ArcGIS API 开发 文档解析——View.hitTest()
return–> 异步的 HitTestResult对象数组
官方释义:返回与指定屏幕坐标相交的图形(具体可参考返回的数据结构示例) ,每次单击交互查找鼠标指针下的所有对象。
两个参数:screenPoint, options
第一个参数:screenPoint 单击视图获取的屏幕坐标,一般可以通过View.on()事件触发得到,这也是为什么通常情况下View.hitTest()方法通常写在View.on()方法内部的原因

第二个参数:options 对象类型, 官方释义:相交的选项,当默认情况下,如果不透明度小于 1,则排除 map.ground。
主要有属性:include、exclude
Include:包含的图层和图形;不指定,则包含所有的图层和图形。
Exclude:排除的图层或图层;不指定,则包含所有的图层和图形。
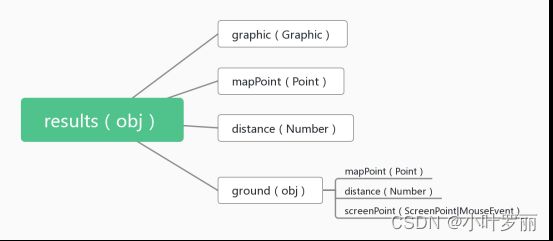
返回的对象:异步的HitTestResult对象数组,当输入屏幕坐标的位置与视图中的图形相交时,将返回结果。如果图形具有非覆盖 IconSymbol3DLayer 符号系统,则只有第一个图形将从 hitTest 返回,数据结构参考:
{
"screenPoint": {
"x": 1110.666748046875,
"y": 704.6666870117188
},
"results": [
{
"graphic": {
"geometry": null,
"symbol": null,
"attributes": {
"OBJECTID": 23259,
"CNSTRCT_YR": 1950
}
},
"mapPoint": {
"spatialReference": {
"latestWkid": 3857,
"wkid": 102100
},
"x": -8237578.175357298,
"y": 4972677.452421391,
"z": 29.343255893327296
},
"distance": 6033.217135564263
}
],
"ground": {
"mapPoint": {
"spatialReference": {
"latestWkid": 3857,
"wkid": 102100
},
"x": -8237575.894557083,
"y": 4972679.5403643185,
"z": 6.689946555570758
},
"distance": 6055.99127013477
}
}
graphic: 视图中与输入屏幕坐标相交的图形。有些图层没有graphic.geometry(例如:SceneLayer 和PointCloudLayer)。graphics.attributes 仅包含客户端加载的属性,因此它可以是所有属性的子集。带有 [“*”] 的 FeatureLayer.outFields 可强制显示所有属性。graphics.symbol 仅存在于来自 GraphicsLayer 或 view.graphics 的图形,但可以使用 getDisplayedSymbol 计算显示的符号系统。
mapPoint :与输入屏幕坐标对应的视图空间参考中的点几何。
distance:从相机位置到此图形上的点几何图形的距离。在全局场景中,距离将以米为单位,而在局部场景中,距离将以视图的空间参考为单位。
ground :地面相交结果。即使地面被从 hitTest 中排除,也将始终返回地面撞击结果。
☞mapPoint:执行 hitTest 时击中地面的点。当地面完全没有被击中时(例如通过点击天空),这可能为空。
☞distance:从相机位置到地面的距离。如果地面完全没有被击中,则距离将为 0。在全局场景中,距离将以米为单位,而在局部场景中,距离将以视图的空间参考为单位。
☞screenPoint:单击视图的屏幕坐标(或本机鼠标事件)
我觉得这个方法更深入的应用在于和地面的相交碰撞检测,返回碰撞的结果,如下面的第一个demo中涉及,官方demo参考地址
view.on("immediate-click", (event) => {
// get the returned hitTestResult
// and draw points on all return mappoints and connect to a line
// (using promise chaining for cleaner code and error handling)
view
.hitTest(event, { exclude: [view.graphics] })
.then((hitTestResult) => {
// print the information to the panel
hitresultground.textContent = `${Math.round(
hitTestResult.ground.distance
)} m`;
hitresultcount.textContent = hitTestResult.results.length;
let lastHit = null;
// 点击后有命中对象
if (hitTestResult.results.length > 0) {
// 最后一个命中对象赋给地面
lastHit =
hitTestResult.results[hitTestResult.results.length - 1];
// 为每个命中对象创建点图形
hitTestResult.results.forEach((result, index) => {
const hitObject = new Graphic({
geometry: result.mapPoint,
symbol:
index === 0 ? firstObjectPointSymbol : objectPointSymbol //第一个命中点和其他点样式区分
});
view.graphics.add(hitObject);
// 修改点击命中图层的透明度
let graphic = result.graphic;
// change the layer to be transparent
graphic.layer.opacity = 0.8;
// highlight the hit object
view.whenLayerView(graphic.layer).then((layerView) => {
highlightedList.push(layerView.highlight(graphic));
});
});
}
// 地面相交点
if (hitTestResult.ground.mapPoint) {
if (lastHit) {
// 确保地面点离相机最远
if (hitTestResult.ground.distance > lastHit.distance) {
// an object under the ground could be more far away,
// check first the distance before set the ground as last point
lastHit = hitTestResult.ground;
}
} else {
lastHit = hitTestResult.ground;
}
// create point graphic for the ground
const hitGround = new Graphic({
geometry: hitTestResult.ground.mapPoint,
symbol: groundPointSymbol
});
view.graphics.add(hitGround);
}
//添加相机点到命中地面点的线图形
if (lastHit) {
// Draw a line to connect all hit objects and ground
let linePoints = [
[
view.camera.position.x,
view.camera.position.y,
view.camera.position.z
],
[lastHit.mapPoint.x, lastHit.mapPoint.y, lastHit.mapPoint.z]
];
view.graphics.add({
geometry: {
type: "polyline",
paths: linePoints,
spatialReference: view.spatialReference
},
symbol: lineSymbol
});
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});
});
第二个demo 更多的主要展示视图的加载和事件间的交互,在hitTest的应用主要是拿到结果的graphic进行查询高亮
view.on("pointer-move", eventHandler);
view.on("pointer-down", eventHandler);
function eventHandler(event) {
// only include graphics from hurricanesLayer in the hitTest
const opts = {
include: hurricanesLayer
};
// the hitTest() checks to see if any graphics from the hurricanesLayer
// intersect the x, y coordinates of the pointer
view.hitTest(event, opts).then(getGraphics);
}
let highlight, currentYear, currentName;
function getGraphics(response) {
// the topmost graphic from the hurricanesLayer
// and display select attribute values from the
// graphic to the user
if (response.results.length) {
const graphic = response.results[0].graphic;
const attributes = graphic.attributes;
const category = attributes.CAT;
const wind = attributes.WIND_KTS;
const name = attributes.NAME;
const year = attributes.YEAR;
const id = attributes.OBJECTID;
if (
highlight &&
(currentName !== name || currentYear !== year)
) {
highlight.remove();
highlight = null;
return;
}
if (highlight) {
return;
}
document.getElementById("info").style.visibility = "visible";
document.getElementById("name").innerHTML = name;
document.getElementById("category").innerHTML =
"Category " + category;
document.getElementById("wind").innerHTML = wind + " kts";
// highlight all features belonging to the same hurricane as the feature
// returned from the hitTest
const query = layerView.createQuery();
query.where = "YEAR = " + year + " AND NAME = '" + name + "'";
layerView.queryObjectIds(query).then((ids) => {
if (highlight) {
highlight.remove();
}
highlight = layerView.highlight(ids);
currentYear = year;
currentName = name;
});
} else {
// remove the highlight if no features are
// returned from the hitTest
if (highlight) {
highlight.remove();
highlight = null;
}
document.getElementById("info").style.visibility = "hidden";
}
}