为RViz创建自定义的显示插件
文章目录
- 前言
- ROS plugin
- 构建插件
-
- 插件编码
- 插件icon
- 导出插件
- 编译插件package
- 使用插件
-
- 1 发布电池电量消息
- 2 RViz添加插件“Battery”
- 总结
前言
ROS有很多场景都会使用RViz进行交互控制,比如navigation。RViz自身提供了很多显示类的信息,比如RobotModel,LaserScan,Odometry等等。如果用户还有其他信息也希望在RViz得到显示,则需要我们自定义该信息及其RViz的一个插件导入到RViz中。本文以机器人的电池电量信息插件作为示例,简要说明如何为RViz创建一个自定义的显示插件
本文说明基于官网的教程:
http://docs.ros.org/en/jade/api/rviz_plugin_tutorials/html/display_plugin_tutorial.html#
ROS plugin
RViz插件属于ROS plugin,其基础原理和开发流程与ROS plugin一致,建议首先阅读官网链接对其理解:
http://wiki.ros.org/pluginlib/Tutorials/Writing%20and%20Using%20a%20Simple%20Plugin
构建插件
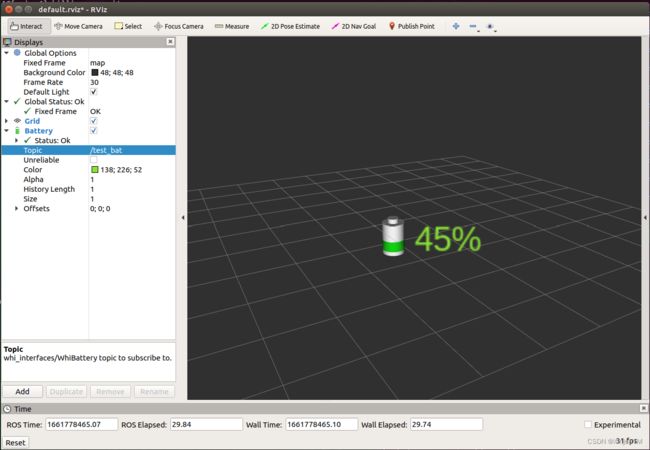
本文以在RViz中显示电池电量为例。能够以百分比形式显示电池当前剩余电量、当电池需要充电时显示颜色变为红色作为提示、能够设置显示字符的大小、电量显示信息能够跟随机器人一起运动
插件编码
完整编码本文不一一罗列,所有源码放入了github,读者可下载参考
类DisplayBat为插件的主类,其负责实现插件与RViz的交互,以及用于显示的属性设置
namespace whi_rviz_plugins
{
class BatteryVisual;
// declare a new subclass of rviz::Display
// every display which can be listed in the "Displays" panel is a subclass of rviz::Display
//
// DisplayBat will show a movable_text showing the power info of battery,
// it will also optionally show a history of recent info vectors, which will be stored in a circular buffer
//
// the DisplayBat class itself just implements the circular buffer, editable parameters, and Display subclass machinery
// the visuals themselves are represented by a separate class, BatteryVisual
// the idiom for the visuals is that when the objects exist, they appear in the scene,
// and when they are deleted, they disappear
class DisplayBat : public rviz::MessageFilterDisplay<whi_interfaces::WhiBattery>
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
// pluginlib::ClassLoader creates instances by calling the default constructor,
// so make sure you have one
DisplayBat();
virtual ~DisplayBat();
// overrides of protected virtual functions from Display as much as possible,
// when Displays are not enabled, they should not be subscribed to incoming data,
// and should not show anything in the 3D view
// these functions are where these connections are made and broken
protected:
virtual void onInitialize();
// a helper function to clear this display back to the initial state
virtual void reset();
private Q_SLOTS:
// these Qt slots get connected to signals indicating changes in the user-editable properties
void updateColorAndAlpha();
void updateHistoryLength();
void updateSize();
private:
// function to handle an incoming ROS message
void processMessage(const whi_interfaces::WhiBattery::ConstPtr& Msg);
private:
// storage for the list of visuals. It is a circular buffer,
// where data gets popped from the front (oldest) and pushed to the back (newest)
boost::circular_buffer<boost::shared_ptr<BatteryVisual>> visuals_;
// user-editable property variables
rviz::ColorProperty* color_property_;
rviz::FloatProperty* alpha_property_;
rviz::IntProperty* history_length_property_;
rviz::FloatProperty* size_property_;
// other properties
std::shared_ptr<Ogre::ColourValue> color_red_{ nullptr };
};
} // end namespace whi_rviz_plugins
类BatteryVisual负责电池电量信息的具体实现,其使用了MovableText作为显示媒介
namespace whi_rviz_plugins
{
class BatteryVisual;
// declare a new subclass of rviz::Display
// every display which can be listed in the "Displays" panel is a subclass of rviz::Display
//
// DisplayBat will show a movable_text showing the power info of battery,
// it will also optionally show a history of recent info vectors, which will be stored in a circular buffer
//
// the DisplayBat class itself just implements the circular buffer, editable parameters, and Display subclass machinery
// the visuals themselves are represented by a separate class, BatteryVisual
// the idiom for the visuals is that when the objects exist, they appear in the scene,
// and when they are deleted, they disappear
class DisplayBat : public rviz::MessageFilterDisplay<whi_interfaces::WhiBattery>
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
// pluginlib::ClassLoader creates instances by calling the default constructor,
// so make sure you have one
DisplayBat();
virtual ~DisplayBat();
// overrides of protected virtual functions from Display as much as possible,
// when Displays are not enabled, they should not be subscribed to incoming data,
// and should not show anything in the 3D view
// these functions are where these connections are made and broken
protected:
virtual void onInitialize();
// a helper function to clear this display back to the initial state
virtual void reset();
private Q_SLOTS:
// these Qt slots get connected to signals indicating changes in the user-editable properties
void updateColorAndAlpha();
void updateHistoryLength();
void updateSize();
private:
// function to handle an incoming ROS message
void processMessage(const whi_interfaces::WhiBattery::ConstPtr& Msg);
private:
// storage for the list of visuals. It is a circular buffer,
// where data gets popped from the front (oldest) and pushed to the back (newest)
boost::circular_buffer<boost::shared_ptr<BatteryVisual>> visuals_;
// user-editable property variables
rviz::ColorProperty* color_property_;
rviz::FloatProperty* alpha_property_;
rviz::IntProperty* history_length_property_;
rviz::FloatProperty* size_property_;
// other properties
std::shared_ptr<Ogre::ColourValue> color_red_{ nullptr };
};
} // end namespace whi_rviz_plugins
插件icon
插件icon用于在RViz中对插件用图标的形式进行显示:

首先,需要为插件简历目录结构“
同时,插件package的CMakeLists文件需要设置icon的安装语句
install(DIRECTORY icons/
DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_SHARE_DESTINATION}/icons)
导出插件
自定义的插件能够被其他ROS软件包找到和理解,需要一个描述文件,本文中该文件为“whi_rviz_plugins.xml”。描述文件的命名完全由用户决定,同时需要将其在package.xml进行导出描述:
同时插件package的CMakeLists文件需要设置该描述文件的安装语句:
## Mark other files for installation (e.g. launch and bag files, etc.)
install(FILES
${PROJECT_NAME}.xml
DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_SHARE_DESTINATION}
)
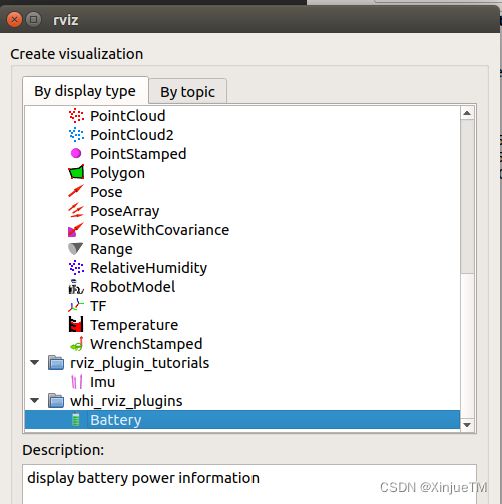
插件描述文件需要将插件的名称、类型、基类类型、以及消息类型进行描述,以便插件使用者能够正确识别
display battery power information
whi_interfaces/WhiBattery
上述文件中path="lib/libwhi_rviz_plugins"为描述插件package生成后的动态库名称(无文件拓展后缀.so)及其所在目录;name="whi_rviz_plugins/Battery"为RViz中看到该插件的名称:
编译插件package
代码准备完毕后,即可编译插件的package。如果读者使用本文github源码,则可以直接输入命令:
cd <your_workspace>
git clone https://github.com/xinjuezou-whi/whi_interfaces.git
git clong https://github.com/xinjuezou-whi/whi_rviz_plugins.git
catkin build
编译完成后为终端添加插件package的环境,继续输入命令:
source <your_workspace>/devel/setup.bash
使用插件
1 发布电池电量消息
电池电量消息定义为:
std_msgs/Header header
uint16 percent
bool need_charge
该消息引入了std_msgs/Header,这是为了能够发送frame_id用于将所显示的电量信息与对应的机器人绑定,能够随机器人一起运动。如果将来同时控制多个机器人时,消息的frame_id与namespace组合能够配对机器人及其对应的电量信息
同时消息定义了电量的百分比,以及是否需要充电的标志位
读者可以依据该消息定义在自己的机器人系统中发布电池信息。如果是快速验证,则可以使用本文package中的Python脚本模拟电量信息的发布,该脚本循环发布主题为“test_bat”的信息,且当电量低于30%时将充电的标志位置为True。如果使用该脚本,则在终端输入命令:
cd <your_workspace>
python src/whi_rviz_plugins/scripts/send_test_msg.py
该脚本运行后,通过命令“rostopic list”,可以看到发布的消息“test_bat”:
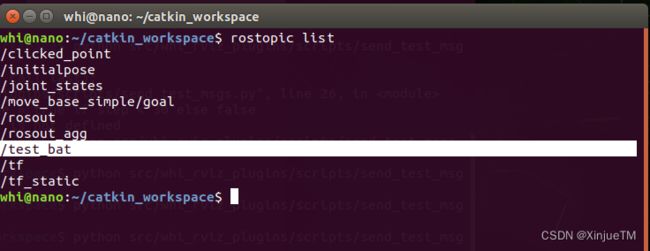
该Python脚本仅用于demo插件的表现,如果使用导航机器人,则需要删除脚本中transform的语句,而使用机器人URDF模型中的静态TF关系,否则会使机器人出现位置转换的错误
2 RViz添加插件“Battery”
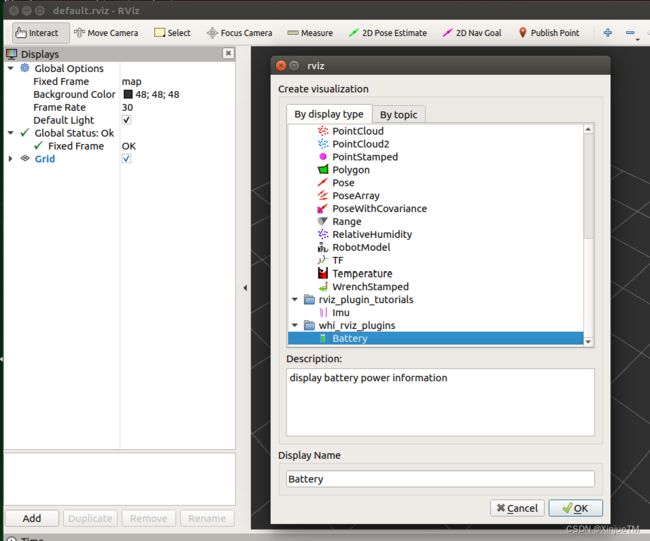
使用命令“rosrun rviz rviz”运行RViz,其启动后,点击“Display”面板中的“Add”按钮,在弹出的对话框中选择页面“By display type”,滚动到最后,将看到插件“whi_rviz_plugins/Battery”,添加:
随后,将在“Displays”列表中看到“Battery”插件,选择所发布的类型为“whi_interfaces/WhiBattery”的目标主题,比如使用“send_test_msg.py”的主题为“test_bat”:
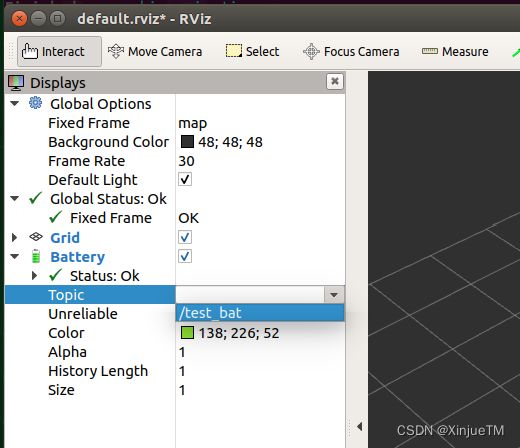
可以修改属性“Color”、“Size”等调整该显示信息的显示效果。同时,通过修改“Offsets”和“Orientation”能调整显示信息的位置和姿态。
位置:
姿态
当将该显示插件用于导航时,姿态调整就特别有帮助,因为导航显示的是 XY 平面内的 2D 场景:
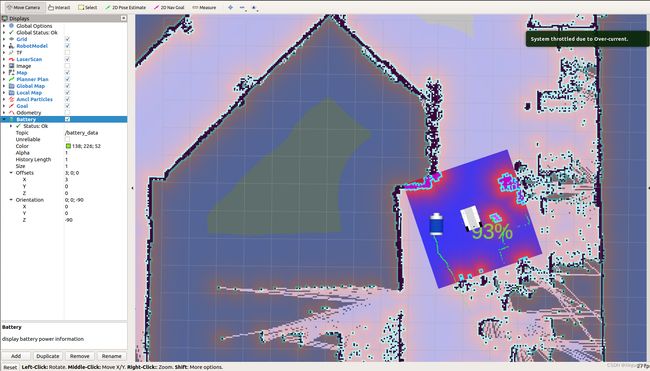
用于导航机器人时,需要注意robot model具备了电池到map的TF关系,下图示例中机器人URDF模型中加入了battery的link,形成了battery->base_link->map的静态TF关系
总结
当需要将用户自定义信息在RViz显示时,通过自定义RViz插件的方式实现,本文说明的插件类型为显示,插件的类型还可以是panel以及交互的tool,在官网的教程中都有涉及,希望通过本文说明能够有类似需求的读者提供一个参考
本文说明的示例package,可以完整的在github下载,如果文中出现了描述错误以及不清晰的地方,欢迎指正,共同交流:[email protected]