NLP之Bi-LSTM(在长句中预测下一个单词)
Bi-LSTM
文章目录
- Bi-LSTM
-
- 1.理论
-
- 1.1 基本模型
- 1.2 Bi-LSTM的特点
- 2.实验
-
- 2.1 实验步骤
- 2.2 实验模型
1.理论
1.1 基本模型
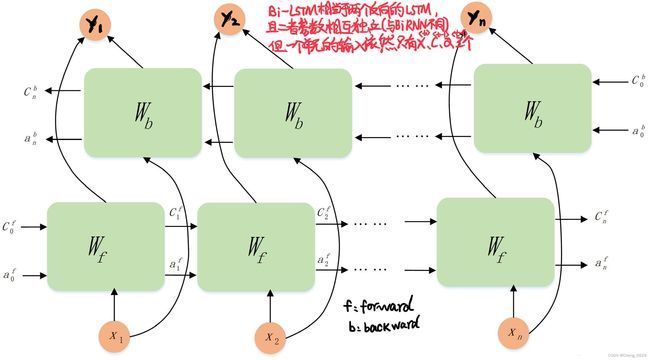
Bi-LSTM模型分为2个独立的LSTM,输入序列分别以正序和逆序输入至2个LSTM模型进行特征提取,将2个输出向量进行拼接后形成的词向量作为该词的最终特征表达(因此底层维度是普通LSTM隐藏层维度的两倍)
1.2 Bi-LSTM的特点
Bi-LSTM的模型设计理念是使t时刻所获得特征数据同时拥有过去和将来之间的信息
- 实验证明,Bi-LSTM模型对文本特征提取效率和性能要优于单个LSTM结构模型
- Bi-LSTM中的2个LSTM参数是相互独立的,它们只共享训练集的word-embedding词向量列表等训练集基本信息。
2.实验
2.1 实验步骤
- 数据预处理,得到字典、样本数等基本数据
- 构建Bi-LSTM模型,设置输入模型的嵌入向量维度,隐藏层α向量和记忆细胞c的维度
- 训练
- 代入数据,设置每个样本的时间步长度
- 得到模型输出值,取其中最大值的索引,找到字典中对应的字母,即为模型预测的下一个字母.
- 把模型输出值和真实值相比,求得误差损失函数,运用Adam动量法梯度下降
- 测试
2.2 实验模型
"""
Task: 基于Bi-LSTM的长句单词预测
Author: ChengJunkai @github.com/Cheng0829
Email: [email protected]
Date: 2022/09/09
"""
import numpy as np
import torch, os, sys, time, re
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
'''1.数据预处理'''
def pre_process(sentence):
# sentence = re.sub("[.,!?\\-]", '', sentence.lower()).split(' ')
word_list = []
'''
如果用list(set(word_sequence))来去重,得到的将是一个随机顺序的列表(因为set无序),
这样得到的字典不同,保存的上一次训练的模型很有可能在这一次不能用
(比如上一次的模型预测碰见a:0,b:1,就输出c:2,但这次模型c在字典3号位置,也就无法输出正确结果)
'''
for word in sentence.split():
if word not in word_list:
word_list.append(word)
word_dict = {w:i for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
number_dict = {i:w for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
print(word_dict)
word_dict["''"] = len(word_dict)
number_dict[len(number_dict)] = "''"
n_class = len(word_dict) # 词库大小:48
max_len = len(sentence.split()) # 句子长度:70
# print(max_len)
return sentence, word_dict, number_dict, n_class, max_len
'''根据句子数据,构建词元的嵌入向量及目标词索引'''
def make_batch(sentence):
input_batch = []
target_batch = []
input_print = []
words = sentence.split()
for i, word in enumerate(words[:-1]):
input = [word_dict[n] for n in words[:(i+1)]]
input = input + [0] * (max_len - 1 - len(input))
# print(np.array(input).shape) # (69,)
target = word_dict[words[i+1]]
'''
input_batch:
由于要预测长句的每一个位置的单词,
所以除了最后一个单词只被预测之外,
所有单词都要参与预测.
因此,训练样本数为:句子长度70-1=69
target_batch:
一个列表,分别存储69个训练样本的目标单词
'''
input_print.append(input)
# np.eye(n_class)[input] : [69,48]
# print(np.eye(n_class)[input].shape)
input_batch.append(np.eye(n_class)[input])
target_batch.append(target)
# print(np.array(input_print)
'''input_print: [69,69]'''
'''input_batch: [69,69,48]'''
input_batch = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(input_batch))
# print(input_batch.shape)
target_batch = torch.LongTensor(np.array(target_batch)) #(69,)
input_batch = input_batch.to(device)
target_batch = target_batch.to(device)
return input_batch, target_batch
'''2.构建模型'''
class BiLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BiLSTM, self).__init__()
# n_class是词库大小,即嵌入向量维度:48
'''bidirectional=True'''
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=hidden_size, bidirectional=True)
self.W = nn.Linear(hidden_size*2, n_class, bias=False)
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(n_class))
def forward(self, X):
'''训练样本数:69, 时间步长度(每一样本长度):69'''
'''X:[batch_size, n_step, n_class] [样本数,时间步长度(每一样本长度),嵌入向量维度(词库大小)]'''
# input : [n_step, batch_size, n_class]
'''transpose转置 -> input:[69,69,48]'''
# input : [输入序列长度(时间步长度),样本数,嵌入向量维度]
input = X.transpose(0, 1) # [69,69,48]
# hidden_state : [num_layers*num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size]
# hidden_state : [层数*网络方向,样本数,隐藏层的维度(隐藏层神经元个数)]
hidden_state = torch.zeros(1*2, len(X), hidden_size).to(device)
# cell_state : [num_layers*num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size]
# cell_state : [层数*网络方向,样本数,隐藏层的维度(隐藏层神经元个数)]
cell_state = torch.zeros(1*2, len(X), hidden_size).to(device)
'''
一个Bi-LSTM细胞单元有三个输入,分别是$输入向量x^{}、隐藏层向量a^{}
和记忆细胞c^{}$;
'''
'''outputs:[时间步长度(每一样本长度),训练样本数,隐藏层向量维度*2] -> [69,69,256]'''
# outputs:[69,69,256] final_hidden_state:[2,69,128] final_cell_state:[2,69,128]
outputs, (final_hidden_state, final_cell_state) = self.lstm(input, (hidden_state, cell_state))
outputs = outputs.to(device)
'''
由于是双向,outputs中各个值是由每一步的两个output拼接而成的,所以维度=2*128=256
final_hidden_state只有final_output的一半参数,所以不能替换
'''
final_output = outputs[-1] # [batch_size, hidden_size*2] -> [69, 256]
Y_t = self.W(final_output) + self.b # Y_t : [batch_size, n_class]
return Y_t
if __name__ == '__main__':
hidden_size = 128 # 隐藏层神经元个数(向量维度)
device = ['cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'][0]
sentence = (
'China is one of the four ancient civilizations in the world. '
'Around 5800 years ago, Yellow River, the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River, '
'and the West Liaohe River showed signs of origin of civilization; '
'around 5,300 years ago, various regions of China entered the stage of civilization; '
'around 3,800 years ago, Central Plains formed a more advanced stage. '
'Mature form of civilization, and radiate cultural influence to Quartet;'
)
# 长句训练太麻烦,所以改用字母
sentence = 'a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z'
# sentence = 'a b c d e f g h i'
'''1.数据预处理'''
sentence, word_dict, number_dict, n_class, max_len = pre_process(sentence)
input_batch, target_batch = make_batch(sentence)
'''2.构建模型'''
'''模型加载'''
model = BiLSTM()
model.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
if os.path.exists('model_param.pt') == True:
# 加载模型参数到模型结构
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_param.pt', map_location=device))
'''3.训练'''
print('{}\nTrain\n{}'.format('*'*30, '*'*30))
loss_record = []
for epoch in range(10000):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input_batch)
'''output:[25,27] target_batch:[25]'''
loss = criterion(output, target_batch)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if loss >= 0.01: # 连续30轮loss小于0.01则提前结束训练
loss_record = []
else:
loss_record.append(loss.item())
if len(loss_record) == 30:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_param.pt')
break
if ((epoch+1) % 1000 == 0):
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'Loss = {:.6f}'.format(loss))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_param.pt')
'''4.测试'''
'''
本实验与之前实验的不同之处在于,把句子单词挨个进行分解,所以看似只有一个样本,
实际有max_len-1个样本,也就是说训练时预测了从首单词到尾单词前的所有单词,
所以输入"a"到输入"a~y"均可输出"a~z"
但由于样本少且高度相似,所以必须按照训练样本的位置进行预测,
因为权重训练的是如何由"a"推出"b",如何由"a b"推出"a b c"......
如果开始单词改成"b",则预测结果不会是"c"
'''
print('{}\nTest\n{}'.format('*'*30, '*'*30))
sentence = 'a b c'
print(sentence)
length = 10
while len(sentence.split()) < length:
words = sentence.split()
input_batch = []
input = []
# 把单词换成序号
for word in words:
if word not in word_dict:
word = "''" # 把不存在赋值为空字符串
input.append(word_dict[word])
# 填充
input = input + [0] * (max_len - 1 - len(input))
input_batch.append(np.eye(n_class)[input])
input_batch = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(input_batch))
input_batch = input_batch.to(device)
predict = model(input_batch).data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
sentence = sentence + ' ' + number_dict[predict.item()]
print(sentence)