【Python】鲸鱼算法实现
文章目录
- 鲸鱼算法
-
- 自编代码
-
- 结果
- 摘录代码
鲸鱼算法
自编代码
# main.py
import numpy as np
from numpy import random
from copy import deepcopy
from function import fun, new_min, new_max, pdist2, jingyu
sub = np.array([-50, -50, -50, -50, -50, -50, -50, -50, -50, -50]) # 自变量下限
up = np.array([50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50]) # 自变量上限
opt = -1 # -1为最小化,1为最大化
# 程序为最小化寻优,如果是最大化寻优更改排序部分程序即可
n = len(sub) # 自变量个数
num = 500 * n # 种群大小
det = 10 * n + 100 # 迭代次数
k = 1.5 + 0.1 * n # k为最大环绕圈数
R = 0.1 * pow(n, 2) # 当鲨鱼进入猎物该范围,则直接对猎物位置进行逼近
Mc = (up - sub) * 0.1 # 猎物行动最大范围
x = np.zeros([num, n])
f = np.zeros(num)
for s in range(num):
rand_data = random.random(n)
rand_data = np.array(rand_data)
x[s, :] = sub + (up - sub) * rand_data
f[s] = fun(x[s, :])
best_x = np.zeros(n)
best_f = 0
# 以最小化为例
if opt == -1:
best_f, a = new_min(f) # 记录历史最优值
best_x = x[a, :] # 记录历史最优解
elif opt == 1:
best_f, a = new_max(f) # 记录历史最优值
best_x = x[a, :] # 记录历史最优解
trace = np.array([deepcopy(best_f)])
xx = np.zeros([num, n])
ff = np.zeros(num)
for ii in range(det):
# 猎物躲避,蒙特卡洛模拟周围1000次,并选择最佳的点作为下一逃跑点
d = pdist2(best_x, x)
d.sort()
z = np.exp(-d[1] / np.mean(Mc)) # 猎物急躁系数
z = max(z, 0.1)
best_t = []
best_c = []
yx = []
dx = []
for i in range(1000):
m = []
for iii in range(n):
randi = random.randint(1, 3)
a = pow(-1, randi)
m.append(a)
m = np.array(m)
random_rand = random.random(n)
xd = best_x + Mc * z * ((det - (ii + 1)) / det) * random_rand * m
xd = np.maximum(sub, xd)
xd = np.minimum(up, xd)
if i < 1:
dx = deepcopy(xd) # (det-ii)/det表示随着追捕,猎物可逃窜的范围越来越小
else:
dx = np.vstack((dx,xd)) # (det-ii)/det表示随着追捕,猎物可逃窜的范围越来越小
yx=np.hstack((yx,fun(xd)))
if opt == -1:
best_t, a = new_min(yx) # 选择最佳逃跑点
best_c = dx[a, :]
if best_t < best_f:
best_f = best_t
best_x = best_c
else:
pass
elif opt == 1:
best_t, a = new_max(yx) # 选择最佳逃跑点
best_c = dx[a, :]
if best_t > best_f:
best_f = best_t
best_x = best_c
else:
pass
# 鲸鱼追捕
for i in range(num):
# 更新公式
if np.sqrt(np.sum((x[i, :] - best_x) ** 2)) <= R:
rand = random.random()
xx[i, :] = x[i, :] + rand * (x[i, :] - best_x)
xx[i, :] = np.maximum(sub, xx[i, :])
xx[i, :] = np.minimum(up, xx[i, :])
ff[i] = fun(xx[i, :])
else:
xx[i, :] = x[i, :] + np.real(jingyu(x[i, :] - best_x, k))
xx[i, :] = np.maximum(sub, xx[i, :])
xx[i, :] = np.minimum(up, xx[i, :])
ff[i] = fun(xx[i, :])
# 引入上一代进行排序,并重新分配角色
F = np.hstack((np.array([best_f]), f, ff))
F= np.array(F)
X = np.vstack(([best_x], x, xx))
X=np.array(X)
temp=np.sort(F,axis=-1,kind='stable')
if opt == -1:
F, b = temp, np.argsort(F) # 按小到大排序
elif opt == 1:
F, b = temp[::-1], np.argsort(-F) # 按大到大排序
X = X[b, :]
f = F[:num]
x = X[:num, :]
if opt == -1:
best_f, a = new_min(f) # 记录历史最优值
elif opt == 1:
best_f, a = new_max(f) # 记录历史最优值
best_x = x[a, :] # 记录历史最优解
trace = np.hstack((trace, [best_f]))
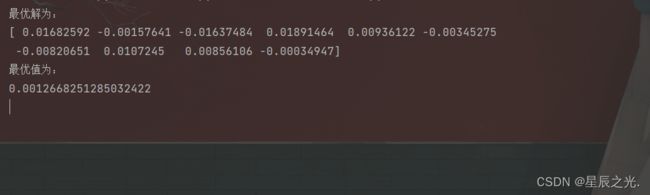
print('最优解为:')
print(best_x)
print('最优值为:')
print(float(best_f))
import numpy as np
def new_min(arr):
min_data = min(arr)
key = np.argmin(arr)
return min_data, key
import numpy as np
def new_max(arr):
max_data = max(arr)
key = np.argmax(arr)
return max_data, key
import numpy as np
def pdist2(best_x, x):
best_x = np.array(best_x)
x = np.array(x)
a = x - best_x
b = pow(a, 2)
c = np.sum(b, axis=1)
d = pow(c, 0.5)
return d
import copy
import numpy as np
from numpy import random
def jingyu(X, K):
n = len(X)
Y = []
y = np.zeros(n - 1)
costheta = np.zeros(n - 1)
theta = np.zeros(n - 1)
k = np.zeros(n - 1)
for i in range(n - 1):
Y = np.append(X[0:i + 1], 0)
y[i] = np.sqrt(np.sum((X[0:i + 2]) ** 2))
# 计算角度(圈数)
costheta[i] = (X[0:i + 2] @ Y) / (np.sqrt(np.sum(X[0:i + 2] ** 2)) * np.sqrt(np.sum(Y ** 2)))
if np.isnan(costheta[i]) == 1:
costheta[i] = 1
if X[i + 1] >= 0:
theta[i] = np.arccos(costheta[i]) / (2 * np.pi)
else:
theta[i] = 2 - np.arccos(costheta[i]) / (2 * np.pi)
theta[i] = theta[i] * 2 * np.pi
# 自适应调节k
if y[i] >= 10:
k[i] = K * np.exp(-2)
else:
k[i] = K * np.exp(-y[i] / 5)
# 位置更新公式,左包围或右包围
f = []
l = 0
yy = copy.deepcopy(y)
rand = random.random()
ttheta = copy.deepcopy(theta)
l = k[0] * rand
yy[0] = yy[0] * np.exp(-l)
ttheta[0] = ttheta[0] + l * 2 * np.pi * (-1) ** (random.randint(1, 3))
f = [yy[0] * np.cos(ttheta[0]), yy[0] * np.sin(ttheta[0])]
f = np.array(f)
if n > 2:
for j in range(n - 2):
a = (j + 1) % 2
if a == 1:
rand = random.random()
l = k[j + 1] * rand
yy[j + 1] = yy[j + 1] * np.exp(-l)
ttheta[j + 1] = ttheta[j + 1] + l * 2 * np.pi * ((-1) ** (random.randint(1, 3)))
f = np.concatenate((f * abs(np.cos(ttheta[j + 1])), np.array([yy[j + 1] * np.sin(ttheta[j + 1])])))
elif a == 0:
rand = random.random()
l = k[j + 1] * rand
yy[j + 1] = yy[j + 1] * np.exp(-l)
ttheta[j + 1] = ttheta[j + 1] + l * 2 * np.pi * ((-1) ** random.randint(1, 3))
f = np.concatenate((f * abs(np.sin(ttheta[j + 1])), np.array([yy[j + 1] * np.cos(ttheta[j + 1])])))
f = f.T
return f
import numpy as np
def fun(data_list):
arr = np.array(data_list)
f = sum(pow(arr, 2))
return f
结果
摘录代码
鲸鱼优化算法(WOA)(学习)_轨迹跟踪杨的博客-CSDN博客_鲸鱼优化算法
%参数初始化,初始时主要设置代理数量和最大迭代次数即可,其他算法相关的参数因为和当前迭代次数相关,需要在迭代中设置。
clc;clear;
dim=2;%变量的维数
SearchAgents_no=30; % 搜索代理数量,种群中个体个数
Max_iteration=500; % 最大迭代次数
ub=15;%上限
lb=-15;%下限
%种群初始化。随机初始化所有代理各个维度上的位置值,需要保证在取值范围内。
Positions=rand(SearchAgents_no,dim).*(ub-lb)+lb;
Leader_score = fobj(Positions(1,:));
for t=1:Max_iteration
fit(t)=Leader_score;
%(评估种群中每个代理的目标值,如有某个代理由于当前最优解,则将其设为最优解。)
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
% 计算每个代理的目标值
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
% 更新最优解
if fitness < Leader_score % 如果是最大化问题,这里就是">"
Leader_score=fitness;
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
%(设置和迭代次数相关的算法参数。)
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iteration); % 等式(3)中a随迭代次数从2线性下降至0
%a2从-1线性下降至-2,计算l时会用到
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iteration);
% Update the Position of search agents(对每个代理的每一维度进行位置更新)
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1为[0,1]之间的随机数
r2=rand(); % r2为[0,1]之间的随机数
A=2*a*r1-a; % 等式(3)
C=2*r2; % 等式(4)
b=1; % 等式(5)中的常数b
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % 等式(5)中的随机数l
p = rand(); % 等式(6)中的概率p
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % 等式(7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % 等式(8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % 等式(1)
Positions(i,j)=Leader_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % 等式(2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% 等式(5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j);
end
end
end
end
k=1:1:500;
plot(k,fit,'r');
function y=fobj(x)
y=2*x(1)^2+x(2)^2-x(1)*x(2)-10*x(1)-4*x(2)+60;
end
鲸鱼优化算法Python实现 - 代码先锋网 (codeleading.com)
import numpy as np
import random
import math
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
'''优化函数'''
# y = x^2, 用户可以自己定义其他函数
def fun(X):
output = sum(np.square(X))
return output
''' 种群初始化函数 '''
def initial(pop, dim, ub, lb):
X = np.zeros([pop, dim])
for i in range(pop):
for j in range(dim):
X[i, j] = random.random() * (ub[j] - lb[j]) + lb[j]
return X, lb, ub
'''边界检查函数'''
def BorderCheck(X, ub, lb, pop, dim):
for i in range(pop):
for j in range(dim):
if X[i, j] > ub[j]:
X[i, j] = ub[j]
elif X[i, j] < lb[j]:
X[i, j] = lb[j]
return X
'''计算适应度函数'''
def CaculateFitness(X, fun):
pop = X.shape[0]
fitness = np.zeros([pop, 1])
for i in range(pop):
fitness[i] = fun(X[i, :])
return fitness
'''适应度排序'''
def SortFitness(Fit):
fitness = np.sort(Fit, axis=0)
index = np.argsort(Fit, axis=0)
return fitness, index
'''根据适应度对位置进行排序'''
def SortPosition(X, index):
Xnew = np.zeros(X.shape)
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
Xnew[i, :] = X[index[i], :]
return Xnew
'''鲸鱼优化算法'''
def WOA(pop, dim, lb, ub, Max_iter, fun):
X, lb, ub = initial(pop, dim, ub, lb) # 初始化种群
fitness = CaculateFitness(X, fun) # 计算适应度值
fitness, sortIndex = SortFitness(fitness) # 对适应度值排序
X = SortPosition(X, sortIndex) # 种群排序
GbestScore = fitness[0]
GbestPositon = np.zeros([1,dim])
GbestPositon[0,:] = X[0, :]
Curve = np.zeros([MaxIter, 1])
for t in range(MaxIter):
Leader = X[0, :] # 领头鲸鱼
a = 2 - t * (2 / MaxIter) # 线性下降权重2 - 0
a2 = -1 + t * (-1 / MaxIter) # 线性下降权重-1 - -2
for i in range(pop):
r1 = random.random()
r2 = random.random()
A = 2 * a * r1 - a
C = 2 * r2
b = 1
l = (a2 - 1) * random.random() + 1
for j in range(dim):
p = random.random()
if p < 0.5:
if np.abs(A) >= 1:
rand_leader_index = min(int(np.floor(pop * random.random() + 1)), pop - 1)
X_rand = X[rand_leader_index, :]
D_X_rand = np.abs(C * X_rand[j] - X[i, j])
X[i, j] = X_rand[j] - A * D_X_rand
elif np.abs(A) < 1:
D_Leader = np.abs(C * Leader[j] - X[i, j])
X[i, j] = Leader[j] - A * D_Leader
elif p >= 0.5:
distance2Leader = np.abs(Leader[j] - X[i, j])
X[i, j] = distance2Leader * np.exp(b * l) * np.cos(l * 2 * math.pi) + Leader[j]
X = BorderCheck(X, ub, lb, pop, dim) # 边界检测
fitness = CaculateFitness(X, fun) # 计算适应度值
fitness, sortIndex = SortFitness(fitness) # 对适应度值排序
X = SortPosition(X, sortIndex) # 种群排序
if fitness[0] <= GbestScore: # 更新全局最优
GbestScore = fitness[0]
GbestPositon[0,:] = X[0, :]
Curve[t] = GbestScore
return GbestScore, GbestPositon, Curve
'''主函数 '''
# 设置参数
pop = 50 # 种群数量
MaxIter = 1000 # 最大迭代次数
dim = 30 # 维度
lb = -100 * np.ones([dim, 1]) # 下边界
ub = 100 * np.ones([dim, 1]) # 上边界
GbestScore, GbestPositon, Curve = WOA(pop, dim, lb, ub, MaxIter, fun)
print('最优适应度值:', GbestScore)
print('最优解:', GbestPositon)
# 绘制适应度曲线
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(Curve, 'r-', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('Iteration', fontsize='medium')
plt.ylabel("Fitness", fontsize='medium')
plt.grid()
plt.title('WOA', fontsize='large')
# 绘制搜索空间
fig = plt.figure(2)
ax = Axes3D(fig)
X = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = X ** 2 + Y ** 2
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow')
plt.show()
鲸鱼优化数学原理及Python实现 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
0. 初始化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
1. 样本点生成模块
def sampleGeneartor():
X = np.arange(0, 5, 0.01)
Y = X**3 - 4*X**2 + 1*X - 3
e = np.random.normal(0, 2, 500)
Y = Y + e
plt.scatter(X, Y, 0.5)
return X, Y
2. WOA优化算法模块
class woa():
#初始化
def __init__(self, X_train, Y_train, LB=np.array([-5, -5, -5, -5]),\
UB= np.array([5, 5, 5, 5]), dim=4, b=1, whale_num=20, max_iter=500):
self.X_train = X_train
self.Y_train = Y_train
self.LB = LB
self.UB = UB
self.dim = dim
self.whale_num = whale_num
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.b = b
#Initialize the locations of whale
self.X = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (whale_num, dim))*(UB - LB) + LB
self.gBest_score = np.inf
self.gBest_curve = np.zeros(max_iter)
self.gBest_X = np.zeros(dim)
#适应度函数
def fitFunc(self, input):
a = input[0]; b = input[1]; c = input[2]; d = input[3]
Y_Hat = a*self.X_train**3 + b*self.X_train**2 + c*self.X_train + d
fitFunc = np.sum((Y_Hat - self.Y_train)**2)/np.shape(Y_Hat)[0]
return fitFunc
#优化模块
def opt(self):
t = 0
while t < self.max_iter:
for i in range(self.whale_num):
self.X[i, :] = np.clip(self.X[i, :], self.LB, self.UB) #Check boundries
fitness = self.fitFunc(self.X[i, :])
# Update the gBest_score and gBest_X
if fitness < self.gBest_score:
self.gBest_score = fitness
self.gBest_X = self.X[i, :].copy()
a = 2*(self.max_iter - t)/self.max_iter
#Update the location of whales
for i in range(self.whale_num):
p = np.random.uniform()
R1 = np.random.uniform()
R2 = np.random.uniform()
A = 2*a*R1 - a
C = 2*R2
l = 2*np.random.uniform() - 1
if p >= 0.5:
D = abs(self.gBest_X - self.X[i, :])
self.X[i, :] = D*np.exp(self.b*l)*np.cos(2*np.pi*l)+self.gBest_X
else:
if abs(A) < 1:
D = abs(C*self.gBest_X - self.X[i, :])
self.X[i, :] = self.gBest_X - A*D
else:
rand_index = np.random.randint(low=0, high=self.whale_num)
X_rand = self.X[rand_index, :]
D = abs(C*X_rand - self.X[i, :])
self.X[i, :] = X_rand - A*D
self.gBest_curve[t] = self.gBest_score
if (t%100 == 0) :
print('At iteration: ' + str(t))
t+=1
return self.gBest_curve, self.gBest_X
4. 主程序
# main
'''
main function
'''
X, Y = sampleGeneartor()
fitnessCurve, para = woa(X, Y, dim=4, whale_num=60, max_iter=2000).opt()
yPre = para[0]*X**3 + para[1]*X**2 + para[2]*X + para[3]
plt.scatter(X, yPre, 0.5)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(fitnessCurve, linewidth='0.5')
plt.show()