Game101现代计算机图形学入门学习笔记(八)
材质与外观
- 一、材质
- 二、漫反射材质(BRDF)
- 三、Glossy材质(BRDF)
- 四、理想的反光材质(BSDF)
- 五、反射
-
- 1、完美的镜面反射
- 三、折射
- 四、菲涅尔项
-
- 1、精确计算
- 2、近似估计
- 五、微平面材质
-
- 1、微平面理论
- 六、Isotropic / Anisotropic材质(BRDFs)
-
- 1、各向同性(Isotropic)
- 2、各向异性( Anisotropic)
- 七、BRDF的属性
-
- 1、非负性
- 2、线性
- 3、可逆性
- 4、能量守恒
- 5、各向同性和各向异性
- 八、BRDF的测量
-
- 1、提高效率
- 九、参考和引用
一、材质
图形学中材质就是 BRDF,因为 BRDF 描述了光线打到物体表面是如何被反射的,它所反射的范围是表面半球。
二、漫反射材质(BRDF)
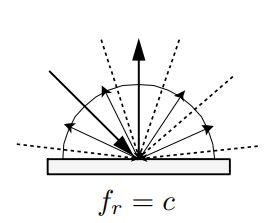
光线在各个方向均匀反射。
L o ( w o ) = π f r L i L_o(w_o)=\pi f_r L_i Lo(wo)=πfrLi
f r = ρ π f_r=\frac{\rho}{\pi} fr=πρ ρ \rho ρ是反射率
三、Glossy材质(BRDF)
四、理想的反光材质(BSDF)
五、反射
1、完美的镜面反射

θ = θ o = θ i \theta=\theta_o=\theta_i θ=θo=θi
w o + w i = 2 c o s θ n ⃗ = 2 ( w i ⋅ n ⃗ ) n ⃗ w_o +w_i =2 cos \theta \vec{n}=2(w_i \cdot \vec{n}) \vec{n} wo+wi=2cosθn=2(wi⋅n)n
从上往下看:
ϕ o = ( ϕ i + π ) m o d 2 π \phi_o=(\phi_i+\pi) mod 2\pi ϕo=(ϕi+π)mod2π
三、折射
折射可以通过 Snell’s Law 进行计算

计算折射角:
η i s i n θ i = η t s i n θ t \eta_i sin\theta_i=\eta_t sin\theta_t ηisinθi=ηtsinθt
c o s θ t = 1 − s i n 2 θ t cos \theta_t=\sqrt{1-sin^2\theta_t} cosθt=1−sin2θt
c o s θ t = 1 − ( η i η t ) 2 s i n 2 θ i cos \theta_t=\sqrt{1-(\frac{\eta_i}{\eta_t})^2 sin^2\theta_i} cosθt=1−(ηtηi)2sin2θi
c o s θ t = 1 − ( η i η t ) 2 ( 1 − c o s 2 θ i ) cos \theta_t=\sqrt{1-(\frac{\eta_i}{\eta_t})^2 (1-cos^2\theta_i)} cosθt=1−(ηtηi)2(1−cos2θi)
四、菲涅尔项
1、精确计算
2、近似估计
- Schlick近似
R ( θ ) = R 0 + ( 1 − R 0 ) ( 1 − c o s θ ) 5 R(\theta)=R_0+(1-R_0)(1-cos\theta)^5 R(θ)=R0+(1−R0)(1−cosθ)5
R 0 = ( n 1 − n 2 n 1 + n 2 ) 2 R_0=(\frac{n_1-n_2}{n _1+n_2})^2 R0=(n1+n2n1−n2)2
五、微平面材质
1、微平面理论
- 微平面理论假设物体表面由不同方向的微小平面组成。每一个微小平面都会根据它的法线方向在一个方向上反射光线。
- 远处看是材质,近处是几何。
- 微平面理论用于模拟三种现象:
1、光滑的平面表面法向分布较为一致,粗糙的平面表面法线分布较为杂乱。
2、在粗糙的表面上,微平面可以遮挡其他的微平面的光线,在其他微平面上投射阴影。
3、菲涅尔现象。
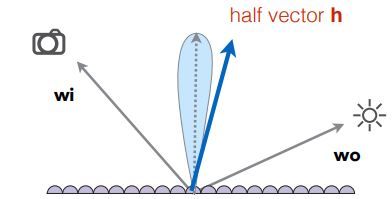
f ( i , o ) = F ( i , h ) G ( i , o , h ) D ( h ) 4 ( n , i ) ( n , o ) f(i,o)=\frac{F(i,h)G(i,o,h)D(h)}{4(n,i)(n,o)} f(i,o)=4(n,i)(n,o)F(i,h)G(i,o,h)D(h)
F ( i , h ) F(i,h) F(i,h):菲涅尔项,根据入射角度得到不同的反射率。
G ( i , o , h ) G(i,o,h) G(i,o,h):几何衰减函数(shadowing masking term),它解释了微平面彼此之间的阴影和遮罩。
D ( h ) D(h) D(h):法线分布函数,只有法线与半程向量相同的光线才会被接收。
六、Isotropic / Anisotropic材质(BRDFs)
潜在表面的方向性不同,会导致呈现不同的高光。当表面法线存在较多方向性时,会出现这种条纹状高光项(Anisotropic),反则会出现圆形状高光项(Isotropic)。

1、各向同性(Isotropic)
各个方向的法线相同。
2、各向异性( Anisotropic)
各个方向的法线都不同。
各向异性BRDF:磨过的金属、尼龙、天鹅绒
七、BRDF的属性
1、非负性
f r ( w i → w r ) ≥ 0 f_r(w_i\rightarrow w_r)\geq0 fr(wi→wr)≥0
2、线性
分成多个部分后做光线传播和整体做光线传播是一样的。
L r ( p , w r ) = ∫ H 2 f r ( p , w i → w r ) L i ( p , w i ) c o s θ i w i L_r(p,w_r)=\int_{H^2}f_r(p,w_i\rightarrow w_r)L_i(p,w_i)cos\theta_i w_i Lr(p,wr)=∫H2fr(p,wi→wr)Li(p,wi)cosθiwi
3、可逆性
f r ( w i → w r ) = f r ( w r → w o ) f_r(w_i\rightarrow w_r) =f_r(w_r\rightarrow w_o) fr(wi→wr)=fr(wr→wo)

4、能量守恒
∀ w r ∫ H 2 f r ( w i → w r ) c o s θ w i ≤ 1 \forall w_r\int_{H^2}f_r(w_i\rightarrow w_r)cos\theta w_i\leq1 ∀wr∫H2fr(wi→wr)cosθwi≤1
5、各向同性和各向异性
1、如果是各向同性: f r ( θ i , ϕ i ; θ r , ϕ r ) = f r ( θ i , θ r , ϕ r − ϕ i ) f_r(\theta_i,\phi_i;\theta_r,\phi_r)=f_r(\theta_i,\theta_r,\phi_r-\phi_i) fr(θi,ϕi;θr,ϕr)=fr(θi,θr,ϕr−ϕi)
则有可逆性:
f r ( θ i , θ r , ϕ i − ϕ r ) = f r ( θ r , θ i , ϕ r − ϕ i ) = f r ( θ i , θ r , ∣ ϕ r − ϕ i ∣ ) f_r(\theta_i,\theta_r,\phi_i-\phi_r)=f_r(\theta_r,\theta_i,\phi_r-\phi_i)=f_r(\theta_i,\theta_r,|\phi_r-\phi_i|) fr(θi,θr,ϕi−ϕr)=fr(θr,θi,ϕr−ϕi)=fr(θi,θr,∣ϕr−ϕi∣)
八、BRDF的测量
- 1、避免去生成模型
- 2、可以精确使用真实世界的材质。
工具: gonioreflectometer
1、提高效率
- 如果具有各向同性,可以将4维降为3维
- 如果具有可逆性,可以只用测量一半
BRDF库:MERL
九、参考和引用
[1] bilibili:GAMES101-现代计算机图形学入门-闫令琪
[2] 材质与外观.pdf
[3] CSDN:GAMES101-现代计算机图形学学习笔记(17)



