C++ 使用thrift开发微服务匹配项目(开发框架搭建)
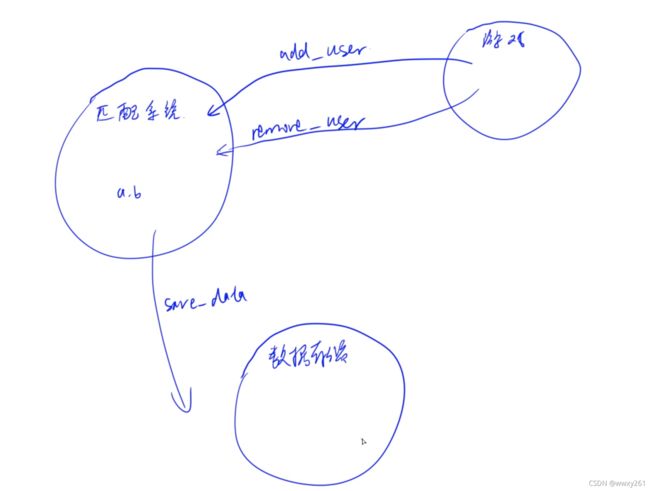
架构
C++ match_service 实现以下两个接口
namespace cpp match_service
struct User {
1: i32 id,
2: string name,
3: i32 score
}
service Match {
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*/
i32 add_user(1: User user, 2: string info),
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*/
i32 remove_user(1: User user, 2: string info),
}save_service实现以下一个接口
namespace cpp save_service
service Save {
/**
* username: myserver的名称
* password: myserver的密码的md5sum的前8位
* 用户名密码验证成功会返回0,验证失败会返回1
* 验证成功后,结果会被保存到myserver:homework/lesson_6/result.txt中
*/
i32 save_data(1: string username, 2: string password, 3: i32 player1_id, 4: i32 player2_id)
}进入match_service/src目录,使用命令根据接口自动生成模版代码
thrift -r --gen cpp ../../thrift/match.thrift同理生成save_service的模版代码
删除Match_server.skeleton.cpp和Save_server.skeleton.cpp文件,将二者的main函数整合成一个,实现完整的业务逻辑。
下面的问题就是这个main怎么写,去thrift的官网,找到服务端的框架逻辑,并像其中添加业务逻辑。
服务端代码原始模版
// This autogenerated skeleton file illustrates how to build a server.
// You should copy it to another filename to avoid overwriting it.
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace std;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
return 0;
}
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
return 0;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
::std::shared_ptr handler(new MatchHandler());
::std::shared_ptr processor(new MatchProcessor(handler));
::std::shared_ptr serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port));
::std::shared_ptr transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory());
::std::shared_ptr protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory);
cout << "Start Match Server" << endl;
server.serve();
return 0;
}
为了便于调试,我们需要有一个客户端,用来发送用户数据到服务器,这里使用python实现。使用命令创建客户端模版
thrift -r --gen py ../../thrift/match.thrift这里从thrift官方教程中复制Python Client的写法,原始模版如下
import sys
import glob
sys.path.append('gen-py')
sys.path.insert(0, glob.glob('../../lib/py/build/lib*')[0])
from tutorial import Calculator
from tutorial.ttypes import InvalidOperation, Operation, Work
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
def main():
# Make socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090)
# Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# Wrap in a protocol
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# Create a client to use the protocol encoder
client = Calculator.Client(protocol)
# Connect!
transport.open()
client.ping()
print('ping()')
sum_ = client.add(1, 1)
print('1+1=%d' % sum_)
work = Work()
work.op = Operation.DIVIDE
work.num1 = 1
work.num2 = 0
try:
quotient = client.calculate(1, work)
print('Whoa? You know how to divide by zero?')
print('FYI the answer is %d' % quotient)
except InvalidOperation as e:
print('InvalidOperation: %r' % e)
work.op = Operation.SUBTRACT
work.num1 = 15
work.num2 = 10
diff = client.calculate(1, work)
print('15-10=%d' % diff)
log = client.getStruct(1)
print('Check log: %s' % log.value)
# Close!
transport.close()修改为如下形式:
from match_client.match import Match
from match_client.match.ttypes import User
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
from sys import stdin
def operate(op, user_id, username, score):
# Make socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('127.0.0.1', 9090)
# Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# Wrap in a protocol
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# Create a client to use the protocol encoder
client = Match.Client(protocol)
# Connect!
transport.open()
user = User(user_id, username, score)
if op == "add":
client.add_user(user, "")
elif op == "remove":
client.remove_user(user, "")
# Close!
transport.close()
def main():
for line in stdin:
op, user_id, username, score = line.split(' ')
operate(op, int(user_id), username, int(score))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
这个就是一个简单的终端客户端,下面进行测试,看一下我们的服务能否跑起来,然后在完善细节逻辑。
这里直接使用g++编译服务端代码(当然实际服务端开发可能使用make和cmake)
编译过程
g++ -c main.cpp match_server/*.cpp save_client/*.cpp链接过程
g++ *.o -o main -lthrift -pthread启动服务端
客户端Python代码无需编译,直接执行。同时开启客户端服务器,测试通过。