倾斜目标检测RRPN (Arbitrary-Oriented Scene Text Detection via Rotation Proposals)
RRPN可以采用一阶段的目标检测流程或二阶段的目标检测流程(Faster RCNN)
一阶段的目标检测只需要计算RRPN IOU, 不需要ROI pooling,
两阶段的需要计算RRPN IOU和RRPN pooling
1.RRPN中的IOU计算
(1)给定预测框和标注框的中心点坐标和宽高,角度。即region1和region2包含5个元素,(cx,cy,w,h,angle)
float computeRectIoU(T const * const region1, T const * const region2)(2) 根据region得到4个端点的(x,y)坐标,共8个值,得到rect_pts1,rect_pts2。注意:倾斜框需要考虑角度的影响
convert_region_to_pts(region1, rect_pts1);
convert_region_to_pts(region2, rect_pts2);template
__DEVICE__ inline void convert_region_to_pts(T const * const roi, T * pts)
{
T cx = roi[0];
T cy = roi[1];
T w = roi[2];
T h = roi[3];
T angle = deg2rad(roi[4]);
T b = cos(angle)*0.5f;
T a = sin(angle)*0.5f;
pts[0] = cx - a*h - b*w;
pts[1] = cy + b*h - a*w;
pts[2] = cx + a*h - b*w;
pts[3] = cy - b*h - a*w;
pts[4] = 2*cx - pts[0];
pts[5] = 2*cy - pts[1];
pts[6] = 2*cx - pts[2];
pts[7] = 2*cy - pts[3];
} (3)根据两个区域region1,region2的4个端点rect_pts1,rect_pts2计算两个区域的相交的面积
float area_inter = computeRectInterArea(rect_pts1, rect_pts2);因为预测框和标注的边界框有很多个,需要计算预测框和边界框两两之间的相交的面积:
N是预测框的个数,M是实际的标注框的个数,关键函数computeRectIoU
for (int64_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
rect_1[0] = xc1[i];
rect_1[1] = yc1[i];
rect_1[2] = w1[i];
rect_1[3] = h1[i];
rect_1[4] = angle1[i];
scalar_t rect_2[5];
for (int64_t j = 0; j < M; j++)
{
rect_2[0] = xc2[j];
rect_2[1] = yc2[j];
rect_2[2] = w2[j];
rect_2[3] = h2[j];
rect_2[4] = angle2[j];
float iou = computeRectIoU(rect_1, rect_2);
iou_data[i*M+j] = iou;
}computeRectIoU:
分几种情况计算两个区域相交的面积:两个区域没有相交,一个区域完全包含在另一个区域中,两个区域间有一定的相交
float computeRectInterArea(const T* rect_pts1, const T* rect_pts2)
{
T inter_pts_f[MAX_RECT_INTERSECTIONS*2];
// int res = rotatedRectangleIntersection2(rect, pixel_rect, inter_pts);
int num_intersects = 0;
int res = rotatedRectangleIntersection(rect_pts1, rect_pts2, inter_pts_f, num_intersects);
float interArea = 0.0f;
if (res == RectIntersectTypes::INTERSECT_NONE)
{
interArea = 0.0f;
} else if (res == RectIntersectTypes::INTERSECT_FULL_1 || res == RectIntersectTypes::INTERSECT_EQ)
{
interArea = contourArea(4, rect_pts1);
} else if (res == RectIntersectTypes::INTERSECT_FULL_2)
{
interArea = contourArea(4, rect_pts2);
} else {
T order_pts_f2[MAX_RECT_INTERSECTIONS * 2];
size_t npoints = convexHull(num_intersects, inter_pts_f, order_pts_f2);
interArea = contourArea(npoints, order_pts_f2);
}countArea(两个区域相交的点的数目,两个区域相交的点的坐标):根据相交区域的点的坐标来计算相交区域的面积
根据相交区域的点的坐标来计算相交区域的面积,注意计算(float)prev[0] * p[1] - (float)prev[1] * p[0]时是有正有负,所以这种计算方式看着不合理,其实是对的
float contourArea(const int npoints, const T* contour, bool oriented=false)
{
if( npoints == 0 )
return 0.;
float a00 = 0.0;
const T* prev = contour + (npoints-1)*2;
for( int i = 0; i < npoints; i++ )
{
const T* p = contour + i*2;
a00 += (float)prev[0] * p[1] - (float)prev[1] * p[0];
prev = p;
}
a00 *= 0.5;
if( !oriented )
a00 = fabs(a00);
return a00;
}得到两个区域的相交的面积后,便可以计算两个区域的iou
mmdetection-rotated/mmdet/csrc_custom/rotate_rect_ops.h
float area1 = region1[2] * region1[3];
float area2 = region2[2] * region2[3];
float iou = area_inter / (area1 + area2 - area_inter + 1e-8);
RRPN中的ROI pooling
(1) 将proposals分为若干个subregion,通过中心点坐标,宽高,角度计算各个subregion的左上角的坐标
(2)根据subregion的左上角坐标,通过取整计算获得该subregion中每个点再特征图上的坐标,获得每个点的特征。遍历该subreigon中的每个点的特征,采用maxpooling对该区域的特征做池化。
结果:
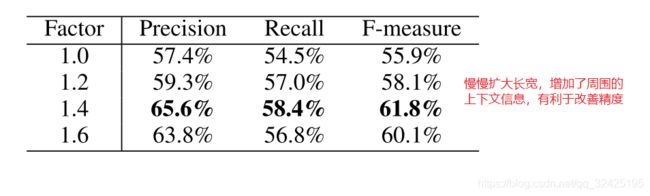
Alibration study:
(1) 周围的上下文的信息:
保留proposals的中心点和角度,将长宽扩大1.x倍数,来查看结果