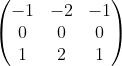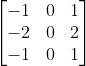锐化滤波器
锐化滤波器在去噪的同时凸显物体的边缘信息,保持图像边缘信息不变或者是增强边缘信息。图像锐化的实质上增强原图像的高频分量,图像锐化滤波器为高通滤波器,边缘和轮廓一般位于灰度突变的地方,因此可以使用灰度差分提取图像边缘和轮廓。
由于轮廓和边缘在一幅图中常常具有任意方向,而差分运算具有方向性,如果差分运算的方向选取不合适,则和差分方向不一致的边缘和轮廓就检测不出来。图像锐化处理对任意方向的边缘和轮廓都有检测能力。
线性锐化滤波器
线性高通滤波器是最常用的线性锐化滤波器。其中心系数为正数,其他系数为负数,所有的系数之和为0.
clc,clear,close all; %清理命令区、清理工作区、关闭显示图形
warning off %消除警告
feature jit off %加速代码运行
im=imread('ColoredChips.png'); %原图像
% im=rgb2gray(im); %二维灰度图
R=imnoise(im(:,:,1),'gaussian',0,0.01) %R+白噪声
G=imnoise(im(:,:,2),'gaussian',0,0.01) %G+白噪声
B=imnoise(im(:,:,3),'gaussian',0,0.01) %B+白噪声
im=cat(3,R,G,B); %原图像+白噪声
w=[-1 -1 -1; %掩膜mask
-1 8 -1;
-1 -1 -1];
im1=linear_sharpen_filter(im,w);
figure('color',[1,1,1])
subplot(121),imshow(im,[]),title('原始图像')
subplot(122),imshow(im1,[]),title('线性锐化滤波器');
function im3=linear_sharpen_filter(im,w)
%线性锐化滤波器
%函数输入:
% im:原始图像,待滤波图像
%函数输出:
% H:M*N阶的矩阵,表示频域滤波器矩阵,数据类型为double
if~isa(im,'double')
im1=double(im)/255;
end
im2=imfilter(im1,w,'replicate');%线性锐化处理
im3=im1-im2; %im3为锐化后的图像
endsobel算子
sobel算子是把图像中每个像素的上下左右四领域的灰度值加权差,在边缘处到达极值而进行边缘检测。
算子模板:
clc,clear,close all; %清理命令区、清理工作区、关闭显示图形
warning off %消除警告
feature jit off %加速代码运行
im=imread('ColoredChips.png'); %原图像
% im=rgb2gray(im); %二维灰度图
R=imnoise(im(:,:,1),'gaussian',0,0.01) %R+白噪声
G=imnoise(im(:,:,2),'gaussian',0,0.01) %G+白噪声
B=imnoise(im(:,:,3),'gaussian',0,0.01) %B+白噪声
im=cat(3,R,G,B); %原图像+白噪声
h=sobel_fspecial('sobel'); %应用sobel算子锐化图像
R1=filter2(h,R);%sobel算子锐化滤波器
G1=filter2(h,G);%sobel算子锐化滤波器
B1=filter2(h,B);%sobel算子锐化滤波器
im1=cat(3,R1,G1,B1); %sobel算子滤波锐化图像
figure('color',[1,1,1])
subplot(121),imshow(im,[]),title('原始图像')
subplot(122),imshow(im1,[]),title('线性锐化滤波器');
function h=sobel_fspecial(type)
if nargin<1
type='sobel';
end
switch type
case 'sobel'%Sobel filter
h=[1 2 1;
0 0 0;
-1 -2 -1];
end
end