(x)=h→0limh2f(x+2h)−2f(x)+f(x−h).
2.
import torch
x = torch.arange(4.0, requires_grad=True)
x.grad # 默认为None
y = 2 * torch.dot(x, x)
y.backward(retain_graph = True)
# y.backward() # 重复反向传播会报错
x.grad
tensor([ 0., 4., 8., 12.])
y.backward()
x.grad
y
tensor([ 0., 8., 16., 24.])
tensor(28., grad_fn=)
对于Pytorch来说,前向过程建立计算图,反向传播后释放。因为计算图的中间结果已经被释放了,所以第二次运行反向传播就会出错。这时在 backward 函数中加上参数 retain_graph=True,计算图中的中间变量在计算完后就不会被释放,就能两次运行反向传播了。
3 .
#3
def f(a):
b = a * 2
while b.norm() < 1000: # L2范数
b = b * 2
if b.sum() > 0:
c = b
else:
c = 100 * b
return c
a = torch.randn(size=(3,), requires_grad=True) # size = ()表示标量
d = f(a)
d.backward()
a.grad
# 报错
RuntimeError: grad can be implicitly created only for scalar outputs
即:提示我们输出y不是一个标量,无法直接求导。
向量/矩阵 不可以直接进行反向传播
d.sum().backward()
# d.backward(torch.ones_like(d))
# 结果张量是一维张量:将一维张量变成标量
a.grad
d.backward(grad_tensors=torch.ones_like(d)) ,等价于d.sum().backward(),可用于解决被求导的对象非标量的问题
4 .
def f2(x):
while x < 1:
x = x * 10
y = x * x
return y
b = torch.randn(size = (), requires_grad = True)
c = f2(b)
c.backward(retain_graph=True) # 可多次反向传播
b.grad == c/b
True
5 .
#5 隐式自动微分
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
from d2l import torch as d2l
def f3(x):
return torch.sin(x)
x = torch.arange(-10, 10, 0.1,requires_grad = True)
y = f3(x)
y.backward(torch.ones_like(y))
d2l.plot(x.detach().numpy(),[y.detach().numpy(), x.grad.numpy()],'x', 'f3(x)', legend=['f3(x)', 'grad'])
# x y需要先用detach()移动到记录的计算图之外
2.6 概率
小结
- 我们可以从概率分布中采样。
- 我们可以使用联合分布、条件分布、Bayes定理、边缘化和独立性假设来分析多个随机变量。
- 期望和方差为概率分布的关键特征的概括提供了实用的度量形式。
课后练习
- 进行 m = 500 m=500 m=500组实验,每组抽取 n = 10 n=10 n=10个样本。改变 m m m和 n n n,观察和分析实验结果。
- 给定两个概率为 P ( A ) P(\mathcal{A}) P(A)和 P ( B ) P(\mathcal{B}) P(B)的事件,计算 P ( A ∪ B ) P(\mathcal{A} \cup \mathcal{B}) P(A∪B)和 P ( A ∩ B ) P(\mathcal{A} \cap \mathcal{B}) P(A∩B)的上限和下限。(提示:使用友元图(韦恩图)来展示这些情况。)
- 假设我们有一系列随机变量,例如 A A A、 B B B和 C C C,其中 B B B只依赖于 A A A,而 C C C只依赖于 B B B,你能简化联合概率 P ( A , B , C ) P(A, B, C) P(A,B,C)吗?(提示:这是一个马尔可夫链。)
- 在 :numref:
subsec_probability_hiv_app中,第一个测试更准确。为什么不运行第一个测试两次,而是同时运行第一个和第二个测试?
1 .
#1
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from torch.distributions import multinomial
from d2l import torch as d2l
fair_probs = torch.ones([6]) / 6
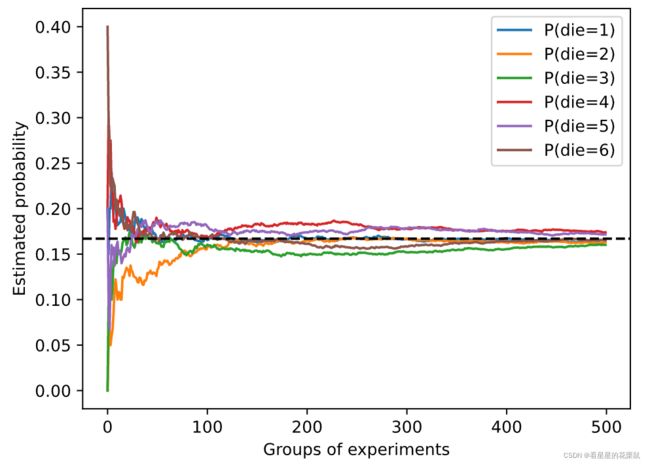
counts = multinomial.Multinomial(10, fair_probs).sample((500,))
cum_counts = counts.cumsum(dim=0)
estimates = cum_counts / cum_counts.sum(dim=1, keepdims=True)
d2l.set_figsize((6, 4.5))
for i in range(6):
d2l.plt.plot(estimates[:, i].numpy(),
label=("P(die=" + str(i + 1) + ")"))
d2l.plt.axhline(y=0.167, color='black', linestyle='dashed')
d2l.plt.gca().set_xlabel('Groups of experiments')
d2l.plt.gca().set_ylabel('Estimated probability')
d2l.plt.legend();
counts = multinomial.Multinomial(5, fair_probs).sample((50,))
cum_counts = counts.cumsum(dim=0)
estimates = cum_counts / cum_counts.sum(dim=1, keepdims=True)
d2l.set_figsize((6, 4.5))
for i in range(6):
d2l.plt.plot(estimates[:, i].numpy(),
label=("P(die=" + str(i + 1) + ")"))
d2l.plt.axhline(y=0.167, color='black', linestyle='dashed')
d2l.plt.gca().set_xlabel('Groups of experiments')
d2l.plt.gca().set_ylabel('Estimated probability')
d2l.plt.legend();
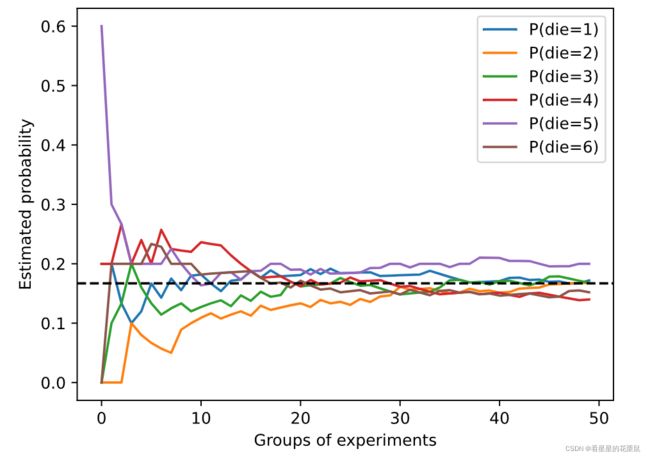
用各点数出现的频率估计概率,实验次数越多,样本数越多,越接近真实概率。
2 .
P ( A ∪ B ) P(A \cup B) P(A∪B) 上限: P ( A ) + P ( B ) P(A)+P(B) P(A)+P(B), 下限: m a x { P ( A ) , P ( B ) } max\{P(A),P(B)\} max{P(A),P(B)}
P ( A ∩ B ) P(A \cap B) P(A∩B) 上限: m i n { P ( A ) , P ( B ) } min\{P(A), P(B)\} min{P(A),P(B)}, 下限: 0 0 0

3 . P ( A B C ) = P ( A ) P ( B ∣ A ) P ( C ∣ B A ) = P ( A ) P ( B ∣ A ) P ( C ∣ B ) P(ABC)=P(A)P(B∣A)P(C∣BA)=P(A)P(B∣A)P(C∣B) P(ABC)=P(A)P(B∣A)P(C∣BA)=P(A)P(B∣A)P(C∣B)
4 . 第二个测试具有不同的特性,不会使错误积累