蓝桥杯省赛专题训练之递归与递推训练(相关真题和模板题)
题目:92. 递归实现指数型枚举
题解:递归。注意不存在的空行也是需要输出的,否则报错。
方法一:
#include方法二:
#include题目:94. 递归实现排列型枚举
#include方法二:用的是next_permutation(a+1,a+1+n)函数
#include题目:717. 简单斐波那契
#include题目:95. 费解的开关
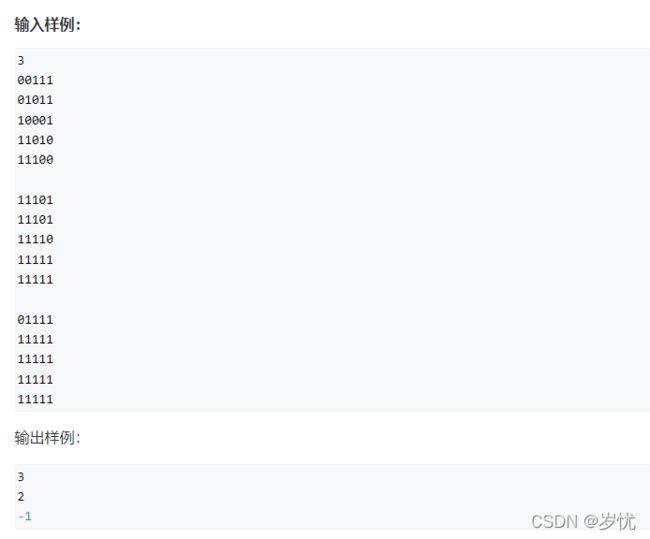
#include题目:93. 递归实现组合型枚举

题解:递归+dfs。因为是从n个里面随便抽取m个,所以需要有两个参数,而像那种求的是n个数的全排列,只需要一个参数去记录已选的数量即可。
#include题目:1209. 带分数

题解:用next_permutation(a+1,a+1+9),对1-9进行全排列,然后再在里面用两层循环进行枚举,寻找符合要求的数。(注意,一般有除法的都建议转换为乘法)
#include题目:116. 飞行员兄弟
#include
// }
// cout<
// }
int minn=30,res=0;
memcpy(b,a,sizeof a);
for(int i=0;i<(1<<16);i++){
memcpy(a,b,sizeof b);
//int t=i;
int ans=0;
bool flag=1;
for(int j=0;j<16;j++){
if(i>>j&1){
ans++;
if(ans>minn){
flag=0;
break;
ans=30;
}
turn_all(j/4,j%4);//注意这里是j不是i
}
}
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
if(a[j][k]=='+'){
flag=0;
ans=40;
break;
}
}
}
//cout<
if(flag){
if(minn>ans){
minn=ans;
res=i;
}
}
}
if(minn<30){
cout<<minn<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<16;i++){
if(res>>i&1){
cout<<i/4+1<<" "<<i%4+1<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
题目:1208. 翻硬币

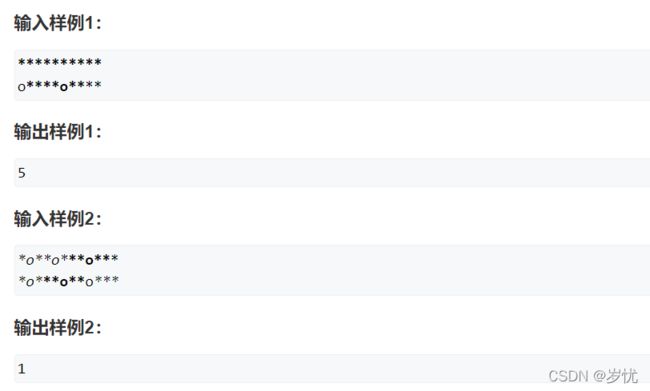
题解:假定每次翻动第i枚硬币时,i+1也翻动。那么我们只需要从第一位开始来判断a[i]与b[i]是否相同,不相同就翻转,并且改变下一位,这就是贪心的最优解
#include