深度学习 | Detectron2使用指南
文章目录
- 1. Detectron2安装
-
- 1.1 Linux
- 1.2 Windows
-
- 1.2.1 VS2019 C++编译环境
- 1.2.2 pycocotools
- 1.2.3 Detectron2
- 2. 自定义数据集
-
- 2.1 关于COCO格式
- 2.2 注册数据集
- 2.3 可视化工具
- 2.4 自定义数据增强
- 3. 自定义模型
-
- 3.1 特征提取网络(backbone)
- 3.2 候选框生成器(proposal_generator)
- 3.3 检测器(roi_heads)
- 3.4 模型框架(meta_arch)
- 4. 模型训练
-
- 4.1 默认训练
- 4.2 自定义训练
- 4.3 完整训练流程
- 5. 配置文件
- 6. 备注

Detectron2是Facebook AI Research的检测和分割框架,其主要基于PyTorch实现,但具有更模块化设计,因此它是灵活且便于扩展的,具体简介可见Github库和Meta AI Blog Post。
@misc{wu2019detectron2,
author = {Yuxin Wu and Alexander Kirillov and Francisco Massa and
Wan-Yen Lo and Ross Girshick},
title = {Detectron2},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2}},
year = {2019}
}
1. Detectron2安装
首先官方要求的环境条件如下:
- Linux or macOS with Python ≥ 3.6
- PyTorch ≥ 1.8 and torchvision that matches the PyTorch installation. Install them together at pytorch.org to make sure of this
- OpenCV is optional but needed by demo and visualization
- gcc & g++ ≥ 5.4 are required
- ninja is optional but recommended for faster build
- Cuda & Cudnn
因此想要安装并使用Detectron2,需要有:
- 环境:Python,Cuda,Cudnn,gcc&g++
- Python包:pytorch,torchvision,python-opencv
- 推荐:Anaconda
1.1 Linux
Linux安装直接按照官方文档的安装步骤即可
python -m pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git'
# (add --user if you don't have permission)
# Or, to install it from a local clone:
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git
python -m pip install -e detectron2
# On macOS, you may need to prepend the above commands with a few environment variables:
CC=clang CXX=clang++ ARCHFLAGS="-arch x86_64" python -m pip install ...
如果以上安装失败,可以尝试直接安装预编译文件,同样在官方文档有提供
1.2 Windows
1.2.1 VS2019 C++编译环境
Windows想要安装Detectron2,需要提前安装Microsoft Visual Studio 2019,然后选择安装“使用C++的桌面开发”,其他均默认即可。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-IEDpxG7n-1647657267595)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Justlovesmile/CDN2/post/20220316165420.png)]
1.2.2 pycocotools
安装方法一:
pip install git+https://github.com/philferriere/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI
安装方法二:
git clone https://github.com/pdollar/coco.git
cd coco/PythonAPI
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
python setup.py build_ext install
如果安装失败(一般都会失败),尝试下载“Microsoft Visual C++ Build Tools.exe” ,官网链接:https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=691126。
如果在安装的过程中因网络问题失败,可以使用离线包,网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1GeJ2c8MxnZP8lAYAwQACzg,提取码1114。
1.2.3 Detectron2
使用Conda(推荐!之前有过同一个包使用conda安装的好用而pip安装的不好用的经历)或者pip下载包:
conda install cython
conda install ninja
conda install pywin32
下载Detectron2到本地:
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git
python -m pip install -e detectron2
或者
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git
cd detectron2
python setup.py build develop
2. 自定义数据集
2.1 关于COCO格式
Detectron2已经写好了COCO格式的数据集图像和标注的读取,因此通常减少工作量,可以自己写一个脚本将数据集转为COCO格式的标注,可参考目标检测 | 常用数据集标注格式以及转换代码。
COCO的文件目录如下:
-coco/
|-train2017/
|-1.jpg
|-2.jpg
|-val2017/
|-3.jpg
|-4.jpg
|-test2017/
|-5.jpg
|-6.jpg
|-annotations/
|-instances_train2017.json
|-instances_val2017.json
|-*.json
其中标注文件(json)最为重要,其格式如下:
{
"info": {//数据集信息,对于训练而言不重要
"year": int,
"version": str,
"description": str,
"contributor": str,
"url": str,
"date_created": datetime,
},
"images": [{
"id": int, //必要
"width": int, //必要
"height": int, //必要
"file_name": str, //必要
"license": int,
"flickr_url": str,
"coco_url": str,
"date_captured": datetime,
},{...}], //列表
"annotations": [{
"id": int, //标注id
"image_id": int, //所属图像id
"category_id": int, //类别id
"segmentation": RLE or [polygon], //图像分割标注
"area": float, //区域面积
"bbox": [x,y,width,height], //目标框左上角坐标以及宽高
"iscrowd": 0 or 1, //是否密集
},{...}], //列表
"categories": [{
"id": int, //类别序号
"name": str, //类别名称
"supercategory": str, //父类别
}], //列表
"licenses": [{//对于训练,不重要
"id": int,
"name": str,
"url": str,
}], //列表
}
2.2 注册数据集
import os
from detectron2.data import DatasetCatalog, MetadataCatalog
from detectron2.data.datasets.register_coco import register_coco_instances
DATA_ALL_CATEGORIES = [
{'id': 1, 'name': 'airplane'},
{'id': 2, 'name': 'ship'},
{'id': 3, 'name': 'storage tank'},
{'id': 4, 'name': 'baseball diamond'},
{'id': 5, 'name': 'tennis court'},
{'id': 6, 'name': 'basketball court'},
{'id': 7, 'name': 'ground track field'},
{'id': 8, 'name': 'harbor'},
{'id': 9, 'name': 'bridge'},
{'id': 10, 'name': 'vehicle'}
]
DATA_SPLITS = {}
DATA_SPLITS['nwpu_all'] = {
'nwpu_all_trainval': (
os.path.join(DATA_ROOT,"positive image set"),
os.path.join(DATA_ROOT,'trainval.json')
),
'nwpu_all_test': (
os.path.join(DATA_ROOT,"positive image set"),
os.path.join(DATA_ROOT,'test.json')
)
}
def _get_data_all_instance_meta():
thing_ids = [k["id"] for k in DATA_ALL_CATEGORIES]
thing_dataset_id_to_contiguous_id = {k: i for i, k in enumerate(thing_ids)}
thing_classes = [k["name"] for k in DATA_ALL_CATEGORIES]
ret = {
"thing_dataset": thing_dataset_id_to_contiguous_id,
"thing_classes": thing_classes,
}
return ret
def _get_builtin_metadata(dataset_name):
if dataset_name == "nwpu_all":
return _get_data_instance_meta(DATA_ALL_CATEGORIES)
def register_all(root):
for dataset_name, splits_per_dataset in DATA_SPLITS.items():
for key, (image_root, json_file) in splits_per_dataset.items():
assert os.path.exists(os.path.join(root, json_file))
register_coco_instances(
key,
_get_builtin_metadata(dataset_name),
os.path.join(root, json_file) if "://" not in json_file else json_file,
os.path.join(root, image_root),
)
DATA_ROOT = "D:/GISP/XIEMINGJIE/Code/Detection/dataset/NWPU VHR-10 dataset/"
register_all(DATA_ROOT)
此时已完成nwpu_all_trainval以及nwpu_all_test数据集的注册,可以通过代码查看:
print(DatasetCatalog.get("nwpu_all_trainval"))
print(DatasetCatalog.get("nwpu_all_test"))
当然,如果不想要使用COCO格式数据集也可以自定义注册函数,可以参考register_coco_instances的代码:
def register_coco_instances(name, metadata, json_file, image_root):
"""
Args:
name (str): the name that identifies a dataset, e.g. "coco_2014_train".
metadata (dict): extra metadata associated with this dataset. You can
leave it as an empty dict.
json_file (str): path to the json instance annotation file.
image_root (str or path-like): directory which contains all the images.
"""
assert isinstance(name, str), name
assert isinstance(json_file, (str, os.PathLike)), json_file
assert isinstance(image_root, (str, os.PathLike)), image_root
# 1. register a function which returns dicts
DatasetCatalog.register(name, lambda: load_coco_json(json_file, image_root, name))
# 2. Optionally, add metadata about this dataset,
# since they might be useful in evaluation, visualization or logging
MetadataCatalog.get(name).set(
json_file=json_file, image_root=image_root, evaluator_type="coco", **metadata
)
其中load_coco_json函数的功能是读取数据集标注文件,并以固定的形式返回,详细可见官网:
# load_coco_json返回的是一个列表
# 返回格式如下:
def load_coco_json(json_file, image_root, dataset_name=None, extra_annotation_keys=None):
# read and do something
# ...
# generate dataset_dicts like: ↓
dataset_dicts = [{'file_name': '...\\images\\001.jpg', 'height': 939, 'width': 1356, 'image_id': 0, 'annotations': [{'iscrowd': 0, 'bbox': [903, 57, 129, 123], 'category_id': 0, 'bbox_mode': <BoxMode.XYWH_ABS: 1>}]}, {...}]
return dataset_dicts
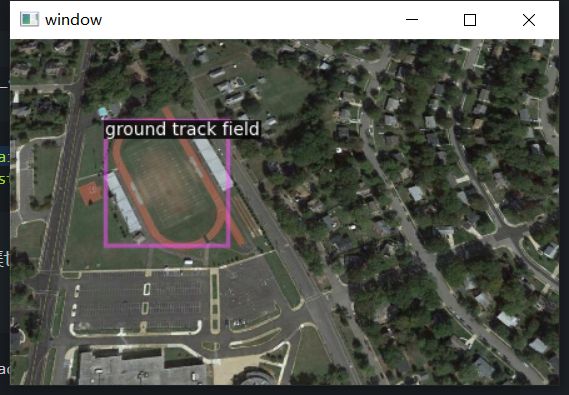
2.3 可视化工具
import random
import cv2
from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog
from detectron2.data import detection_utils as utils
from detectron2.utils.visualizer import Visualizer
datasets_dicts = DatasetCatalog.get("nwpu_all_trainval_1shot")
for data in random.sample(datasets_dicts, 1):
img = utils.read_image(data["file_name"])
visual = Visualizer(img, metadata=MetadataCatalog.get("nwpu_all_trainval"),scale=0.5)
vis = visual.draw_dataset_dict(data)
cv2.imshow("window", vis.get_image()[:, :, ::-1])
cv2.waitKey()
2.4 自定义数据增强
在注册了数据集之后就可以用detectron2.data.build_detection_train_loader和detectron2.data.build_detection_test_loader构建Dataloader,即数据集的加载方式。
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
import detectron2.data.transforms as T
from detectron2.model_zoo import model_zoo
from detectron2.data import build_detection_train_loader
from detectron2.data import DatasetMapper # the default mapper
cfg = get_cfg()
cfg.merge_from_file(model_zoo.get_config_file("COCO-Detection/retinanet_R_50_FPN_1x.yaml"))
cfg.DATASETS.TRAIN = ("nwpu_all_trainval",)
mapper = DatasetMapper(cfg,is_train=True,augmentations=[T.Resize((800, 800))])
train_loader = build_detection_train_loader(cfg,mapper=mapper)
build_detection_train_loader()的参数如下:
build_detection_train_loader(
dataset,
*,
mapper,
sampler=None,
total_batch_size,
aspect_ratio_grouping=True,
num_workers=0,
collate_fn=None,
)
其中mapper对应的就是数据增强部分,默认为detectron2.data.DatasetMapper,sampler对应的采样策略部分,通常只需要关注mapper即可。
class DatasetMapper:
@configurable
def __init__(self,is_train: bool):
pass
@classmethod
def from_config(cls, cfg, is_train: bool = True):
pass
def _transform_annotations(self, dataset_dict, transforms, image_shape):
pass
def __call__(self, dataset_dict):
pass
return dataset_dict
官方给的自定义简化DataMapper:
from detectron2.data import detection_utils as utils
import detectron2.data.transforms as T
def mapper(dataset_dict):
dataset_dict = copy.deepcopy(dataset_dict) # it will be modified by code below
# can use other ways to read image
image = utils.read_image(dataset_dict["file_name"], format="BGR")
# "Data Augmentation"
auginput = T.AugInput(image)
transform = T.Resize((800, 800))(auginput)
image = torch.from_numpy(auginput.image.transpose(2, 0, 1))
annos = [
utils.transform_instance_annotations(annotation, [transform], image.shape[1:])
for annotation in dataset_dict.pop("annotations")
]
return {
# create the format that the model expects
"image": image,
"instances": utils.annotations_to_instances(annos, image.shape[1:])
}
dataloader = build_detection_train_loader(cfg, mapper=mapper)
因此自定义的数据增强需要满足,输入为dataset_dict,输出为:
{
"images": image_tensor,
"instances": utils.annotations_to_instances => Instances类
}
3. 自定义模型
Detectron2的模型是分模块的,它将目标检测模型拆分为了4个核心模块:backbone,proposal_generator,roi_heads以及meta_arch。
3.1 特征提取网络(backbone)
在detectron2.modeling.backbone路径下可以看到,目前只有ResNet、FPN和RegNet
可直接使用的backbone:
build_resnet_backbone
build_resnet_fpn_backbone
build_retinanet_resnet_fpn_backbone
官方的自定义backbone的案例:
from detectron2.modeling import BACKBONE_REGISTRY, Backbone, ShapeSpec
@BACKBONE_REGISTRY.register()
class ToyBackbone(Backbone):
def __init__(self, cfg, input_shape):
super().__init__()
# create your own backbone
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=16, padding=3)
def forward(self, image):
return {"conv1": self.conv1(image)}
def output_shape(self):
return {"conv1": ShapeSpec(channels=64, stride=16)}
3.2 候选框生成器(proposal_generator)
同样可以自定义注册
@PROPOSAL_GENERATOR_REGISTRY.register()
class ToyRPN(RPN):
def __init__(self,*args, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
pass
@RPN_HEAD_REGISTRY.register()
class ToyRPNHead(StandardRPNHead):
def __init__(self,*args, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
pass
3.3 检测器(roi_heads)
@ROI_MASK_HEAD_REGISTRY.register()
@ROI_KEYPOINT_HEAD_REGISTRY.register()
@ROI_HEADS_REGISTRY.register()
@ROI_BOX_HEAD_REGISTRY.register()
3.4 模型框架(meta_arch)
@META_ARCH_REGISTRY.register()
class ToyNet(nn.Module):
@configurable
def __init__(self,*args, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
pass
@classmethod
def from_config(cls, cfg):
pass
def forward_training(self,*args, **kwargs):
pass
def loss(self,*args, **kwargs):
pass
@torch.no_grad()
def label_anchors(self,*args, **kwargs):
pass
def forward_inference(self,*args, **kwargs):
pass
def inference_single_image(self,*args, **kwargs):
pass
具体可参考官方复现的projects
4. 模型训练
4.1 默认训练
一般而言,我们可以继承使用默认的目标检测任务训练器DefalutTrainer,而DefalutTrainer又是继承自TrainerBase,TrainerBase中又使用到了HookBase。我的理解是HookBase和TrainerBase是将一个训练过程抽象并拆分成阶段步骤的过程,先看HookBase:
class HookBase:
def before_train(self):
"""
Called before the first iteration.
"""
pass
def after_train(self):
"""
Called after the last iteration.
"""
pass
def before_step(self):
"""
Called before each iteration.
"""
pass
def after_step(self):
"""
Called after each iteration.
"""
pass
def state_dict(self):
return {}
对于训练而言,它将一个完整的训练拆分成:
class TrainerBase:
def __init__(self):
self._hooks: List[HookBase] = []
def register_hooks(self, hooks: List[Optional[HookBase]]) -> None:
hooks = [h for h in hooks if h is not None]
for h in hooks:
assert isinstance(h, HookBase)
h.trainer = weakref.proxy(self)
self._hooks.extend(hooks)
def train(self, start_iter: int, max_iter: int):
self.iter = self.start_iter = start_iter
self.max_iter = max_iter
with EventStorage(start_iter) as self.storage:
try:
self.before_train()
for self.iter in range(start_iter, max_iter):
self.before_step()
self.run_step()
self.after_step()
finally:
self.after_train()
def before_train(self):
for h in self._hooks:
h.before_train()
def after_train(self):
self.storage.iter = self.iter
for h in self._hooks:
h.after_train()
def before_step(self):
self.storage.iter = self.iter
for h in self._hooks:
h.before_step()
def after_step(self):
for h in self._hooks:
h.after_step()
def run_step(self):
raise NotImplementedError
def state_dict(self):
pass
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
pass
简化一点,它将一个训练过程抽象成:
hook.before_train()
for iter in range(start_iter, max_iter):
hook.before_step()
trainer.run_step()
hook.after_step()
iter += 1
hook.after_train()
具体到目标检测任务,DefaultTrainer:
class DefaultTrainer(TrainerBase):
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
pass
def build_hooks(self):
pass
def build_writers(self):
pass
def train(self):
pass
@classmethod
def test(cls, cfg, model, evaluators=None):
pass
#
# a lot of
# def ...(...):
# .....
#
@classmethod
def build_train_loader(cls, cfg):
return build_detection_train_loader(cfg)
@classmethod
def build_test_loader(cls, cfg, dataset_name):
return build_detection_test_loader(cfg, dataset_name)
@classmethod
def build_evaluator(cls, cfg, dataset_name):
pass
4.2 自定义训练
由于Detectron2已经将训练过程模块化,因此只需要修改对应模块即可,而一般而言,我们只需要修改数据加载和evaluate部分:
from detectron2.engine import DefaultTrainer
class Trainer(DefaultTrainer):
@classmethod
def build_evaluator(cls, cfg, dataset_name, output_folder=None):
evaluator_list = []
pass
return DatasetEvaluators(evaluator_list)
@classmethod
def build_test_loader(cls, cfg, dataset_name):
return build_detection_test_loader(cfg, dataset_name, mapper=my_mapper(cfg,"test"))
@classmethod
def build_train_loader(cls, cfg):
return build_detection_train_loader(cfg, mapper=my_mapper(cfg, "train"))
4.3 完整训练流程
参考tools/train_net.py或者tools/plain_train_net.py,已经写的非常详细了,注意别忘了导入自己写好的注册数据集以及注册模型的文件,只要导入了就会自动注册,就可以在配置文件中使用。
5. 配置文件
参考configs文件夹下的yaml文件格式,,可以通过__BASE__继承基础配置文件,还可以直接覆盖之前的配置,如retinanet_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml:
_BASE_: "../Base-RetinaNet.yaml"
MODEL:
WEIGHTS: "detectron2://ImageNetPretrained/MSRA/R-50.pkl"
RESNETS:
DEPTH: 50
SOLVER:
STEPS: (210000, 250000)
MAX_ITER: 270000
查看全部配置项:
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
cfg = get_cfg()
print(cfg)
# 或者
print(cfg.dump())
在python文件中修改配置:
cfg.SOLVER.BASE_LR = 0.001
# 或者
cfg.merge_from_list(["SOLVER.BASE_LR", "0.001"])
合并多个文件中的配置项:
cfg.merge_from_file("my_cfg.yaml")
由于配置项本质上还是转换成了字典类型,因此可以直接从python文件导入配置,并且也提供了python格式的配置文件该怎么进行训练的示例,参考tools/lazyconfig_train_net.py:
# config.py
NEW_MODEL = dict(NUM=1,SIZE=dict(W=2,H=3))
NEW_OPT = dict(NAME="hhhh")
# ---
from detectron2.config import LazyConfig
cfg = LazyConfig.load("config.py")
assert cfg.NEW_MODEL.SIZE.W==2
# cfg = LazyConfig.load(args.config_file)
# cfg = LazyConfig.apply_overrides(cfg, args.opts)
并且Detectron2还提供了一个帮助创建配置字典的函数,LazyCall:
from detectron2.config import LazyCall as L
from detectron2.modeling.backbone import RegNet
from detectron2.modeling.backbone.regnet import SimpleStem, ResBottleneckBlock
bottom_up = L(RegNet)(
stem_class=SimpleStem,
stem_width=32,
block_class=ResBottleneckBlock,
depth=23,
w_a=38.65,
w_0=96,
w_m=2.43,
group_width=40,
norm="SyncBN",
out_features=["s1", "s2", "s3", "s4"],
)
print(bottom_up)
6. 备注
后续更新请看我的个人知识博客